Question: Please complete to TODOs for the methods indexOf(val) and remove(int index) in LinkedList.Java DoubleLinkedList.Java /** * This class is similar to the built-in doubly linked
Please complete to TODOs for the methods indexOf(val) and remove(int index) in LinkedList.Java
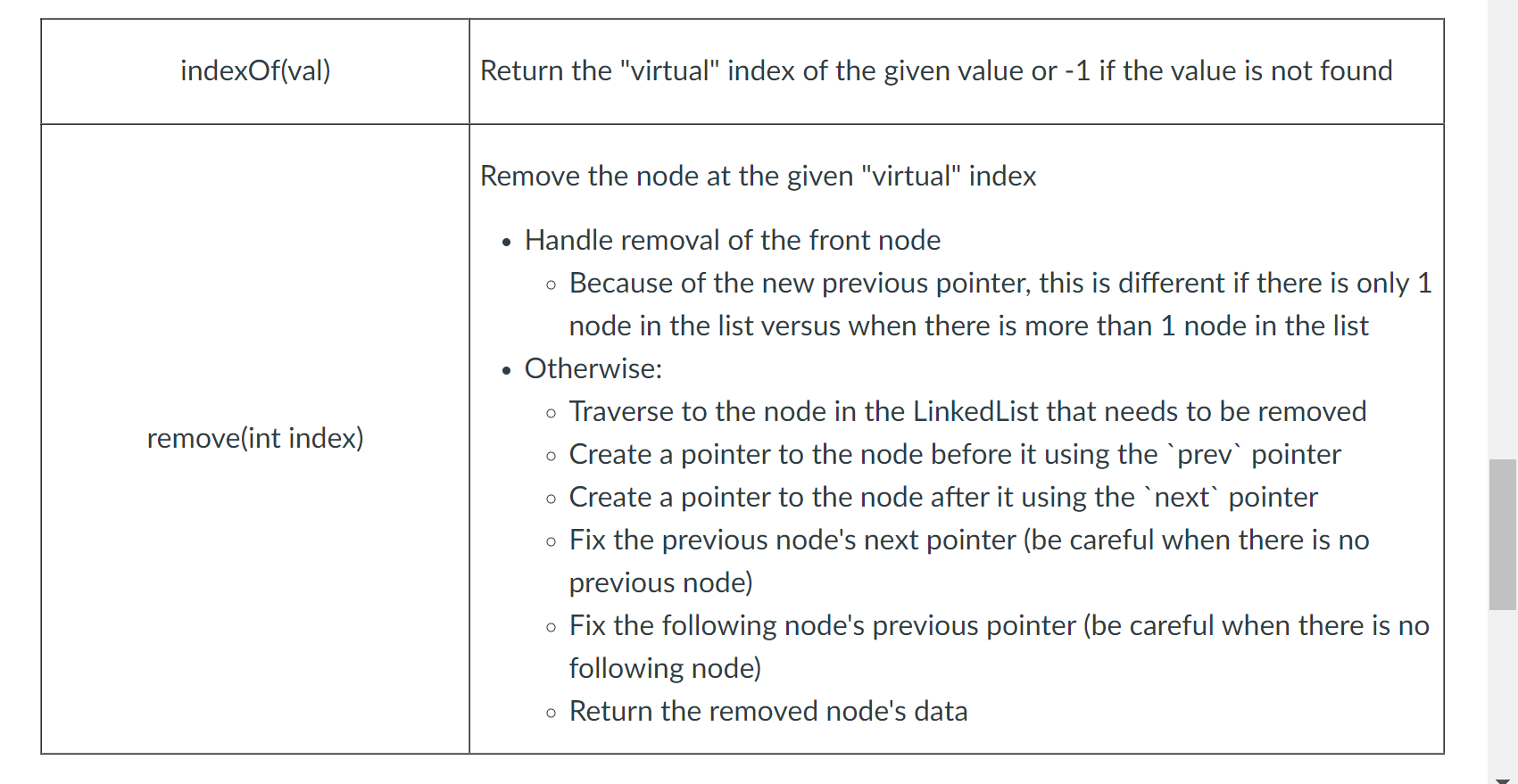
DoubleLinkedList.Java /** * This class is similar to the built-in doubly linked list that Java has (java.util.LinkedList) but with reduced * functionality * @paramthe type of object stored in the list */ public class DoublyLinkedList implements List { private ListNode front; private int size; // number of nodes in the list /** * Constructor creates an empty list */ public DoublyLinkedList() { front = null; size = 0; // no nodes in the list } /** * Creates a new 'front' node without a prev or next * @param val object to add */ public DoublyLinkedList(E val) { front = new ListNode(val, null, null); size = 1; // one node in the list } /** * Adds a new node to the end of the list * Note: Reuses the add(index, value) method * @param val */ public void add(E val) { add(size, val); } /** * Adds a new node at the specified index with the data 'val' * @param index should be between 0 and size * @param val data to add */ public void add(int index, E val) { if (index size) { throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Cannot add at Index " + index); } // add a new node with val as the data to the front of the list if (index == 0) { front = new ListNode(val, front, null); // If there were more nodes in the list prior to the add(0, val) adjust the .prev to point to this // new node if ( front.next != null) { front.next.prev = front; } } else { ListNode current = front; // TODO: traverse to the node before where you need to add the new node // Example: add(2, f) was called // when front ----> a ----> b ----> c ----> d ----> null // null a ----> b ----> c ----> d ----> null // null after = current.next; // TODO: construct a new ListNode(f, node c, node b) named insert ListNode insert = new ListNode(val, after, current); // TODO: Connect the insert node into the current list current.next = insert; // TODO: if node is NOT being added to the end of an existing list, adjust prev if (after != null){ after.prev = insert; } } size++; } // Returns the data at a given "virtual" index // throws IndexOutOfBounds if the index is invalid (not 0 to size) /** * Returns the data at a given "virtual" index * @param index should be between 0 and size - 1 * @return */ public E get(int index) { if (index > size - 1 || index current = front; for (int i = 0; i Part 2 TODO: return the "virtual" index of val, or -1 if not found public int indexOf(E val) { return -1; } // Part 2 TODO: return the data of the node at the index provided public E remove(int index) { if (index size - 1) { throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index " + index + " does not exist."); } E removed = null; // will save the data value about to be removed ListNode current = front; // use current to move through the list // if removing at index 0 if (index == 0) { // TODO handle this case appropriately } else { // TODO handle this case appropriately } size--; return removed; } // Returns the number of nodes in the list // O(1) because we are continuously tracking size during construct/add/remove public int size() { return size; } @Override public String toString() { if (size() == 0) { return "[]"; } StringBuilder build = new StringBuilder(); ListNode current = front; while (current.next != null) { build.append(current.data); build.append(", "); current = current.next; } // current is on the last node build.append(current.data); return "[" + build + "] size=" + size(); } }
