Question: PLEASE DO IT STEP BY STEP CORRECTLY WITHOUT USING SHORTCUTS I WILL THUMBS UP THANK YOU. 120 Case 3 profit for the past year are
 PLEASE DO IT STEP BY STEP CORRECTLY WITHOUT USING SHORTCUTS I WILL THUMBS UP THANK YOU.
PLEASE DO IT STEP BY STEP CORRECTLY WITHOUT USING SHORTCUTS I WILL THUMBS UP THANK YOU.
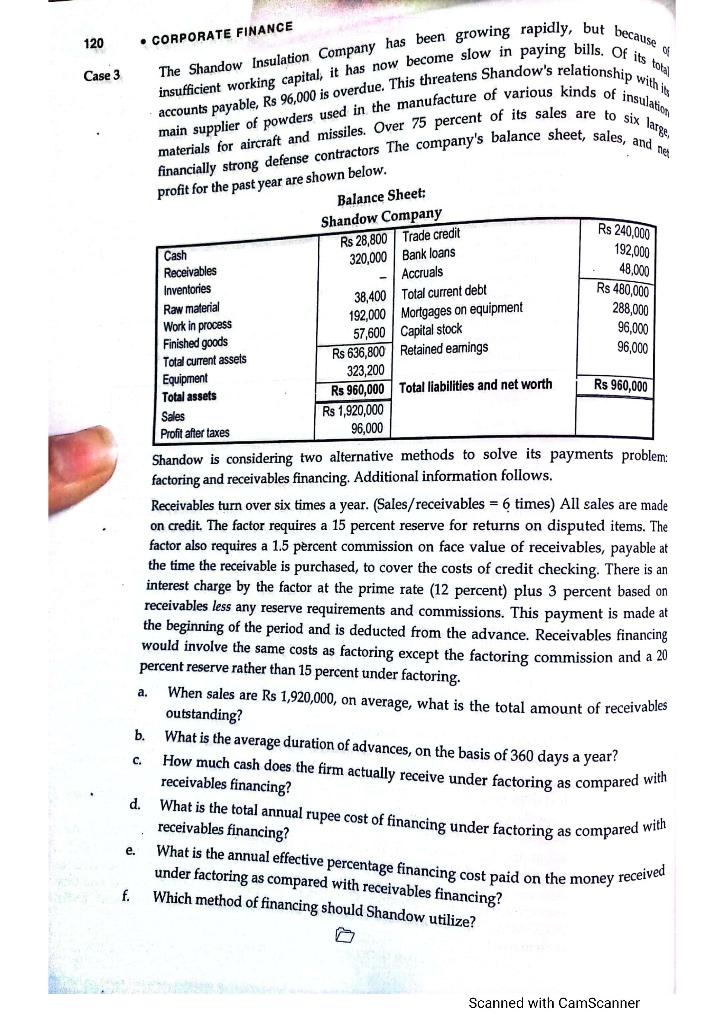
120 Case 3 profit for the past year are shown below. CORPORATE FINANCE The Shandow Insulation Company has been growing rapidly, but because insufficient working capital, it has now become slow in paying bills. Of its to accounts payable, Rs 96,000 is overdue. This threatens Shandow's relationship with a main supplier of powders used in the manufacture of various kinds of insulation financially strong defense contractors The company's balance sheet, sales, and that materials for aircraft and missiles. Over 75 percent of its sales are to six large Balance Sheet: Shandow Company Cash Rs 28,800 Trade credit Receivables 320,000 Bank loans Inventories Accruals Raw material 38,400 Total current debt Work in process 192,000 Mortgages on equipment Finished goods 57,600 Capital stock Total current assets Rs 636,800 Retained earnings Equipment 323,200 Total assets Rs 960,000 Total liabilities and net worth Sales R$ 1,920,000 Profit after taxes 96,000 Rs 240,000 192,000 48,000 Rs 480,000 288,000 96,000 96,000 Rs 960,000 Shandow is considering two alternative methods to solve its payments problem: factoring and receivables financing. Additional information follows. Receivables turn over six times a year. (Sales/receivables = 6 times) All sales are made on credit. The factor requires a 15 percent reserve for returns on disputed items. The factor also requires a 1.5 percent commission on face value of receivables, payable at the time the receivable is purchased, to cover the costs of credit checking. There is an interest charge by the factor at the prime rate (12 percent) plus 3 percent based on receivables less any reserve requirements and commissions. This payment is made at the beginning of the period and is deducted from the advance. Receivables financing would involve the same costs as factoring except the factoring commission and a 20 percent reserve rather than 15 percent under factoring. When sales are Rs 1,920,000, on average, what is the total amount of receivables outstanding? a. b. c. d. What is the average duration of advances, on the basis of 360 days a year? How much cash does the firm actually receive under factoring as compared with receivables financing? What is the total annual rupee cost of financing under factoring as compared with receivables financing? What is the annual effective percentage financing cost paid on the money received under factoring as compared with receivables financing? Which method of financing should Shandow utilize? e. f. Scanned with CamScanner 120 Case 3 profit for the past year are shown below. CORPORATE FINANCE The Shandow Insulation Company has been growing rapidly, but because insufficient working capital, it has now become slow in paying bills. Of its to accounts payable, Rs 96,000 is overdue. This threatens Shandow's relationship with a main supplier of powders used in the manufacture of various kinds of insulation financially strong defense contractors The company's balance sheet, sales, and that materials for aircraft and missiles. Over 75 percent of its sales are to six large Balance Sheet: Shandow Company Cash Rs 28,800 Trade credit Receivables 320,000 Bank loans Inventories Accruals Raw material 38,400 Total current debt Work in process 192,000 Mortgages on equipment Finished goods 57,600 Capital stock Total current assets Rs 636,800 Retained earnings Equipment 323,200 Total assets Rs 960,000 Total liabilities and net worth Sales R$ 1,920,000 Profit after taxes 96,000 Rs 240,000 192,000 48,000 Rs 480,000 288,000 96,000 96,000 Rs 960,000 Shandow is considering two alternative methods to solve its payments problem: factoring and receivables financing. Additional information follows. Receivables turn over six times a year. (Sales/receivables = 6 times) All sales are made on credit. The factor requires a 15 percent reserve for returns on disputed items. The factor also requires a 1.5 percent commission on face value of receivables, payable at the time the receivable is purchased, to cover the costs of credit checking. There is an interest charge by the factor at the prime rate (12 percent) plus 3 percent based on receivables less any reserve requirements and commissions. This payment is made at the beginning of the period and is deducted from the advance. Receivables financing would involve the same costs as factoring except the factoring commission and a 20 percent reserve rather than 15 percent under factoring. When sales are Rs 1,920,000, on average, what is the total amount of receivables outstanding? a. b. c. d. What is the average duration of advances, on the basis of 360 days a year? How much cash does the firm actually receive under factoring as compared with receivables financing? What is the total annual rupee cost of financing under factoring as compared with receivables financing? What is the annual effective percentage financing cost paid on the money received under factoring as compared with receivables financing? Which method of financing should Shandow utilize? e. f. Scanned with CamScanner
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


