Question: Please help explain and help with chart design. Questions 1-5. Thank you. 6.5.7 Babbage difference engine emulation circuit The Babbage difference engine is a mechanical
Please help explain and help with chart design. Questions 1-5. Thank you.
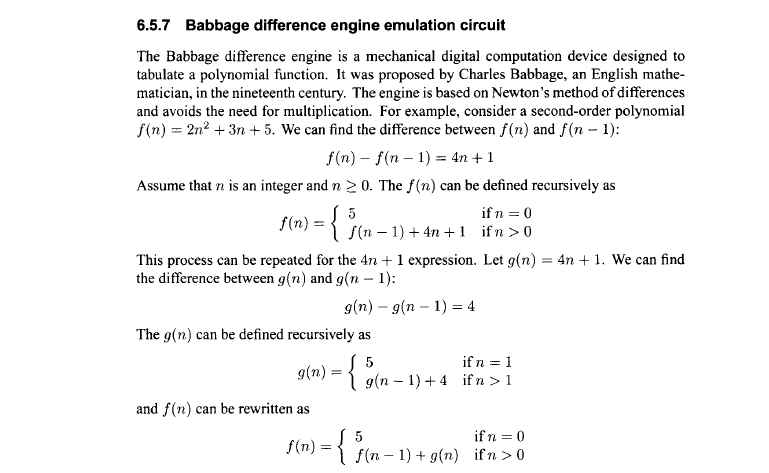
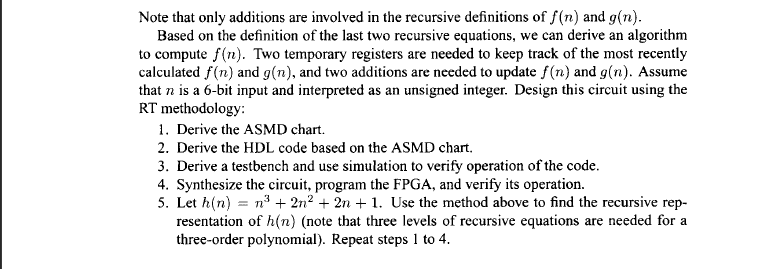
6.5.7 Babbage difference engine emulation circuit The Babbage difference engine is a mechanical digital computation device designed to tabulate a polynomial function. It was proposed by Charles Babbage, an English mathe- matician, in the nineteenth century. The engine is based on Newton's method of differences and avoids the need for multiplication. For example, consider a second-order polynomial f(n) 2n2 3n 5. We can find the difference between f(n) and f(n 1): f(n) f(n 1) 34n 1 Assume that n is an integer and n 0. The n) can be defined recursively as if n 0 f(n) 1) An 1 if n 0 This process can be repeated for the An 1 expression. Let g(n) 4n 1. We can find the difference between g(n) and g(n -1): The g(n) can be defined recursively as if n g(n) g(n 1) 4 if n 1 and f(n) can be rewritten as f(n) 1) g (n) if n 0 6.5.7 Babbage difference engine emulation circuit The Babbage difference engine is a mechanical digital computation device designed to tabulate a polynomial function. It was proposed by Charles Babbage, an English mathe- matician, in the nineteenth century. The engine is based on Newton's method of differences and avoids the need for multiplication. For example, consider a second-order polynomial f(n) 2n2 3n 5. We can find the difference between f(n) and f(n 1): f(n) f(n 1) 34n 1 Assume that n is an integer and n 0. The n) can be defined recursively as if n 0 f(n) 1) An 1 if n 0 This process can be repeated for the An 1 expression. Let g(n) 4n 1. We can find the difference between g(n) and g(n -1): The g(n) can be defined recursively as if n g(n) g(n 1) 4 if n 1 and f(n) can be rewritten as f(n) 1) g (n) if n 0
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


