Question: Please help! Especially with the dec 31 entry in the journal and the final question. Thank you! Instructions Campbell Inc. produces and sells outdoor equipment.

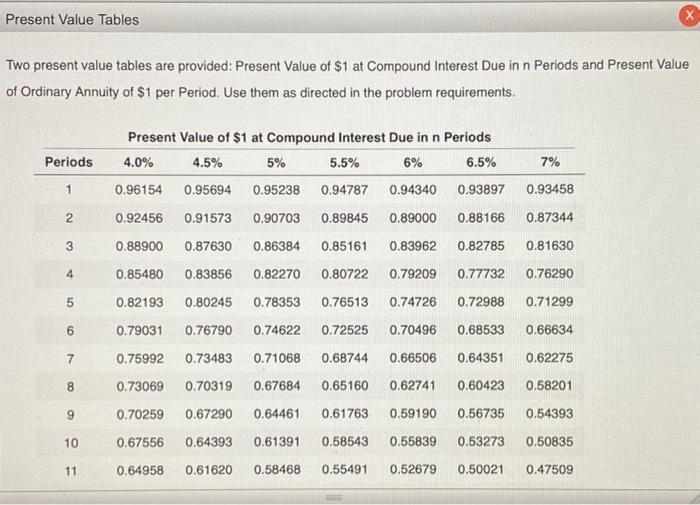
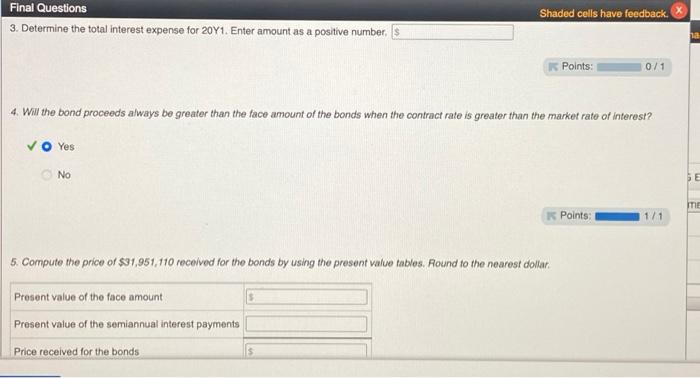
Instructions Campbell Inc. produces and sells outdoor equipment. On July 1, 20Y1, Campbell issued $30,000,000 of 10-year, 10% bonds at a market (effective) interest rate of 9%, receiving cash of $31,951,110. Interest on the bonds is payable semiannually on December 31 and June 30. The fiscal year of the company is the calendar year. Required: 1. Journalize the entry to record the amount of cash proceeds from the issuance of the bonds on July 1, 20Y1.* 2. Journalize the entries to record the following:" a. The first semiannual interest payment on December 31, 20Y1, and the amortization of the bond premium, using the straight-line method. (Round to the nearest dollar.) b. The interest payment on June 30, 20Y2, and the amortization of the bond premium, using the straight-line method. (Round to the nearest dollar.) 3. Determine the total interest expense for 20Y1. 4. Will the bond proceeds always be greater than the face amount of the bonds when the contract rate is greater than the market rate of interest? 5. Compute the price of $31,951,110 received for the bonds by using the present value tables. (Round to the nearest dollar.) *Refer to the Chart of Accounts for exact wording of account titles. Present Value Tables Two present value tables are provided: Present Value of $1 at Compound Interest Due in n Periods and Present Value of Ordinary Annuity of $1 per Period. Use them as directed in the problem requirements. Present Value of $1 at Compound Interest Due in n Periods Periods 4.0% 4.5% 5% 5.5% 6% 6.5% 7% 1 0.96154 0.95694 0.95238 0.94787 0.94340 0.93897 0.93458 2 0.92456 0.91573 0.90703 0.89845 0.89000 0.88166 0.87344 3 0.88900 0.87630 0.86384 0.85161 0.83962 0.82785 0.81630 4 0.85480 0.83856 0.82270 0.80722 0.79209 0.77732 0.76290 5 0.82193 0.80245 0.78353 0.76513 0.74726 0.72988 0.71299 6 0.79031 0.76790 0.74622 0.72525 0.70496 0.68533 0.66634 7 0.75992 0.73483 0.71068 0.68744 0.66506 0.64351 0.62275 8 0.73069 0.70319 0.67684 0.65160 0.62741 0.60423 0.58201 9 0.70259 0.67290 0.64461 0.61763 0.59190 0.56735 0.54393 10 0.67556 0.64393 0.61391 0.58543 0.55839 0.53273 0.50835 11 0.64958 0.61620 0.58468 0.55491 0.52679 0.50021 0.47509 Final Questions Shaded cells have feedback. 3. Determine the total interest expense for 20Y1. Enter amount as a positive number. Points: 0/1 4. Will the bond proceeds always be greater than the face amount of the bonds when the contract rate is greater than the market rate of interest? O Yes No E ME Points: 1/1 5. Compute the price of $31,951,110 received for the bonds by using the present value tables. Round to the nearest dollar. Present value of the face amount $ Present value of the semiannual interest payments Price received for the bonds
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


