Question: Please complete the year 2 column based on the journal entries above. Year 1 is already completed based on the journal entries from year 1.

 Please complete the year 2 column based on the journal entries above. Year 1 is already completed based on the journal entries from year 1.
Please complete the year 2 column based on the journal entries above. Year 1 is already completed based on the journal entries from year 1.
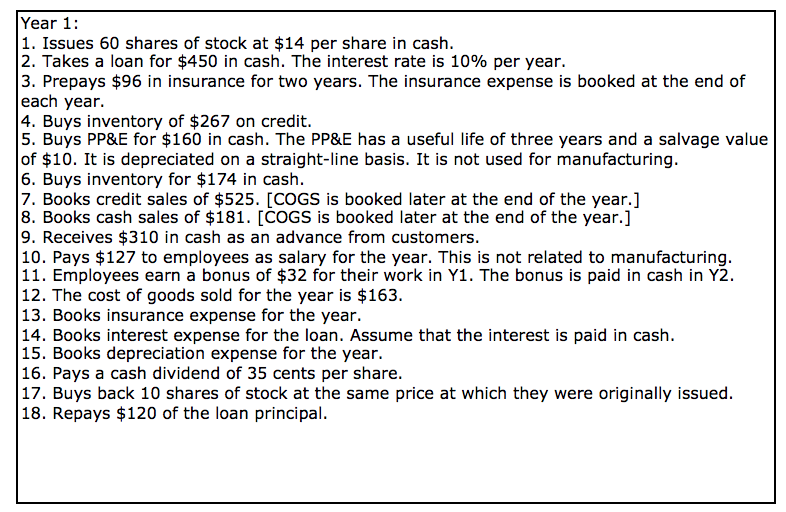
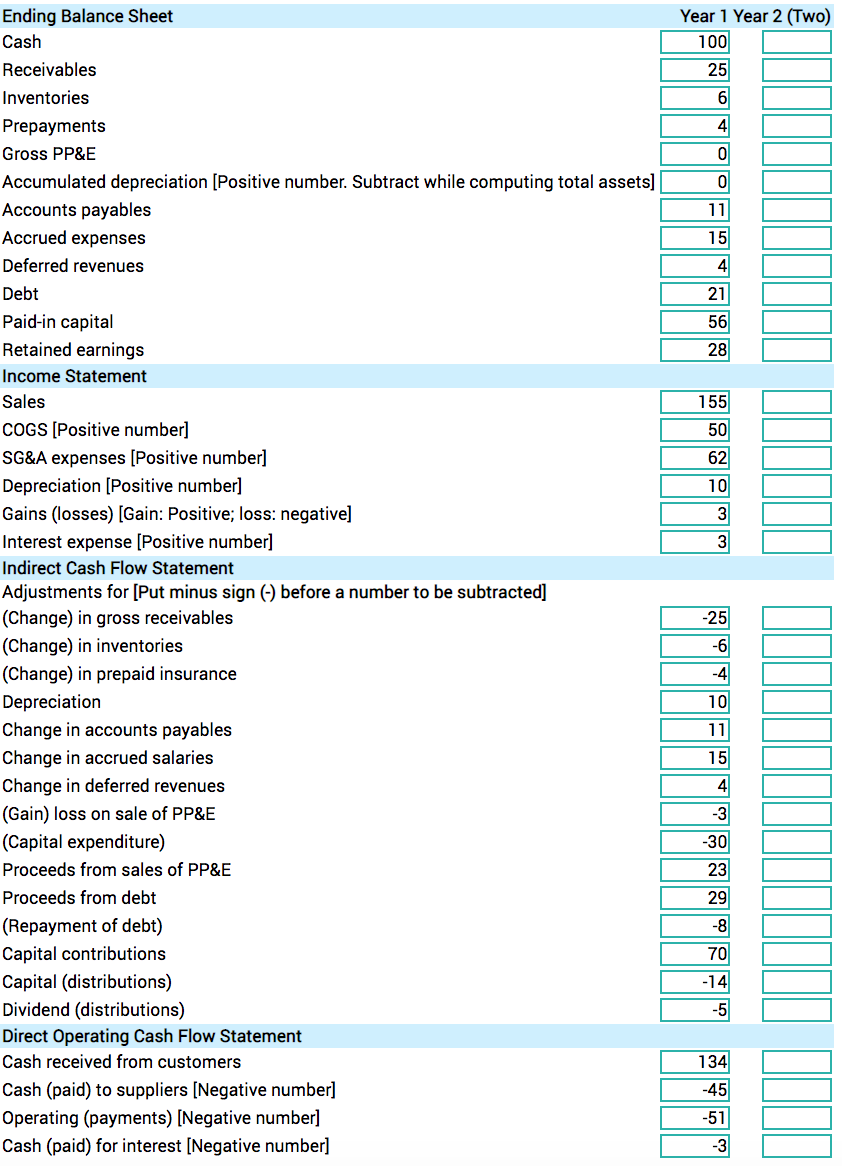
each year. Year 1: 1. Issues 60 shares of stock at $14 per share in cash. 2. Takes a loan for $450 in cash. The interest rate is 10% per year. 3. Prepays $96 in insurance for two years. The insurance expense is booked at the end of 4. Buys inventory of $267 on credit. 5. Buys PP&E for $160 in cash. The PP&E has a useful life of three years and a salvage value of $10. It is depreciated on a straight-line basis. It is not used for manufacturing. 6. Buys inventory for $174 in cash. 7. Books credit sales of $525. [COGS is booked later at the end of the year.] 8. Books cash sales of $181. [COGS is booked later at the end of the year.] 9. Receives $310 in cash as an advance from customers. 10. Pays $127 to employees as salary for the year. This is not related to manufacturing. 11. Employees earn a bonus of $32 for their work in Y1. The bonus is paid in cash in Y. 12. The cost of goods sold for the year is $163. 13. Books insurance expense for the year. 14. Books interest expense for the loan. Assume that the interest is paid in cash. 15. Books depreciation expense for the year. 16. Pays a cash dividend of 35 cents per share. 17. Buys back 10 shares of stock at the same price at which they were originally issued. 18. Repays $120 of the loan principal. Year 2: 1. Collects receivables from the prior year in full. 2. Books revenues for advances received in the prior year in full. 3. Books the remaining inventory as COGS. 4. Pays bonuses due from the prior year in full. 5. Pays amounts due to suppliers from the prior year in full. 6. Books depreciation expense. 7. Books insurance expense. 8. Sells its entire PP&E for $68 in cash. 9. Books interest expense for the loan. Assume that the interest is paid in cash. 10. Repays loan in full. Year 1 Year 2 (Two) 100 25 6 11 15 4 21 56 28 155 50 62 10 3 3 Ending Balance Sheet Cash Receivables Inventories Prepayments Gross PP&E Accumulated depreciation [Positive number. Subtract while computing total assets) Accounts payables Accrued expenses Deferred revenues Debt Paid-in capital Retained earnings Income Statement Sales COGS [Positive number] SG&A expenses [Positive number] Depreciation (Positive number] Gains (losses) (Gain: Positive; loss: negative] Interest expense (Positive number] Indirect Cash Flow Statement Adjustments for [Put minus sign (-) before a number to be subtracted] (Change) in gross receivables (Change) in inventories (Change) in prepaid insurance Depreciation Change in accounts payables Change in accrued salaries Change in deferred revenues (Gain) loss on sale of PP&E (Capital expenditure) Proceeds from sales of PP&E Proceeds from debt (Repayment of debt) Capital contributions Capital (distributions) Dividend (distributions) Direct