Question: Please don't comment if cannot answer 3. Any forecast of financial requirements involves la determining how much money the firm will the same period, and
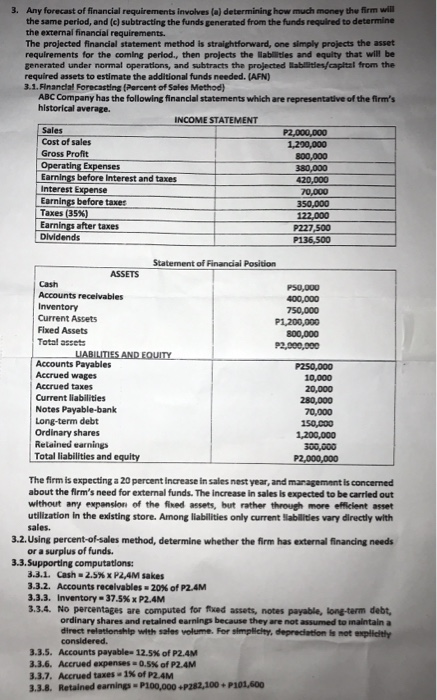
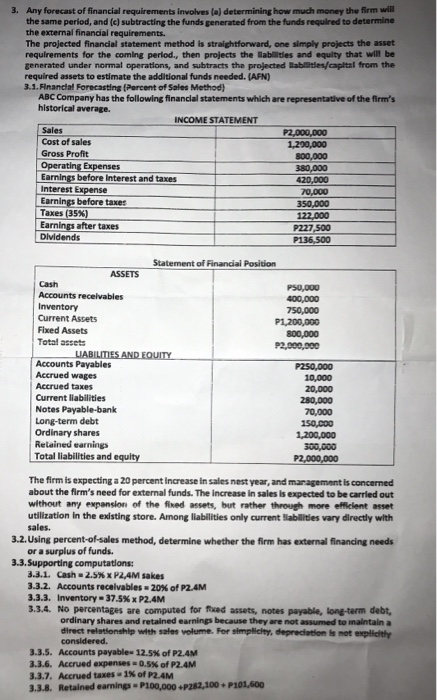
3. Any forecast of financial requirements involves la determining how much money the firm will the same period, and (c) subtracting the funds generated from the funds required to determine the external financial requirements. The projected financial statement method is straightforward, one simply projects the asset requirements for the coming period, then projects the abilities and equity that will be generated under normal operations, and subtracts the projected lates/capital from the required assets to estimate the additional funds needed. (AFN) 3.1. Financial Forecasting (Percent of Sales Method) ABC Company has the following financial statements which are representative of the firm's historical average INCOME STATEMENT Sales 22,000,000 Cost of sales 1,290,000 Gross Profit 300,000 Operating Expenses 380,000 Earnings before interest and taxe 420,000 Interest Expense 70.000 Earnings before taxes 350,000 Taxes (35%) 122.000 Earnings after taxes P227,500 Dividends P136,500 Statement of Financial Position ASSETS Cash P50,000 Accounts receivables 400,000 Inventory 750,000 Current Assets P1,200,000 Fixed Assets 300,000 Total assets P2,000,000 LIABILITIES AND EQUITY Accounts Payables P250,000 Accrued wages 10,000 Accrued taxes 20,000 Current liabilities 280,000 Notes Payable-bank 70,000 Long-term debt 150.000 Ordinary shares 1,200,000 Retained earnings 300,000 Total liabilities and equity P2,000,000 The firm is expecting a 20 percent increase in sales nest year, and management is concerned about the firm's need for external funds. The increase in sales is expected to be carried out without any expansion of the fined assets, but rather through more efficient asset utilization in the existing store. Among liabilities only current abilities vary directly with sales. 3.2. Using percent-of-sales method, determine whether the firm has external financing needs or a surplus of funds. 3.3. Supporting computations 3.3.1. Cash 2.5% XP2.4M sakes 3.3.2. Accounts receivables - 20% of P2.4M 3.3.3. Inventory - 37.5% x P2.4M 3.3.4. No percentages are computed for fixed assets, notes payable, long-term debt, ordinary shares and retained earnings because they are not assumed to maintain a direct relationship with sales volume. For simplicity, depreciation is not explicity considered 3.3.5. Accounts payable 12.5% of P2.4M 3.3.6. Accrued expenses 0.5% of P2.4M 3.3.7. Accrued taxes - 1 of P2.4M 3.3.8. Retained earning-P100,000P282,100 P101,600 Any forecast of financial requirements involves a determining how much money the firm w the same period, and (c) subtracting the funds generated from the funds required to determine the external financial requirements The projected financial statement method is straightforward, one simply projects the asset requirements for the coming period, then projects the abilities and equity that will be generated under normal operations, and subtracts the projected tables/capital from the required assets to estimate the additional funds needed. (AFN) 3.1. Financial Forecasting (Percent of Sales Method) ABC Company has the following financial statements which are representative of the firm's historical average INCOME STATEMENT Sales 22,000,000 Cost of sales 1,200,000 Gross Profit 300,000 Operating Expenses 380,000 Earnings before Interest and taxes 420,000 Interest Expense 70.000 Earnings before taxes 350,000 Taxes (35%) 122.000 Earnings after taxes P227,500 Dividends P136.500 Statement of Financial Position ASSETS Cash P50,000 Accounts receivables 400,000 Inventory 750,000 Current Assets P1,200,000 Fixed Assets 300,000 Total assets P2,000,000 LIABILITIES AND EQUITY Accounts Payables P250,000 Accrued wages 10,000 Accrued taxes 20,000 Current liabilities 280,000 Notes Payable-bank 70,000 Long-term debt 150.000 Ordinary shares 1,200,000 Relained earnings 300,000 Total liabilities and equity P2,000,000 The firm is expecting a 20 percent increase in sales nast year, and management is concerned about the firm's need for external funds. The increase in sales is expected to be carried out without any expansion of the fixed assets, but rather through more efficient asset utilization in the existing store. Among liabilities only current abilities vary directly with sales. 3.2. Using percent-of-sales method, determine whether the firm has external financing needs or a surplus of funds. 3.3. Supporting computations 3.3.1. Cash 2.5% X P2.4M sakes 3.3.2. Accounts receivables - 20% of P2.4M 3.3.3. Inventory = 37.5% x P2.4M 3.3.4. No percentages are computed for fixed assets, notes payable, long-term debt, ordinary shares and retained earnings because they are not assumed to maintain a direct relationship with sales volume. For simplicity, depreciation is not explicit considered. 3.3.5. Accounts payable- 12.5of P2.4M 3.3.6. Accrued expenses 0.5% of P2.4M 3.3.7. Accrued taxes - 1 of P2.4M 3.3.8. Retained earnings - P100,000 P262,100.101,600
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


