Question: please do Part c, part A and B are already answered please make the answer clear As the ladder slides down, x coordinate increases from
please do Part c, part A and B are already answered please make the answer clear

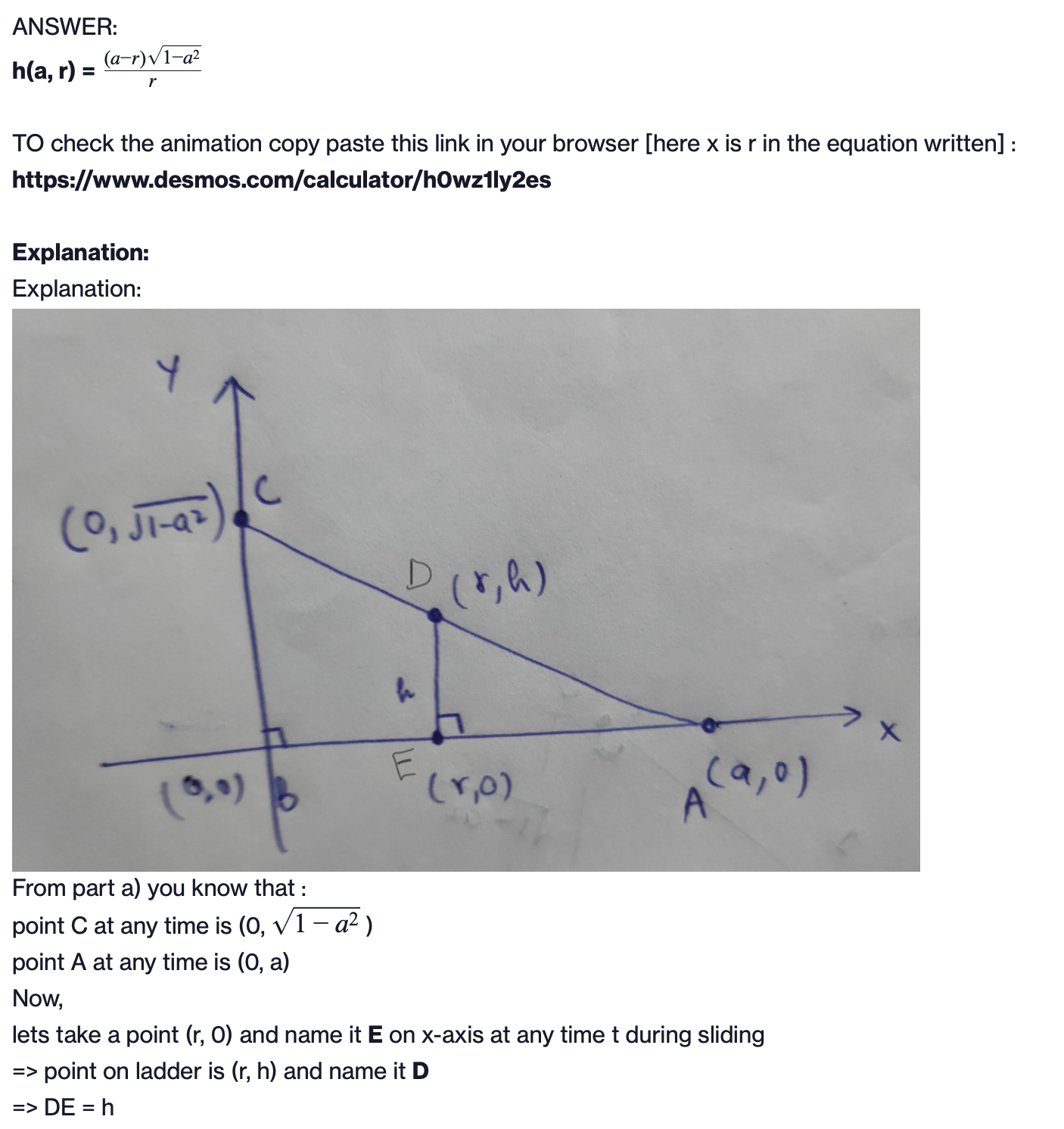


As the ladder slides down, x coordinate increases from 0 to 1 and y coordinate decreases from 1 to 0. We state the Pythagorean Theorem equation that is a + b = hypotenuse Note that hypotenuse will always be equal to 1 since this denotes the constant length of the ladder that is 1. Let's define a as the length or distance of the bottom of the ladder from the wall (x coordinate) as the whole ladder slides down the wall. This 'a' now is an arbitrary variable. Going back to the equation: 2 a + b = hypotenuse --> a b We isolate b so that we get "blah" in our x-y coordinate (0,blah) b = V1 -a2ANSWER: Ma, r) = '\"");' \"'2 TO check the animation copy paste this link in your browser [here x is r in the equation written] : https:/lwww.desmos.com/calculator/hsz1ly2es Explanation: Explanation: From part a) you know that : point C at any time is (0, V 1 a2 ) point A at any time is (0, a) Now, lets take a point (r, 0) and name it E on xaxis at any time t during sliding => point on ladder is (r, h) and name it D => DE = h \f(2) In this problem we nd a formula for the \"envelope\" of the shape traced out by a ladder sliding down a wall. See the animated gure on Canvas. (3-) (10) Suppose the ladder has length 1 and begins upright with its top at (0,1) and its bottom at (0,0). We imagine the bottom of the ladder has position (a, 0) as c ranges from 0 to 1. Use the Pythagorean Theorem to nd the coordinates of the top of the ladder when the bottom is at ((1,0). (Hint: your answer should have the form (0, blah) where blah depends on a.) Consider a xed 1' in [0,1]. As bottom of the ladder slides from 0 to 1 (i.e. as 0. moves from 0 to 1), the ladder intersects the vertical line .7: = r at some point (ah) whenever a. is in [131]. Use similar triangles to nd a formula for h in terms of o and 1". Call this Ma, P). Go to this desmos link https://ww.desmos .com/calculator/dpwlmlfiwb (press the play button in the row that says \"a = 0\" to watch the animation). In the 5th row, enter the expression (1", Ma: 1" where h(a, r) is the function you just found. Set the r slider to be something like 0.3, and watch the animation. Do you understand what you are seeing? The maximum of the function h.(a, 1') for a in the domain [1", 1] represents the height of the \"envelope\" when a: = 1'. Take the derivative of h with respect to a (treat 1" as a constant), nd a critical point in the domain [1", 1] (it ought to depend on r) and conrm that It has a local maximum at this point
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


