Question: please complete the following on C. Partial code is given use it to complete 1. please state which hash table collisiom resution method was used?
please complete the following on C.
Partial code is given use it to complete
1. please state which hash table collisiom resution method was used?
2. which hash function (division or multiplication) was used? how was string converted to a number?
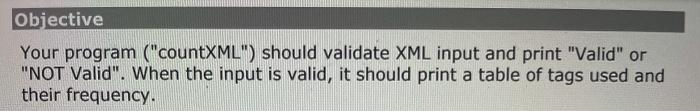
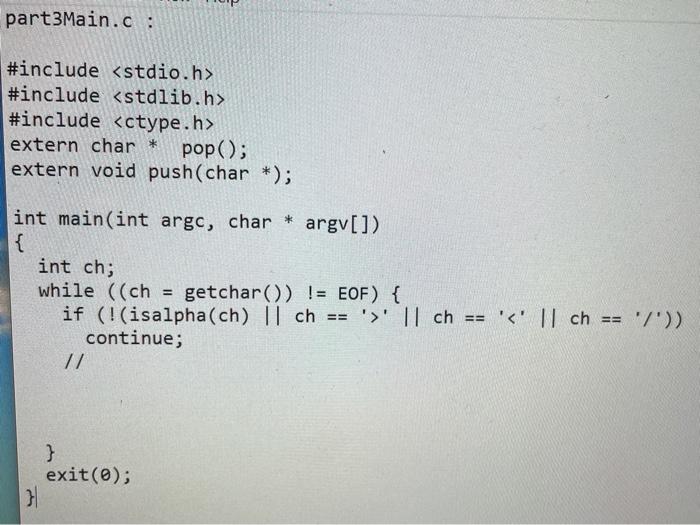
part3Main.c:
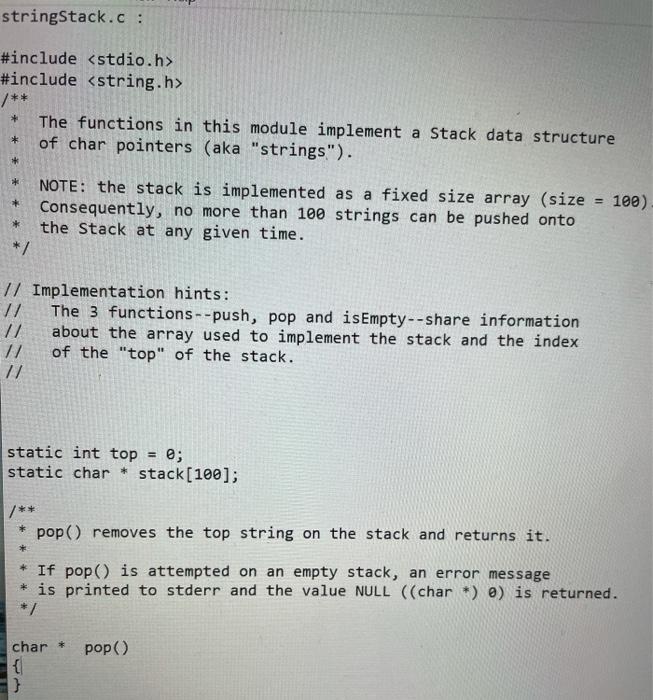
stringStack.c
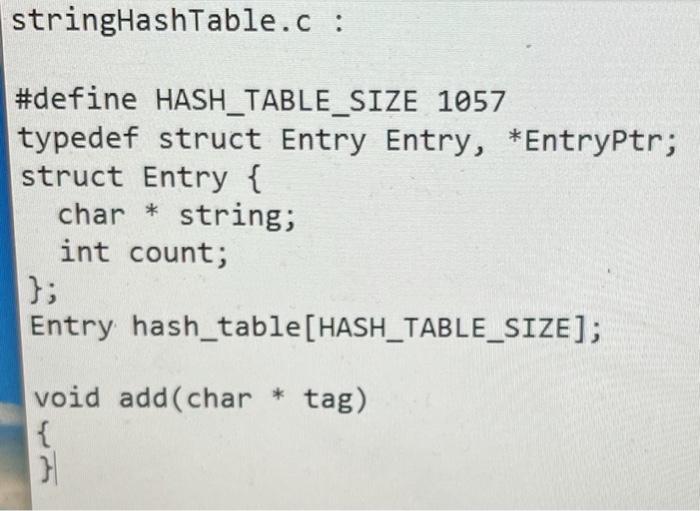
stringHashTable.c:
Part 3: Validation/counting of arbitrary tags We now allow tag names of arbitrary length composed of upper- and lower- case alphabetic characters. Thus a tag like is quite legal. Although the overall architecture of the software to do this is the same as Part 2, the fact that the universe of keys is now unbounded (i.e. strings of arbitrary length vs. single lower-case characters) has consequences: C programming (strings vs. characters) Parts 1 and 2 of this lab did not have to deal with tag names that were more than 1 character long. Hence: 1. Reading the input one character at a time was sufficient. 2. The stack only had to have integer entries. 3. Comparison of an end-tag identifier with a popped identifier could be done with the == operator. Alas, all of these simplifications do not apply when the tag ID is a string. In particular: 1. A different Stack implementation with entries that are strings (i.e. char pointers) is needed. 2. The string (char pointer) has to be allocated (and freed) dynamically. 3. Comparisons between strings to determine equality cannot be done with the == operator. (Use instead the "strcmp()" function.) Direct mapping vs. Hash table When the number of tag names is unlimited, direct-mapping of the name to an array index is out of the question. (Even if we limited tags to 9 characters, the universe of possibilities is more than 144 quadrillion-1.4 10^16!) Since each tag has an associated count and we want to find the tag efficiently, a hash table must be used. Objective Your program ("countXML") should validate XML input and print "Valid" or "NOT Valid". When the input is valid, it should print a table of tags used and their frequency. C source code files You also need to implement a string Stack (including push(), pop() and isEmptyO) operations. You must use