Question: please fill in the table. Problem Setup Consider the market for widgets, with the following elements. In the market for widgets, consumers have a market


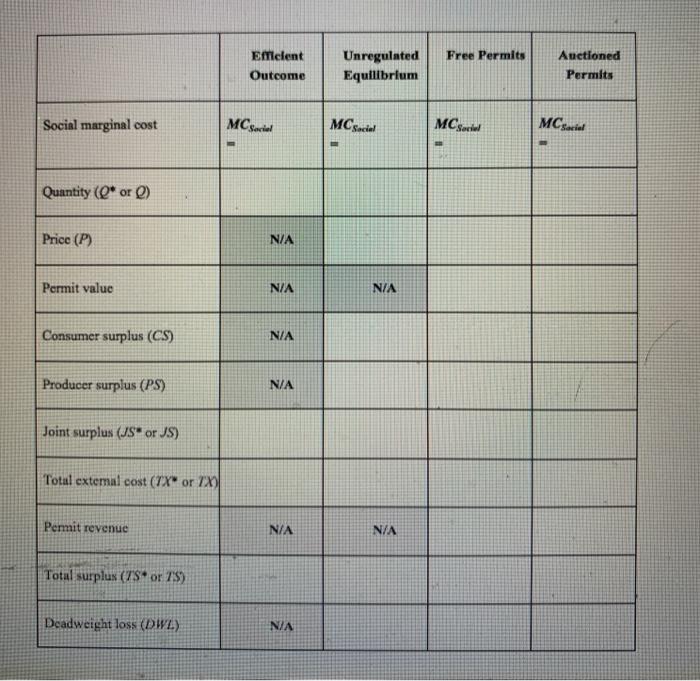
Problem Setup Consider the market for widgets, with the following elements. In the market for widgets, consumers have a market demand (marginal benefit) curve of P=MB = 250 - Q. In this problem, there is no distinction between private and social marginal benefit. The widget suppliers have a market supply (private marginal cost) curve of P= MCA Private 100+ Q. The production of widgets generates a negative externality in the form of pollution, with marginal external cost of X = 50. Due to this externality, there will be a difference between private and social marginal cost. Analyze the following scenarios describing possible outcomes in the market for widgets. Efficient Outcome Find the equation for social marginal cost (MC), using the information above. Determine the efficient quantity (@"). Calculate the joint surplus (JS"), total external cost (TX), and the total surplus (TS) based on the efficient quantity . Unregulated Equilibrium Find the market equilibrium, defined by the market quantity (0) and price (P) Determine the consumer surplus (CS), producer surplus (PS).joint surplus (JS), total external cost (TX), and the total surplus (78) for the equilibrium outcome. Calculate the deadweight loss (DWL) for the equilibrium outcome. . Free Permits Equilibrium Assume that the regulator sets up a tradable permit (cap-and-trade) program with the allowed number of widgets (the cap) set to The permits are given to the widget suppliers at no charge, and they can buy and sell them to/from each other. Find the new equilibrium, defined by the market quantity () and price (P). Find the value of a permit. How much would a producer be willing to pay to acquire an additional permit? Determine the consumer surplus (CS), producer surplus (PS).joint surplus (JS), and total external cost (TX) for the equilibrium outcome. Determine the permit revenue collected by the government. Determine the total surplus (TS) for the equilibrium outcome Calculate the deadweight loss (DWZ) for the equilibrium outcome. . . . Auctioned Permits Equilibrium Assume that the regulator sets up a tradable permit (cap-and-trade program) with the allowed number of widgets (the cap) set to The permits are auctioned to the widget suppliers, who will pay the amount that an additional permit would be worth in equilibrium. Suppliers can can buy and sell permits to from each other. Find the new equilibrium, defined by the market quantity (O) and price Find the value of a permit. How much would a producer be willing to pay to acquire an additional permit? Determine the consumer surplus (CS), producer surplus (PS), joint surplus (JS), and total external cost (FX) for the equilibrium outcome Determine the permit revenue collected by the government Detennine the total surplus (7) for the equilibrium outcome Calculate the deadweight loss (DWZ.) for the equilibrium outcome . . . Pages: 2 of 3 Words 211 of 1 TRK Son Free Permits Eficient Outcome Unregulated Equilibrium Auctioned Permits Social marginal cost MC Social MCScie! MCsarial Quantity (Q* or ) Price (P) N/A Permit value NA N/A Consumer surplus (CS) N/A Producer surplus (PS) N/A Joint surplus (JS* or JS) Total extemal cost (TX" or 7X) Pemit revenue N/A N/A Total surplus (TS* or 7:S) Deadweight loss (DW) NA Problem Setup Consider the market for widgets, with the following elements. In the market for widgets, consumers have a market demand (marginal benefit) curve of P=MB = 250 - Q. In this problem, there is no distinction between private and social marginal benefit. The widget suppliers have a market supply (private marginal cost) curve of P= MCA Private 100+ Q. The production of widgets generates a negative externality in the form of pollution, with marginal external cost of X = 50. Due to this externality, there will be a difference between private and social marginal cost. Analyze the following scenarios describing possible outcomes in the market for widgets. Efficient Outcome Find the equation for social marginal cost (MC), using the information above. Determine the efficient quantity (@"). Calculate the joint surplus (JS"), total external cost (TX), and the total surplus (TS) based on the efficient quantity . Unregulated Equilibrium Find the market equilibrium, defined by the market quantity (0) and price (P) Determine the consumer surplus (CS), producer surplus (PS).joint surplus (JS), total external cost (TX), and the total surplus (78) for the equilibrium outcome. Calculate the deadweight loss (DWL) for the equilibrium outcome. . Free Permits Equilibrium Assume that the regulator sets up a tradable permit (cap-and-trade) program with the allowed number of widgets (the cap) set to The permits are given to the widget suppliers at no charge, and they can buy and sell them to/from each other. Find the new equilibrium, defined by the market quantity () and price (P). Find the value of a permit. How much would a producer be willing to pay to acquire an additional permit? Determine the consumer surplus (CS), producer surplus (PS).joint surplus (JS), and total external cost (TX) for the equilibrium outcome. Determine the permit revenue collected by the government. Determine the total surplus (TS) for the equilibrium outcome Calculate the deadweight loss (DWZ) for the equilibrium outcome. . . . Auctioned Permits Equilibrium Assume that the regulator sets up a tradable permit (cap-and-trade program) with the allowed number of widgets (the cap) set to The permits are auctioned to the widget suppliers, who will pay the amount that an additional permit would be worth in equilibrium. Suppliers can can buy and sell permits to from each other. Find the new equilibrium, defined by the market quantity (O) and price Find the value of a permit. How much would a producer be willing to pay to acquire an additional permit? Determine the consumer surplus (CS), producer surplus (PS), joint surplus (JS), and total external cost (FX) for the equilibrium outcome Determine the permit revenue collected by the government Detennine the total surplus (7) for the equilibrium outcome Calculate the deadweight loss (DWZ.) for the equilibrium outcome . . . Pages: 2 of 3 Words 211 of 1 TRK Son Free Permits Eficient Outcome Unregulated Equilibrium Auctioned Permits Social marginal cost MC Social MCScie! MCsarial Quantity (Q* or ) Price (P) N/A Permit value NA N/A Consumer surplus (CS) N/A Producer surplus (PS) N/A Joint surplus (JS* or JS) Total extemal cost (TX" or 7X) Pemit revenue N/A N/A Total surplus (TS* or 7:S) Deadweight loss (DW) NA
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


