Question: Please help explain how I get each answer I have to do a similar problem like this. 1. Waterbury Manufacturing, Inc., plans to develop a
Please help explain how I get each answer I have to do a similar problem like this. 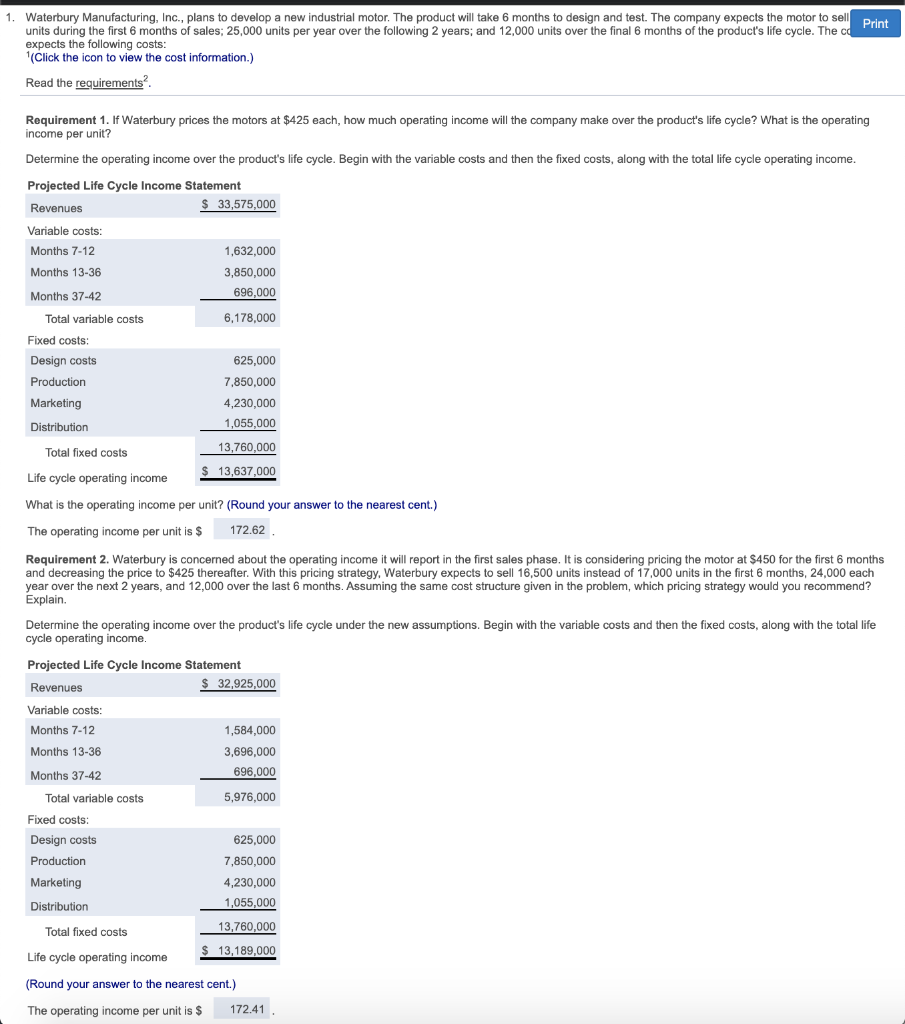
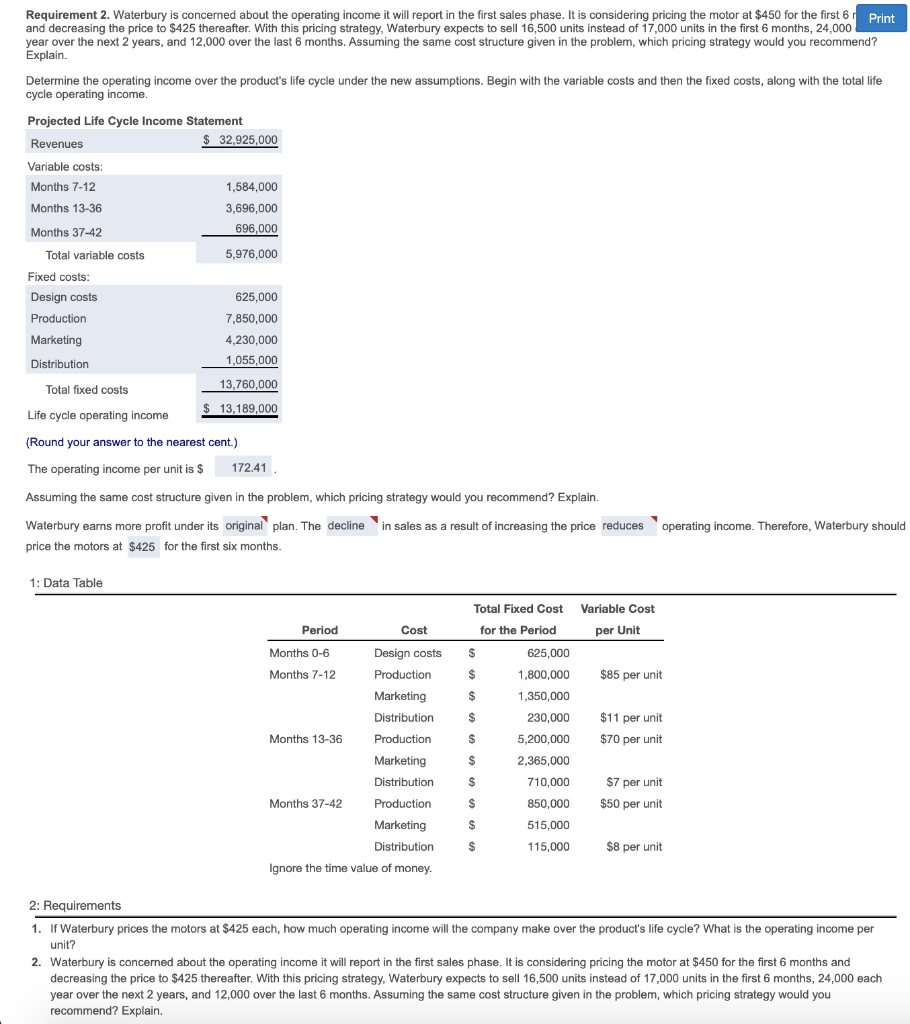
1. Waterbury Manufacturing, Inc., plans to develop a new industrial motor. The product will take 6 months to design and test. The company expects the motor to sell Print units during the first 6 months of sales: 25,000 units per year over the following 2 years; and 12,000 units over the final 6 months of the product's life cycle. The ca expects the following costs: (Click the icon to view the cost information.) Read the requirements Requirement 1. If Waterbury prices the motors at $425 each, how much operating income will the company make over the product's life cycle? What is the operating income per unit? Determine the operating income over the product's life cycle. Begin with the variable costs and then the fixed costs, along with the total life cycle operating income. Projected Life Cycle Income Statement Revenues $ 33,575,000 Variable costs: : Months 7-12 1,632,000 Months 13-36 3,850,000 Months 37-42 696,000 Total variable costs 6,178,000 Fixed costs: Design costs 625,000 Production 7,850,000 Marketing 4,230,000 Distribution 1,055,000 Total fixed costs 13,760,000 Life cycle operating income $ 13,637,000 What is the operating income per unit? (Round your answer to the nearest cent.) The operating income per unit is $ 172.62 Requirement 2. Waterbury is concerned about the operating income it will report in the first sales phase. It is considering pricing the motor at $450 for the first 6 months and decreasing the price to $425 thereafter. With this pricing strategy. Waterbury expects to sell 16,500 units instead of 17,000 units in the first 6 months, 24.000 each year over the next 2 years, and 12,000 over the last 6 months. Assuming the same cost structure given in the problem, which pricing strategy would you recommend? Explain Determine the operating income over the product's life cycle under the new assumptions. Begin with the variable costs and then the fixed costs, along with the total life cycle operating income. Projected Life Cycle Income Statement Revenues $ 32,925,000 1,584,000 3,696,000 696,000 Variable costs: Months 7-12 Months 13-36 Months 37-42 Total variable costs Fixed costs: Design costs Production Marketing 5,976,000 625,000 7,850,000 4,230,000 Distribution 1,055,000 Total fixed costs 13,760,000 Life cycle operating income $ 13,189,000 (Round your answer to the nearest cent.) The operating income