=================================================
ListNode.Java /** * A node that can be used in a doubly linked list * The class is generic so any Java Object can be stored in it * @param*/ public class ListNode { public E data; public ListNode next; public ListNode prev; /** * Creates a ListNode with all null values */ public ListNode() { this(null, null, null); } /** * Creates a Solitary ListNode * @param data */ public ListNode(E data) { this(data, null, null); } /** * Creates a ListNode with * @param data any Java object * @param next points to the next ListNode in the list * @param prev points to the previous ListNode in the list */ public ListNode(E data, ListNode next, ListNode prev) { this.data = data; this.next = next; this.prev = prev; } public String toString() { return "[" + this.data + "]"; } }
===============================================================
List.Java
public interface List{ void add(E value); // TODO - we will work on this together in Part 1 void add(int index, E value); E get(int index); // TODO: Individually or complete with a partner - Part 2 int indexOf(E value); // TODO: Individually or complete with a partner - Part 2 E remove(int index); int size(); }
=========================================================
LinkedListTester.Java import java.util.Scanner; /** * This class constructs a DoublyLinkedList of Characters and tests out the * methods: add(index, value), add(value), remove(index), indexOf(value), * get(index) * */ public class DoublyLinkedListTester { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in); DoublyLinkedList doubleList = new DoublyLinkedList(); System.out.println(doubleList); String option = ""; do { option = displayOptions(console); if (option.startsWith("ai")) { System.out.print("Add at what index? > "); int index = Integer.parseInt(console.nextLine()); System.out.print("Add what? > "); char value = console.nextLine().charAt(0); doubleList.add(index, value); } else if (option.startsWith("a")) { System.out.print("Add What? > "); char value = console.nextLine().charAt(0); doubleList.add(value); } else if (option.startsWith("g")) { System.out.print("Get what index? > "); int index = Integer.parseInt(console.nextLine()); char got = doubleList.get(index); System.out.println("--- Got " + got + " ---"); } else if (option.startsWith("io")) { System.out.print("Index of what? > "); char value = console.nextLine().charAt(0); int index = doubleList.indexOf(value); if (index >= 0) System.out.println("--- Found at index: " + index + " ---"); else System.out.println("--- Not found --- returned: " + index); } else if (option.startsWith("ri")) { System.out.print("Remove what index? > "); int index = Integer.parseInt(console.nextLine()); char removed = doubleList.remove(index); System.out.println("--- Removed " + removed + " ---"); } System.out.println(doubleList); } while (!option.startsWith("d")); } private static String displayOptions(Scanner console) { System.out.println(" Options: (a) add to the end (ai) add at index (io) indexOf a value"); System.out.println(" (g) get by index (ri) remove at index (d) done"); System.out.print("Which option? > "); return console.nextLine().toLowerCase(); } }
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


