Question: please help . choose the correct answer choices.thanks. The List interface extends the Collection interface in Java's java.lang library. In general, get() is less efficient
please help . choose the correct answer choices.thanks.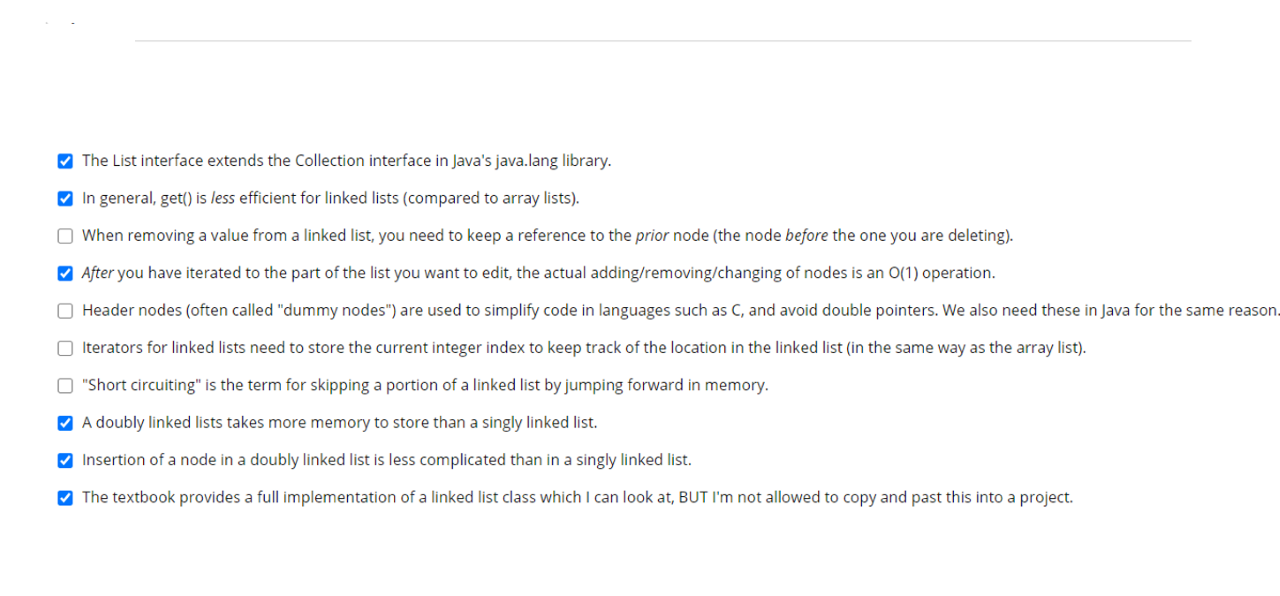
The List interface extends the Collection interface in Java's java.lang library. In general, get() is less efficient for linked lists (compared to array lists). When removing a value from a linked list, you need to keep a reference to the prior node (the node before the one you are deleting). After you have iterated to the part of the list you want to edit, the actual adding/removing/changing of nodes is an O(1) operation. Header nodes (often called "dummy nodes") are used to simplify code in languages such as C, and avoid double pointers. We also need these in Java for the same reason Iterators for linked lists need to store the current integer index to keep track of the location in the linked list (in the same way as the array list). "Short circuiting" is the term for skipping a portion of a linked list by jumping forward in memory. A doubly linked lists takes more memory to store than a singly linked list. Insertion of a node in a doubly linked list is less complicated than in a singly linked list. The textbook provides a full implementation of a linked list class which I can look at, BUT I'm not allowed to copy and past this into a project
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