per unit is $ 172.41 Requirement 2. Waterbury is concerned about the operating income it will report in the first sales phase. It is considering pricing the motor at $450 for the first 6 Print and decreasing the price to $425 thereafter. With this pricing strategy, Waterbury expects to sell 16,500 units instead of 17,000 units in the first 6 months, 24,000 year over the next 2 years, and 12,000 over the last 6 months. Assuming the same cost structure given in the problem, which pricing strategy would you recommend? Explain. Determine the operating income over the product's life cycle under the new assumptions. Begin with the variable costs and then the fixed costs, along with the total life cycle operating income. Projected Life Cycle Income Statement Revenues $ 32,925,000 Variable costs: Months 7-12 1,584,000 Months 13-36 3,696,000 Months 37-42 696,000 Total variable costs 5,976,000 Fixed costs: Design costs 625,000 Production 7,850,000 Marketing 4,230,000 Distribution 1,055,000 Total fixed costs 13,760,000 Life cycle operating income $ 13,189,000 (Round your answer to the nearest cent.) The operating income per unit is $ 172.41 Assuming the same cost structure given in the problem, which pricing strategy would you recommend? Explain. Waterbury earns more profit under its original plan. The decline in sales as a result of increasing the price reduces operating income. Therefore, Waterbury should price the motors at $425 for the first six months. 1: Data Table 230,000 Period Cost Months 0-6 Design costs Months 7-12 Production Marketing Distribution Months 13-36 Production Marketing Distribution Months 37-42 Production Marketing Distribution Ignore the time value of money. Total Fixed Cost Variable Cost for the Period per Unit $ 625,000 $ 1,800,000 $85 per unit $ 1,350,000 $ $11 per unit $ 5,200,000 $70 per unit $ 2,365,000 $ 710,000 $7 per unit $ 850,000 $50 per unit $ 515,000 $ 115,000 $8 per unit 2: Requirements 1. If Waterbury prices the motors at $425 each, how much operating income will the company make over the product's life cycle? What is the operating income per unit? 2. Waterbury is concerned about the operating income it will report in the first sales phase. It is considering pricing the motor at $450 for the first 6 months and decreasing the price to $425 thereafter. With this pricing strategy, Waterbury expects to sell 16,500 units instead of 17,000 units in the first 6 months, 24,000 each year over the next 2 years, and 12,000 over the last 6 months. Assuming the same cost structure given in the problem, which pricing strategy would you recommend? Explain
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


