Question: Please carefully take your time to do these Work and Energy questions from PCS211! 17. [-I4 Points] SERPSE10 7.7.P.O31.MI. MY NOTES ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE
Please carefully take your time to do these Work and Energy questions from PCS211!
![from PCS211! 17. [-I4 Points] SERPSE10 7.7.P.O31.MI. MY NOTES ASK YOUR TEACHER](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f718d0eb9e6_77666f718d0c4124.jpg)
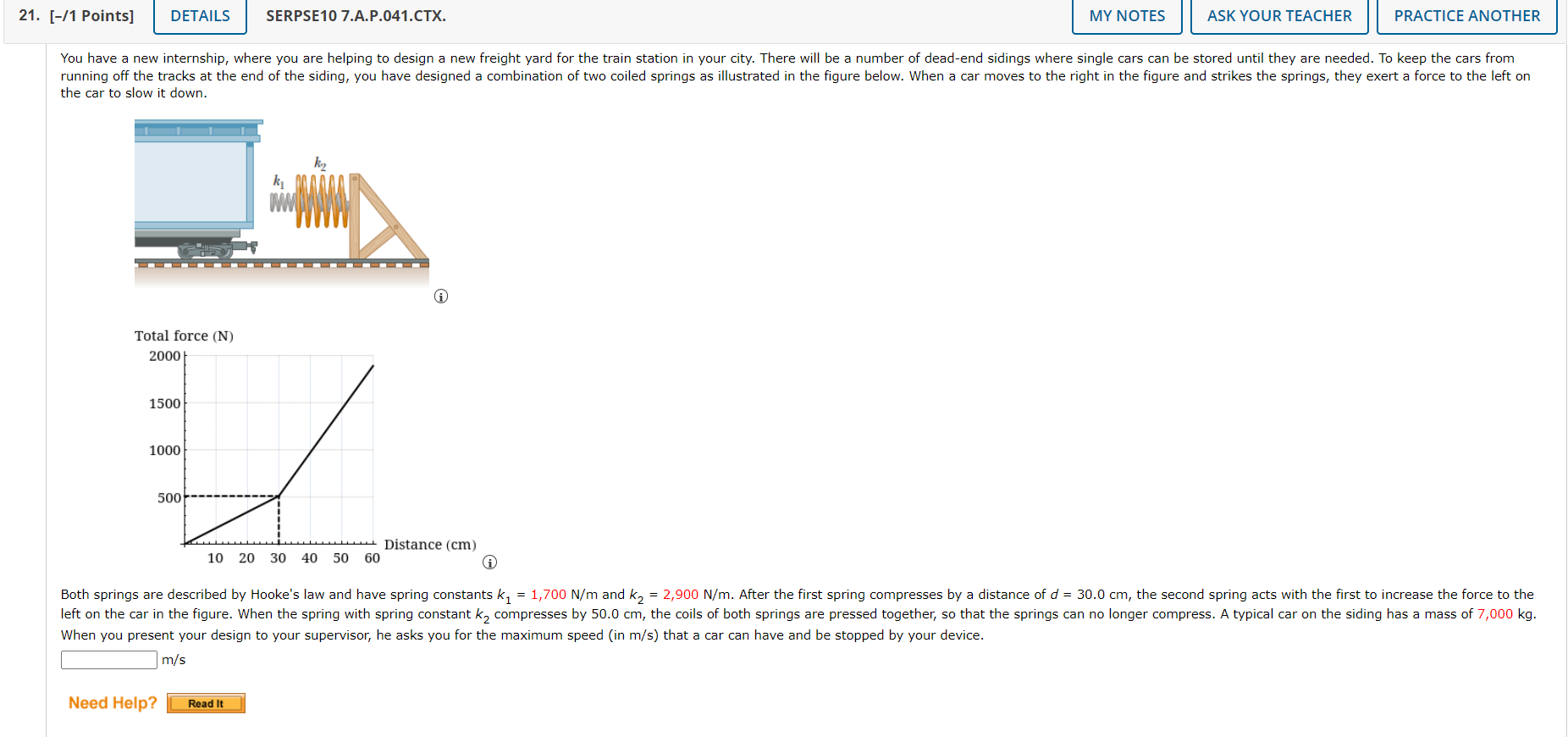
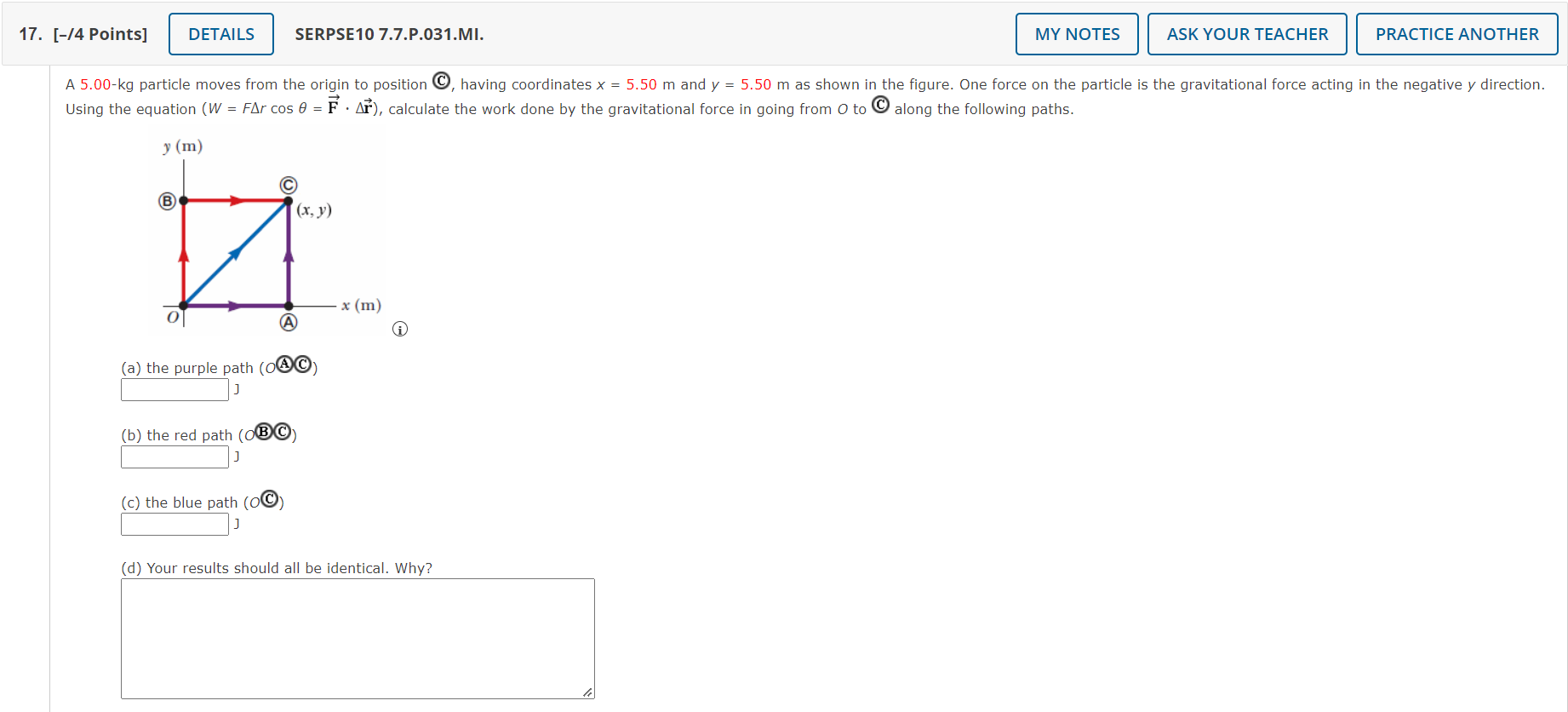
17. [-I4 Points] SERPSE10 7.7.P.O31.MI. MY NOTES ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER A 5.007kg particle moves from the origin to position , having Coordinatesx = 5.50 m and y = 5.50 m as shown in the gure. One force on the particle is the gravitational force acting in the negative y direction. _, Using the equation (W : FA!" cos 8 : F - AF), calculate the work done by the gravitational force in going from O to along the following paths. 3' (In) [a] the purple path (0%] :1 [b] the red path (o) J (c) the blue path (o) :1 [d] Your results should all be identical. Why? 18. [-/0 Points] DETAILS SERPSE10 7.7.P.033.MI. MY NOTES ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER A force acting on a particle moving in the xy plane is given by F = (2yi + x2j), where F is in newtons and x and y are in meters. The particle moves from the origin to a final position having coordinates x = 4.30 m and y = 4.30 m, as shown in the figure below. y (m) B (x, y) x (m) (a) Calculate the work done by F on the particle as it moves along the purple path (AC). (b) Calculate the work done