Question: PLEASE HELP I AM SO STUCK!!! All information in the screen shots below Complete the sales, production, raw material, direct labor, manufacturing overhead, COGS, and
PLEASE HELP I AM SO STUCK!!!
All information in the screen shots below
- Complete the sales, production, raw material, direct labor, manufacturing overhead, COGS, and SG&A Exp schedules.
- Watch these videos for the productionLinks to an external site. and raw materialsLinks to an external site. schedule.
- Use Ch. 14 in the textbook for examples for each schedule and statement.
- The textbook is good but it doesn't not include production and raw material schedules. This sample assignmentLinks to an external site. will help you understand the entire assignment and show an example of the production and raw material schedules. If the links DO NOT work, click "NEXT SECTION" to find the information you need.
- Complete the Proforma Income Statement and Proforma Cash Budget.
- Calculate the Interest Expense.
- Using the Note, Interest, Tax tab, determine how much money you need to borrow on your notes payable to maintain your minimum cash balance.
- As needed, enter the interest and tax amounts on the Proforma Income Statement and Proforma Cash Budget.
- Complete the Stockholder's Equity tab.
- Complete the Proforma Balance Sheet.
| The Company, Snap, Crackle, Pop, assembles a specialized device used to adjust people's spine. Arrangements have been made for the component parts (bundled in packets; one packet is used to assemble one unit) to be produced in Nigeria, shipped to Boise, then assembled and sold by Snap, Crackle, Pop |