separate C source code files for each of these. The files are: part3Main.c The main() function in this file reads stdin and implements the algorithm. You are provided with a skeleton implementation of main() in the file "part3Main.c" stringStack.c Again, you are provided with a skeletal version of this file. You need to implement the 3 functions (push, pop and isEmpty). The comments describing what these functions do must not be modified. stringHashTable.c Again, you are provided with a skeletal version of this file. You need to implement the add() function. The comments describing the function do must not be modified. You may implement the hash table using any method (for example, chaining or open-addressing to resolve collisions). You can also use any hash function you wish (eg. division vs. multiplication). The size of the hash table is defined by a constant "HASH_TABLE_SIZE". The hash table itself must be an array of hash table entries. It must be a global variable called "hash_table". part3Main.c : #include #include #include extern char * pop(); extern void push(char *); int main(int argc, char * argv[]) { int ch; while ((ch = getchar()) != EOF) { if (!(isalpha(ch) || ch == '' || ch == ' #include /** + The functions in this module implement a Stack data structure of char pointers (aka "strings"). * * * 100) NOTE: the stack is implemented as a fixed size array (size Consequently, no more than 100 strings can be pushed onto the Stack at any given time. */ * // Implementation hints: The 3 functions--push, pop and isEmpty--share information about the array used to implement the stack and the index 17 of the "top" of the stack. // static int top ; static char * stack(100); 7** pop() removes the top string on the stack and returns it. * If pop() is attempted on an empty stack, an error message * is printed to stderr and the value NULL ((char*) 0) is returned. */ char * pop) 3 push(thing2push) adds the "thing2push" to the top of the stack. If there is no more space available on the Stack, an error message is printed to stderr. * */ void push(char * thing2push) { } /** * isEmpty() returns a non-zero integer (not necessarily 1) if the * stack is empty; otherwise, it returns (zero). int isEmpty() { 3 S stringHashTable.c : #define HASH_TABLE_SIZE 1057 typedef struct Entry Entry, *Entryptr; struct Entry { char * string; int count; }; Entry hash_table[HASH_TABLE_SIZE]; void add(char * tag) { 31