Question: please help A personal computer manufacturer is interested in comparing assembly times for two keyboard assembly processes. Process 1 is the standard process used for
please help
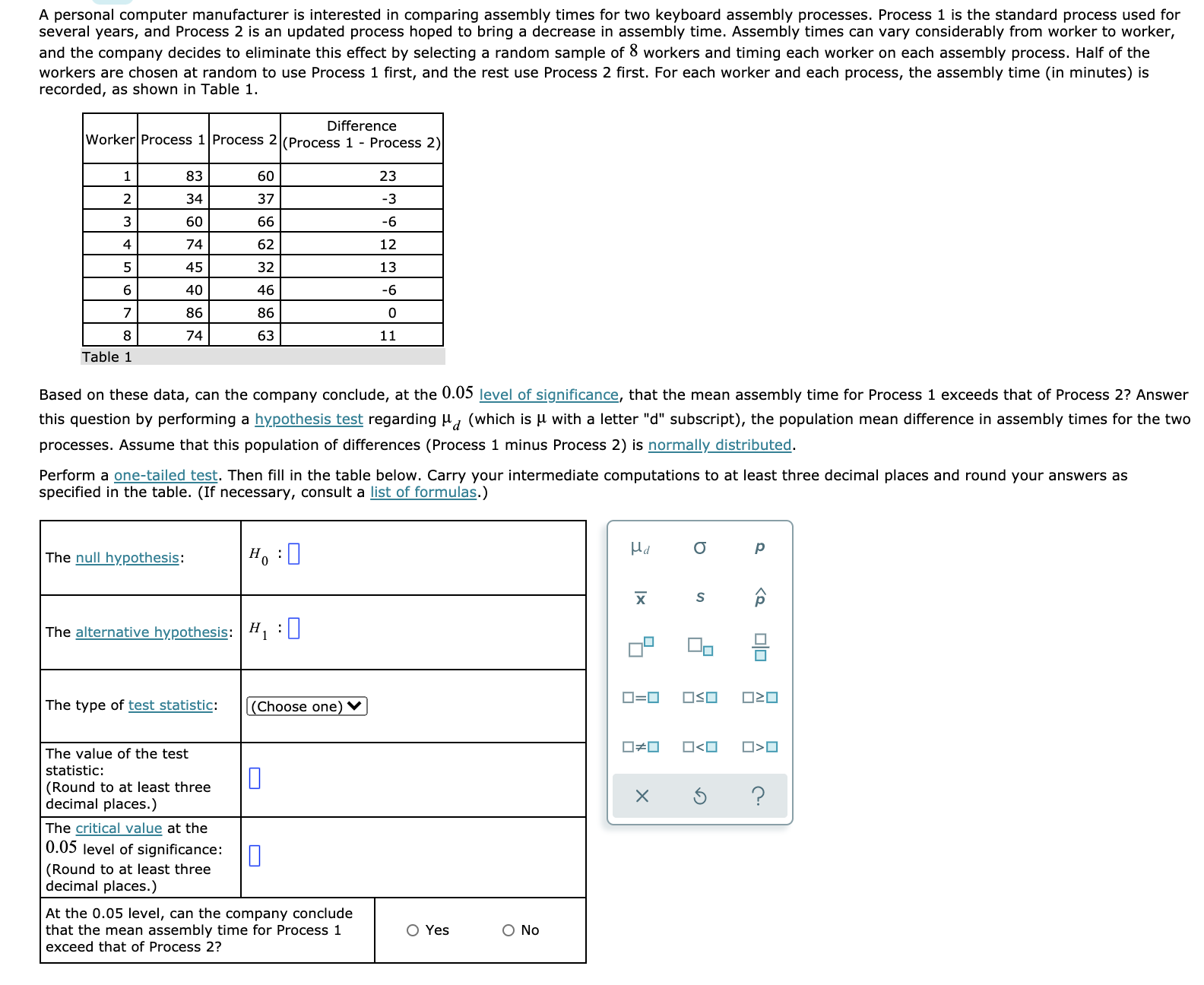
A personal computer manufacturer is interested in comparing assembly times for two keyboard assembly processes. Process 1 is the standard process used for several years, and Process 2 is an updated process hoped to bring a decrease in assembly time. Assembly times can vary considerably from worker to worker, and the company decides to eliminate this effect by selecting a random sample of 3 workers and timing each worker on each assembly process. Half of the workers are chosen at random to use Process 1 rst, and the rest use Process 2 rst. For each worker and each process, the assembly time (in minutes) is recorded, as shown in Table 1. Difference Worker Process 1 Process 2 (process 1 - Process 2) Table 1 Based on these data, can the company conclude, at the 0.05 level of significance, that the mean assembly time for Process 1 exceeds that of Process 2? Answer this question by performing a hypothesis test regarding \"d (which is [.1 with a letter "d" subscript), the population mean difference in assembly times for the two processes. Assume that this population of differences (Process 1 minus Process 2) is normally distributed. Perform a one-tailed test. Then ll in the table below. Carry your intermediate computations to at least three decimal places and round your answers as specied in the table. (If necessary, consult a list of formulas.) The null hypothesis: The alternative hypothesis: The type of test statistic: The value of the test statistic: D (Round to at least three decimal places.) The critical value at the 0.05 level of signicance: D (Round to at least three decimal places.) At the 0.05 level, can the company conclude that the mean assembly time for Process 1 exceed that of Process 2
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