by F on the particle as it moves along the red path (o(B C). (c) Calculate the work done by F on the particle as it moves along the blue path (C). (d) Is F conservative or nonconservative? nonconservative O conservative (e) Explain your answer to part (d).21. [-/1 Points] DETAILS SERPSE10 7.A.P.041.CTX. MY NOTES ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER You have a new internship, where you are helping to design a new freight yard for the train station in your city. There will be a number of dead-end sidings where single cars can be stored until they are needed. To keep the cars from running off the tracks at the end of the siding, you have designed a combination of two coiled springs as illustrated in the figure below. When a car moves to the right in the figure and strikes the springs, they exert a force to the left on the car to slow it down. Total force (N) 2000 1500 1000 500 Let Distance (cm) 10 20 30 40 50 60 Both springs are described by Hooke's law and have spring constants kj = 1,700 N/m and k2 = 2,900 N/m. After the first spring compresses by a distance of d = 30.0 cm, the second spring acts with the first to increase the force to the left on the car in the figure. When the spring with spring constant k2 compresses by 50.0 cm, the coils of both springs are pressed together, so that the springs can no longer compress. A typical car on the siding has a mass of 7,000 kg. When you present your design to your supervisor, he asks you for the maximum speed (in m/s) that a car can have and be stopped by your device. |m/s Need Help? Read It
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


