Question: Please, attach MATLAB code that you used to make computations. Note: A number Z appears in each of the three Problems. It is obtained by

Please, attach MATLAB code that you used to make computations.
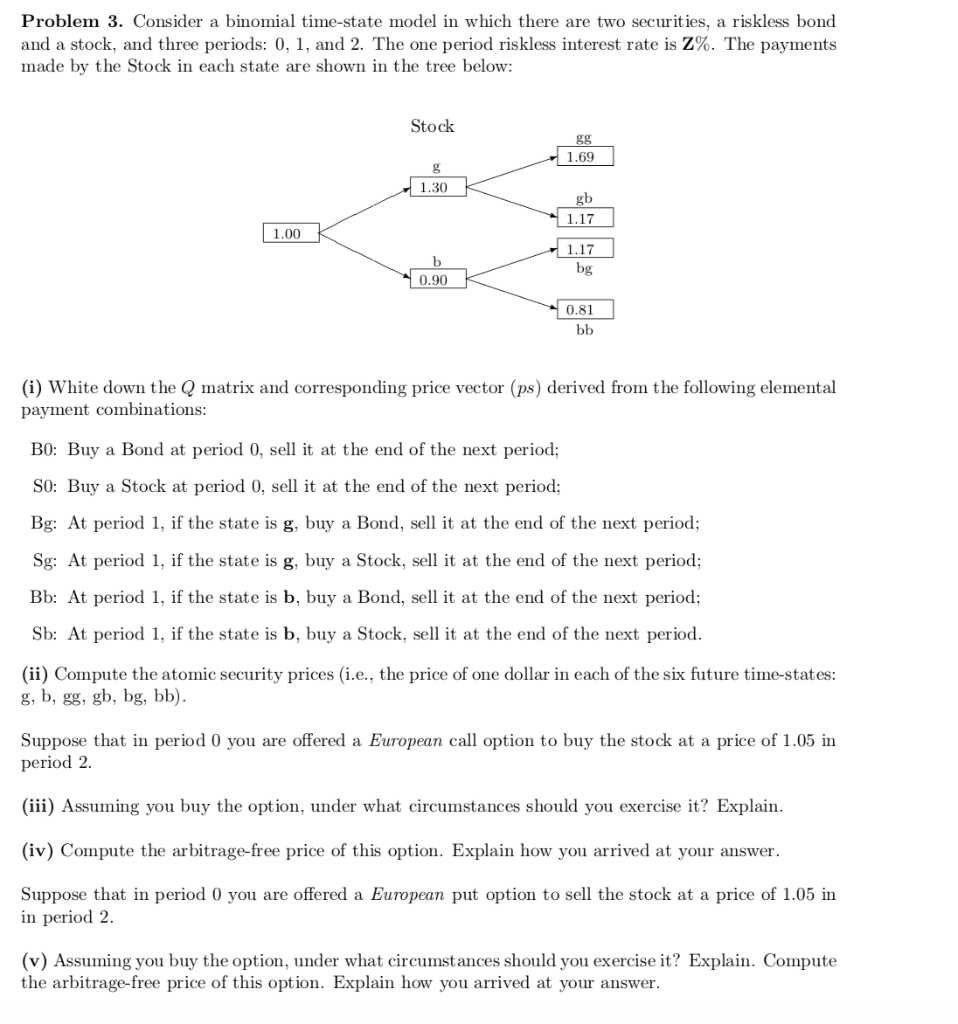
Note: A number Z appears in each of the three Problems. It is obtained by dividing the last two digits of your student number by 10 and adding 0.05 to the result. For example, if your student number is 21339, then Z=39/10 + 0.05 = 3.95. Problem 3. Consider a binomial time-state model in which there are two securities, a riskless bond and a stock, and three periods: 0, 1, and 2. The one period riskless interest rate is Z%. The payments made by the Stock in each state are shown in the tree below: Stock gg 1.69 1.30 K 1.00 K 1.17 0.90 K bg 0.81 (i) White down the Q matrix and corresponding price vector (ps) derived from the following elemental payment combinations: BO: Buy a Bond at period 0, sell it at the end of the next period; SO: Buy a Stock at period 0, sell it at the end of the next period; Bg: At period 1, if the state is g, buy a Bond, sell it at the end of the next period; Sg: At period 1, if the state is g, buy a Stock, sell it at the end of the next period; Bb: At period 1, if the state is b, buy a Bond, sell it at the end of the next period; Sb: At period 1, if the state is b, buy a Stock, sell it at the end of the next period. (ii) Compute the atomic security prices (i.e., the price of one dollar in each of the six future time-states: g, b, gg, gb, bg, bb). Suppose that in period 0 you are offered a European call option to buy the stock at a price of 1.05 in period 2. (iii) Assuming you buy the option, under what circumstances should you exercise it? Explain. (iv) Compute the arbitrage-free price of this option. Explain how you arrived at your answer. Suppose that in period 0 you are offered a European put option to sell the stock at a price of 1.05 in in period 2. (v) Assuming you buy the option, under what circumstances should you exercise it? Explain. Compute the arbitrage-free price of this option. Explain how you arrived at your answer. Note: A number Z appears in each of the three Problems. It is obtained by dividing the last two digits of your student number by 10 and adding 0.05 to the result. For example, if your student number is 21339, then Z=39/10 + 0.05 = 3.95. Problem 3. Consider a binomial time-state model in which there are two securities, a riskless bond and a stock, and three periods: 0, 1, and 2. The one period riskless interest rate is Z%. The payments made by the Stock in each state are shown in the tree below: Stock gg 1.69 1.30 K 1.00 K 1.17 0.90 K bg 0.81 (i) White down the Q matrix and corresponding price vector (ps) derived from the following elemental payment combinations: BO: Buy a Bond at period 0, sell it at the end of the next period; SO: Buy a Stock at period 0, sell it at the end of the next period; Bg: At period 1, if the state is g, buy a Bond, sell it at the end of the next period; Sg: At period 1, if the state is g, buy a Stock, sell it at the end of the next period; Bb: At period 1, if the state is b, buy a Bond, sell it at the end of the next period; Sb: At period 1, if the state is b, buy a Stock, sell it at the end of the next period. (ii) Compute the atomic security prices (i.e., the price of one dollar in each of the six future time-states: g, b, gg, gb, bg, bb). Suppose that in period 0 you are offered a European call option to buy the stock at a price of 1.05 in period 2. (iii) Assuming you buy the option, under what circumstances should you exercise it? Explain. (iv) Compute the arbitrage-free price of this option. Explain how you arrived at your answer. Suppose that in period 0 you are offered a European put option to sell the stock at a price of 1.05 in in period 2. (v) Assuming you buy the option, under what circumstances should you exercise it? Explain. Compute the arbitrage-free price of this option. Explain how you arrived at your
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