Operating Cash Flow Statement Cash received from customers Cash (paid) to suppliers [Negative number] Operating (payments) [Negative number] Cash (paid) for interest [Negative number] -25 -6 10 11 4 -3 -30 23 29 134 -45 -51 -3 each year. Year 1: 1. Issues 60 shares of stock at $14 per share in cash. 2. Takes a loan for $450 in cash. The interest rate is 10% per year. 3. Prepays $96 in insurance for two years. The insurance expense is booked at the end of 4. Buys inventory of $267 on credit. 5. Buys PP&E for $160 in cash. The PP&E has a useful life of three years and a salvage value of $10. It is depreciated on a straight-line basis. It is not used for manufacturing. 6. Buys inventory for $174 in cash. 7. Books credit sales of $525. [COGS is booked later at the end of the year.] 8. Books cash sales of $181. [COGS is booked later at the end of the year.] 9. Receives $310 in cash as an advance from customers. 10. Pays $127 to employees as salary for the year. This is not related to manufacturing. 11. Employees earn a bonus of $32 for their work in Y1. The bonus is paid in cash in Y. 12. The cost of goods sold for the year is $163. 13. Books insurance expense for the year. 14. Books interest expense for the loan. Assume that the interest is paid in cash. 15. Books depreciation expense for the year. 16. Pays a cash dividend of 35 cents per share. 17. Buys back 10 shares of stock at the same price at which they were originally issued. 18. Repays $120 of the loan principal. Year 2: 1. Collects receivables from the prior year in full. 2. Books revenues for advances received in the prior year in full. 3. Books the remaining inventory as COGS. 4. Pays bonuses due from the prior year in full. 5. Pays amounts due to suppliers from the prior year in full. 6. Books depreciation expense. 7. Books insurance expense. 8. Sells its entire PP&E for $68 in cash. 9. Books interest expense for the loan. Assume that the interest is paid in cash. 10. Repays loan in full. Year 1 Year 2 (Two) 100 25 6 11 15 4 21 56 28 155 50 62 10 3 3 Ending Balance Sheet Cash Receivables Inventories Prepayments Gross PP&E Accumulated depreciation [Positive number. Subtract while computing total assets) Accounts payables Accrued expenses Deferred revenues Debt Paid-in capital Retained earnings Income Statement Sales COGS [Positive number] SG&A expenses [Positive number] Depreciation (Positive number] Gains (losses) (Gain: Positive; loss: negative] Interest expense (Positive number] Indirect Cash Flow Statement Adjustments for [Put minus sign (-) before a number to be subtracted] (Change) in gross receivables (Change) in inventories (Change) in prepaid insurance Depreciation Change in accounts payables Change in accrued salaries Change in deferred revenues (Gain) loss on sale of PP&E (Capital expenditure) Proceeds from sales of PP&E Proceeds from debt (Repayment of debt) Capital contributions Capital (distributions) Dividend (distributions) Direct Operating Cash Flow Statement Cash received from customers Cash (paid) to suppliers [Negative number] Operating (payments) [Negative number] Cash (paid) for interest [Negative number] -25 -6 10 11 4 -3 -30 23 29 134 -45 -51 -3
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


