Question: Please give me the CALCULATED complete solutions for the following. Don't use chatgpt, or I would have to give you a downvote. Also, please recheck
Please give me the CALCULATED complete solutions for the following. Don't use chatgpt, or I would have to give you a downvote. Also, please recheck your answers so that they are correct, and don't just copy and past from other chegg resources. Thank you.


Here are the Key Results
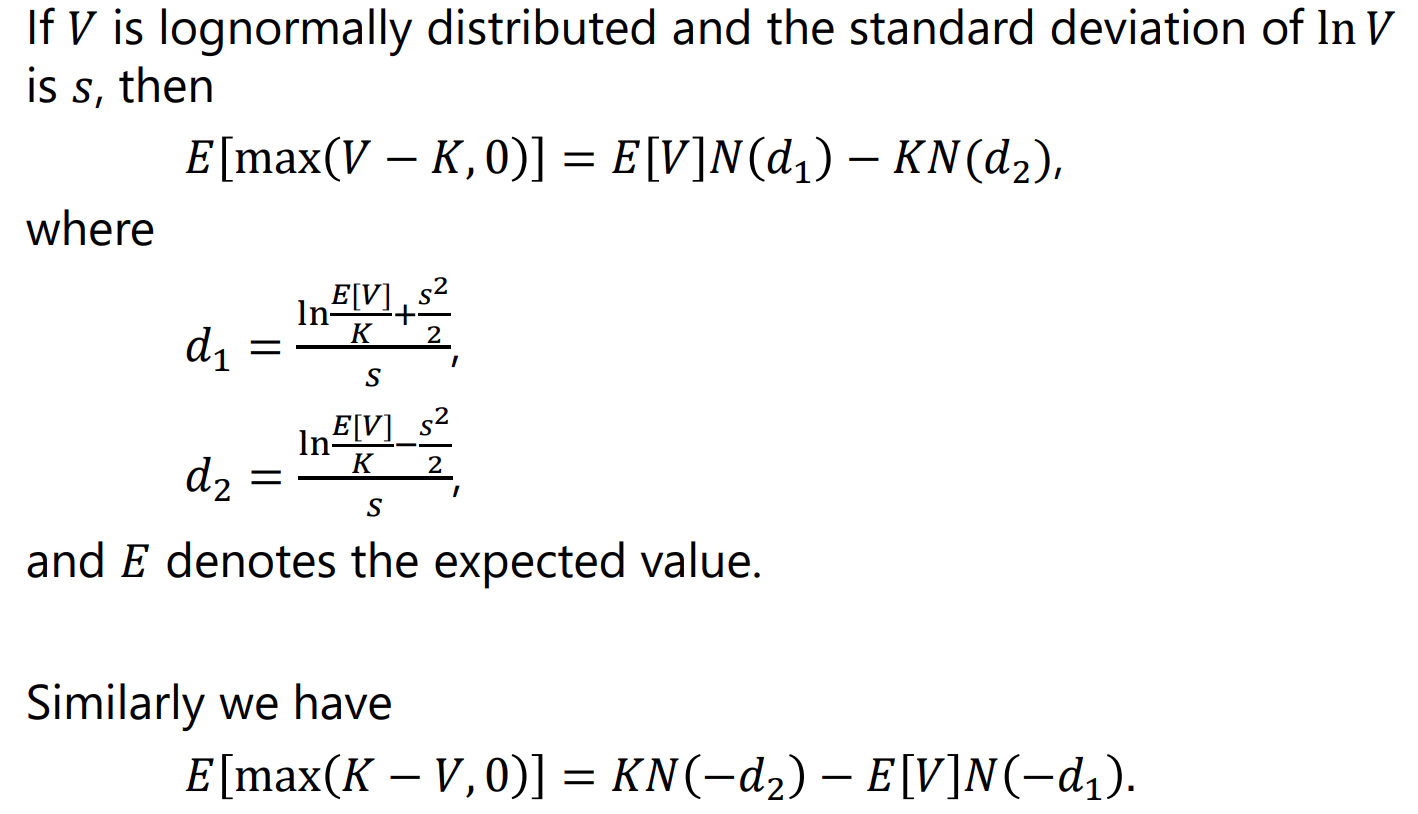
We consider pricing a European call option on a stock S which pays a known dividend yield at a rate (continuously compounded). The current stock price is S0 and the stock price volatility is . Let us derive the option pricing formula to price this option at time zero. Note that in a risk-neutral world, the expected total return from the stock must be r (the risk-free interest rate (continuously compounded)). The dividends provide a return of . The expected growth rate of the stock price, therefore, must be r. To value the option dependent on a stock that provides a dividend yield equal to , we set the expected growth rate of the stock price equal to r and discount the expected payoff at rate r. (a) What is the expected stock price at maturity T in a risk-neutral world? (b) Assume that the stock price at maturity ST follows a lognormal distribution in a risk-neutral world and the standard deviation of lnST is T. Then what is the expected payoff from the call option with the strike price of K in a risk-neutral world? (Hint: Use "Key Results" in Lecture I0.) (c) Find the option pricing formula by discounting at rate r the result obtained in (b). (d) Compute the option price assuming that the current stock price is $60, the strike price is $58, the option maturity is 12 months, the risk-free interest rate is 5.2% per annum (continuously compounded), the volatility is 22% per annum and the dividend yield is 4.7% per annum (continuously compounded). If V is lognormally distributed and the standard deviation of lnV is s, then E[max(VK,0)]=E[V]N(d1)KN(d2), where d1=slnKE[V]+2s2,d2=slnKE[V]2s2, and E denotes the expected value. Similarly we have E[max(KV,0)]=KN(d2)E[V]N(d1)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