| You have developed the prototypes, established a market, and now you are putting together a budget for the first three months of operations. The Company will start manufacturing and distribution on January 1, 20xx. No expenses occur nor does cash leave the company before January 1, 20xx. |
| Follow the Directions as outlined in Canvas. |
| Use the following assumptions in making your budget calculations: |
| a. Assume all 12 months have 30 days to make the calculations easier. This is commonly done in the business world. |
| b. Projected sales in units are 1584 in January and increase by 265 units each month through the remainder of the year. |
| c. Sales price includes COST PLUS AN ADDITIONAL 150% OF COST (cost includes raw material, direct labor and overhead). All sales are on account and are collected 38% in the month of sale, 38% in the next month, and 20% in the second following month. The remaining accounts receivable are uncollectible and recorded as bad debt expense IN THE MONTH OF SALE. |
| d. Production Tab only: The company wants to have at least 30% of the next month's projected sales in ending finished goods inventory on hand. (Since the company is just starting, beginning January finished good will be zero.) |
| e. Direct Materials Tab only: At the start of each month, management plans to have enough packets of raw materials on hand to cover the next 30 days' production requirements. Each packet of raw material costs $140.00. The company will have 2305 packets on hand on January 1, 20xx. ALL RAW MATERIALS PACKETS PURCHASED DURING LATE DECEMBER HAVE NOT BEEN PAID. Raw materials are payable on the 10th day of the month after the purchase. |
