Question: please help ASAP Using Mariana J Beard numbers ASAP A water-mercury manometer was used to measure pressure drops of a fixed bed, as shown in
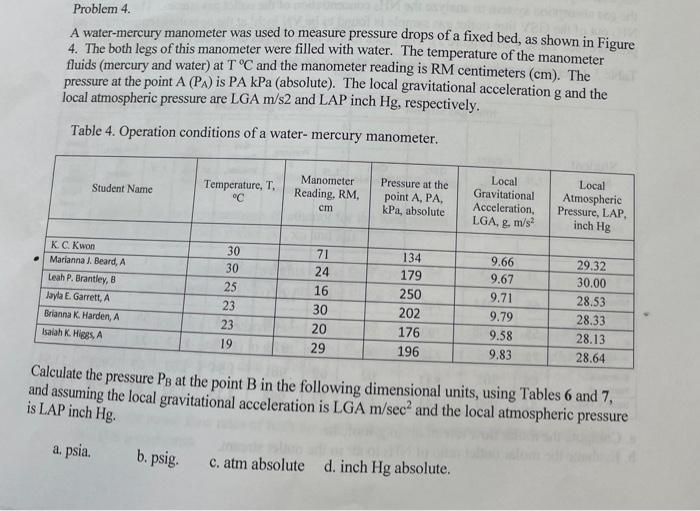
A water-mercury manometer was used to measure pressure drops of a fixed bed, as shown in Figure 4. The both legs of this manometer were filled with water. The temperature of the manometer fluids (mercury and water) at TC and the manometer reading is RM centimeters (cm). The pressure at the point A(PA) is PAkPa (absolute). The local gravitational acceleration g and the local atmospheric pressure are LGAm/s2 and LAP inch Hg, respectively. Table 4. Operation conditions of a water- mercury manometer. Calculate the pressure PB at the point B in the following dimensional units, using Tables 6 and 7 , and assuming the local gravitational acceleration is LGAm/sec2 and the local atmospheric pressure is LAP inch Hg. a. psia. b. psig. c. atm absolute d. inch Hg absolute. A water-mercury manometer was used to measure pressure drops of a fixed bed, as shown in Figure 4. The both legs of this manometer were filled with water. The temperature of the manometer fluids (mercury and water) at TC and the manometer reading is RM centimeters (cm). The pressure at the point A(PA) is PAkPa (absolute). The local gravitational acceleration g and the local atmospheric pressure are LGAm/s2 and LAP inch Hg, respectively. Table 4. Operation conditions of a water- mercury manometer. Calculate the pressure PB at the point B in the following dimensional units, using Tables 6 and 7 , and assuming the local gravitational acceleration is LGAm/sec2 and the local atmospheric pressure is LAP inch Hg. a. psia. b. psig. c. atm absolute d. inch Hg absolute
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


