Question: Please do this in C++ // --------------------------------------------------------------------------- // Assignment #1 The Subset-Sum Problem Part A - int Version #include #include #include using namespace std; //
Please do this in C++
// --------------------------------------------------------------------------- // Assignment #1 The Subset-Sum Problem Part A - int Version
#include
// global scope helpers double computeMasterSum( vector
// --------------- Sublist Prototype --------------- class Sublist { public: Sublist(vector
private: int sum; vector
// ------------------ main ------------------
int main() { int target = 0; vector
dataSet.push_back( 20 ); dataSet.push_back( 12 ); dataSet.push_back( 22 ); dataSet.push_back( 15 ); dataSet.push_back( 25 ); dataSet.push_back( 19 ); dataSet.push_back( 29 ); dataSet.push_back( 18 ); dataSet.push_back( 11 ); dataSet.push_back( 13 ); dataSet.push_back( 17 );
choices.clear(); cin >> target; cout
// dispose of easy case immediately to save lots of time masterSum = (int) computeMasterSum( dataSet ); if ( target >= masterSum ) { cout
choices[bestSublist].showSublist(); return 0; } }
// global scope functions --------------------------- // Helper method to compute full sum double computeMasterSum( vector
void showEntireVector( vector
// --------------- Sublist Method Definitions ---------------
void Sublist::showSublist() const { int k;
cout
Sublist Sublist::addItem(int indexOfItemToAdd ) { // code provided by student // // }
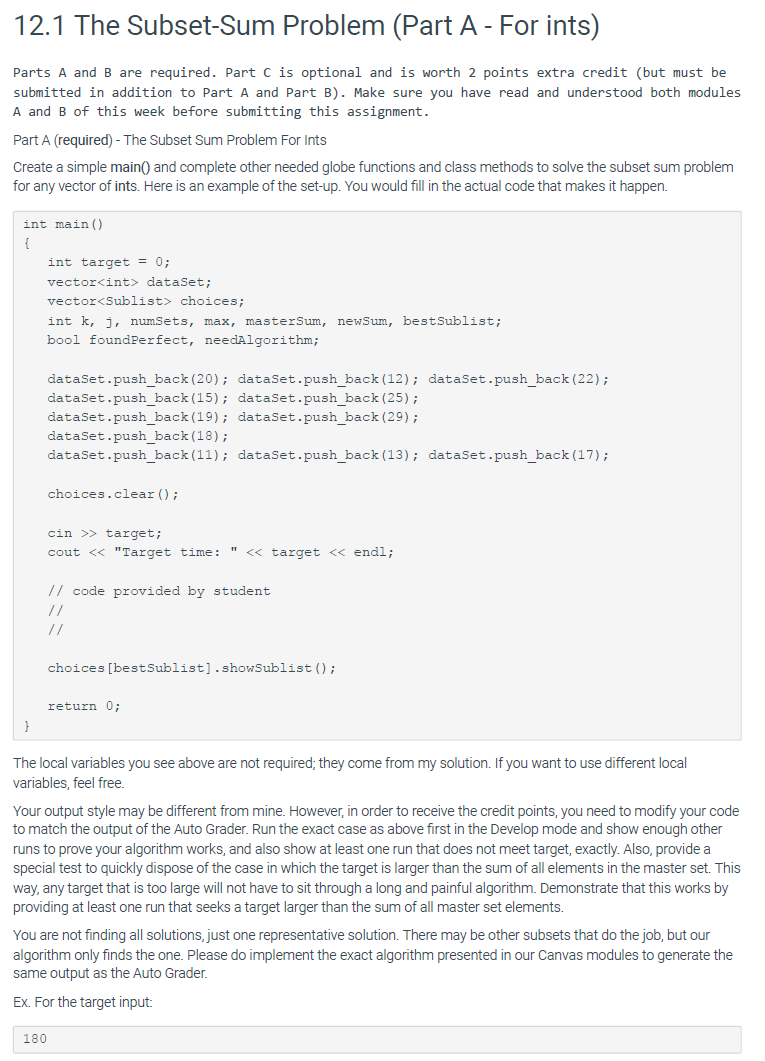
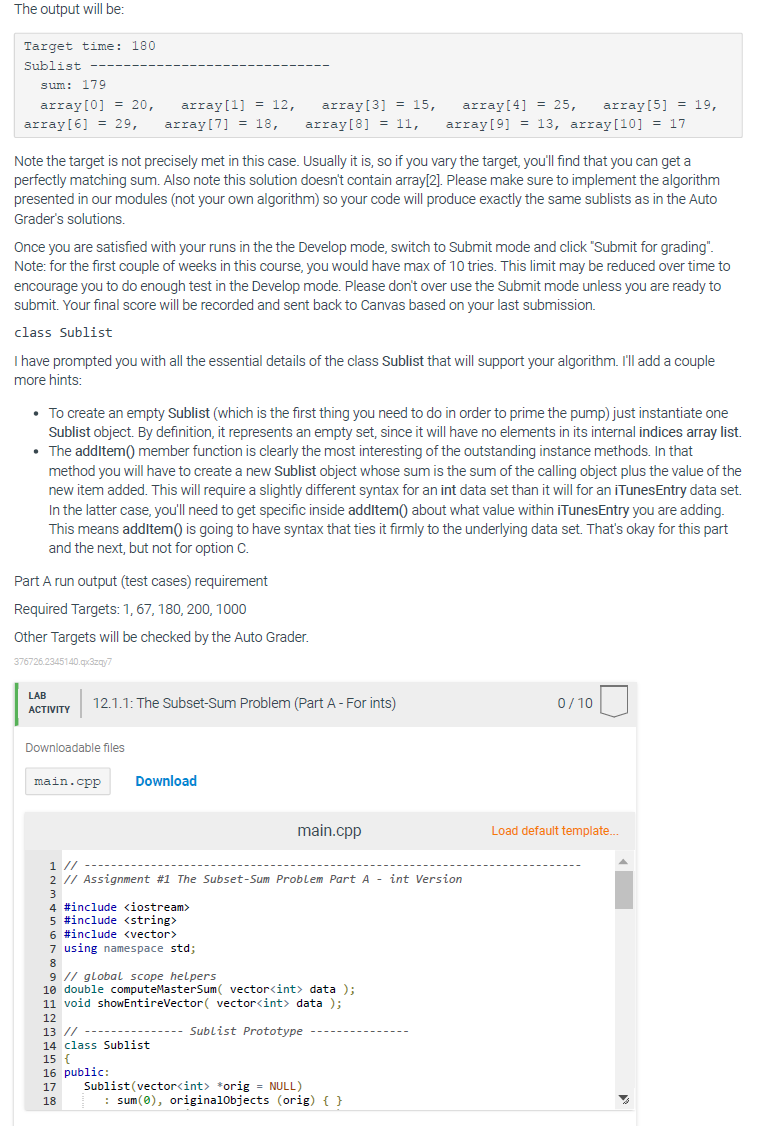
12.1 The Subset-Sum Problem (Part A - For ints) Parts A and B are required. Part C is optional and is worth 2 points extra credit (but must be submitted in addition to Part A and Part B). Make sure you have read and understood both modules A and B of this week before submitting this assignment. Part A (required) - The Subset Sum Problem For Ints Create a simple main() and complete other needed globe functions and class methods to solve the subset sum problem for any vector of ints. Here is an example of the set-up. You would fill in the actual code that makes it happen. int main() { int target = 0; vector int> dataSet; vector
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