| f. Five hours of direct labor are required to assemble each device. The direct labor cost (including fringe benefits) is $22.00 per hour. Wages earned by employees during the first half of each month are paid on the third Friday of the current month. Wages earned in the second half of the month are paid on the first Friday of the next month. Assume that the workforce is stable each month (hence, wages and salaries are the same every day of the month). |
| g.Manufacturing overhead incurred averages 75% of direct labor cost. Manufacturing overhead percentage includes warehouse rent, insurance, utilities, etc. Manufacturing overhead is paid 40% in the current month with the remaining balance paid the following month. |
| h.Sales commissions are 14% of sales price. 100% of sales commissions are payable on the 15th day of the month after the sale. |
| i. Administrative salaries and fringe benefits are $60,000 per month. Administrative salaries are paid one-half on the third Friday of the current month and one-half is on the first Friday of the next month. |
| j. Rent on administrative office space is $10,000 per month. Rent for each month is due on the first day of each month. |
| k. On January 1, 20xx the Company will pay an $84,000 annual insurance liability premium covering January through December, 20xx. This insurance policy is a different policy than MOH insurance. |
| l. Other administrative expenses are estimated to be 7.5% of sales. Other administrative expenses are paid in the month after the expense occurs. |
| m. The federal and state income tax rate is estimated at 25%. Taxes accrue on each month's income and will be paid quarterly on April 15, July 15, etc. Note: Your company is successful, and YOU WILL NEED TO PAY TAXES. |
| n. The company has a $750,000 line of credit secured to its inventory and accounts receivable through a private investor. Borrowing against this line must be in increments of $25,000 and happen on the 16th day of the month. Repayments must also occur in $25,000 increments on the 16th day of the month. Your borrowings and repayments should be adjusted to provide a minimum ending cash balance of $25,000 each month. |
| o. Interest for the line of credit is calculated at an annual rate of 6% assuming a 360 year. Interest expense is payable on the 1st day of the month after the borrowing occurred. |
| p. Beginning cash balance on January 1, 20xx is projected to be $34,080. This money was raised through issuing common stock and should be recorded accordingly. |
| Check Figures: |
| Production--March, Required Production, Units: 2194. If you get the wrong number, read D. |
| Raw Materials--March, Packets to Purchase, Units 2459. If you get the wrong number, read E between the first comma and the first period. |
| Income Statement--January, Sales: $1,316,700 |
| Income Statement--January, Operating Income: $377,262 |
| Income Statement--January, Net Income: $282,665 |
| Cash Budget--January, Total Budget Disbursements: $634,906 |
| Cash Budget--January, Ending Cash: $49,520 |
| Balance Sheet--January, Total Assets: $1,344,634 |
| Balance Sheet--February, Total Assets: $1,783,294 |
| Balance Sheet--March, Total Assets: $2,374,203 |
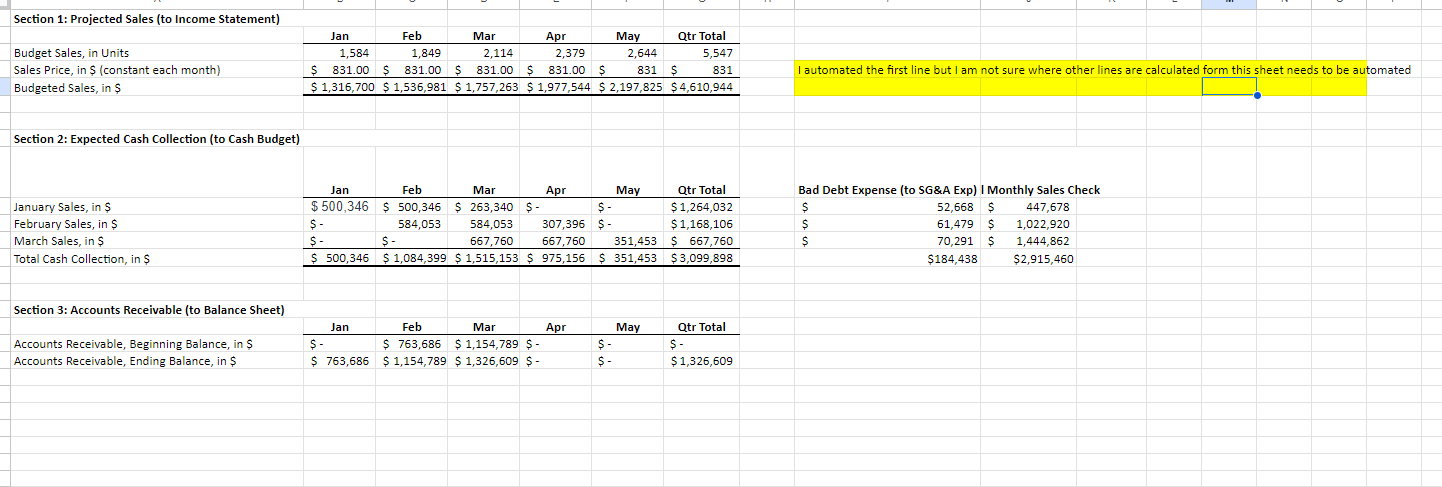
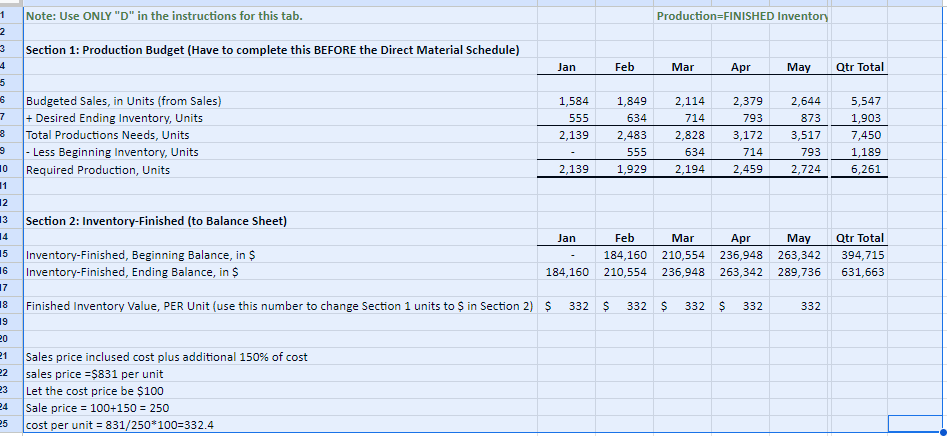
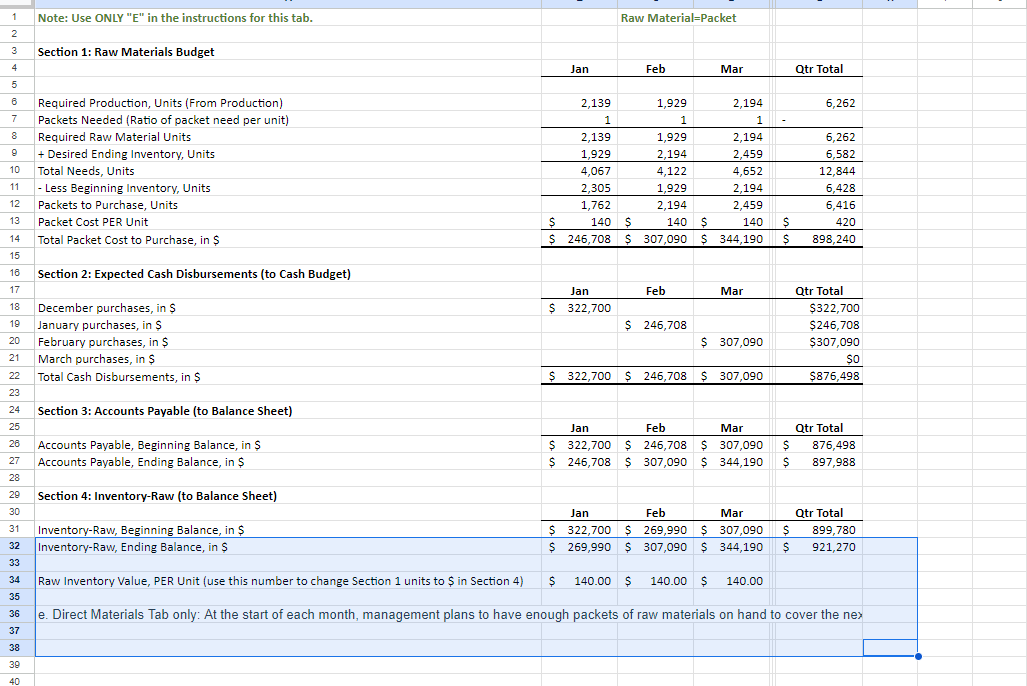
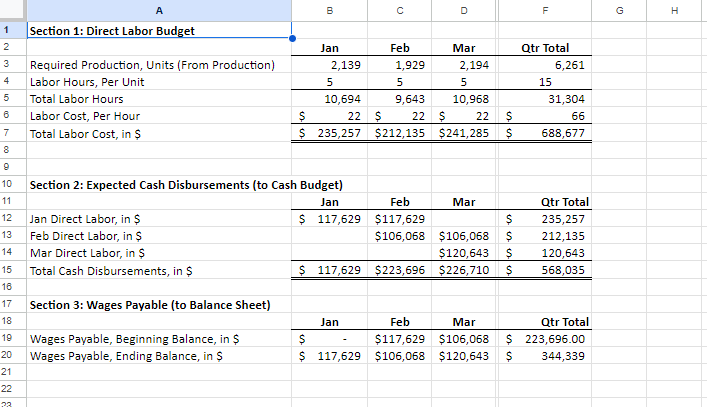
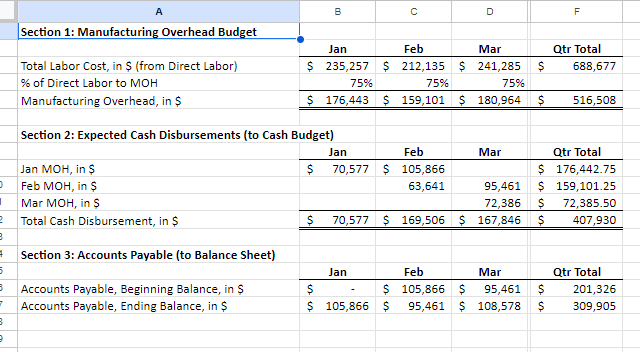
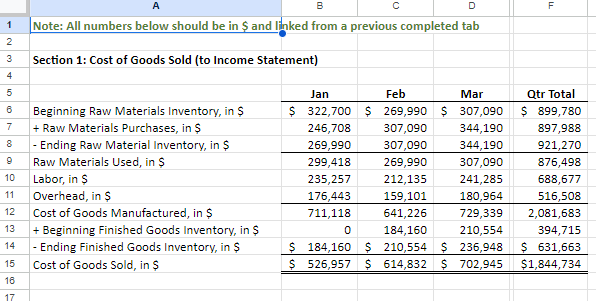
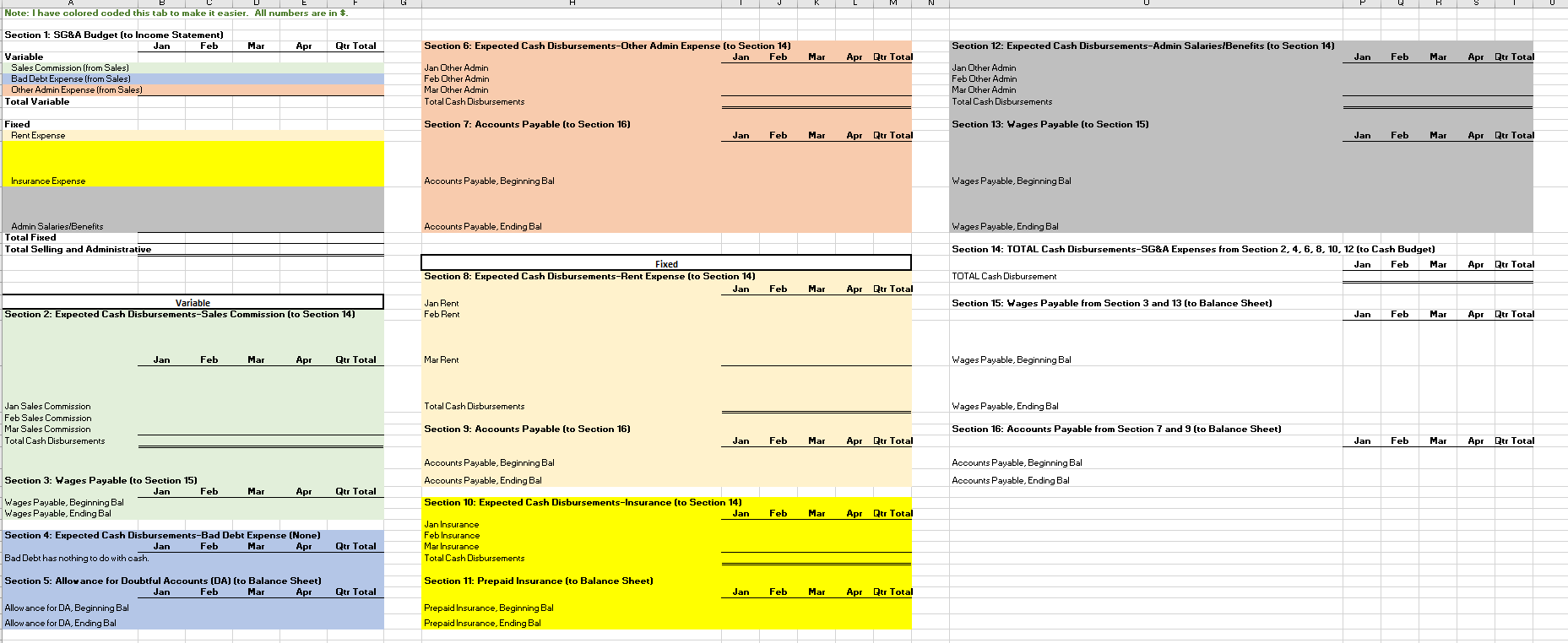
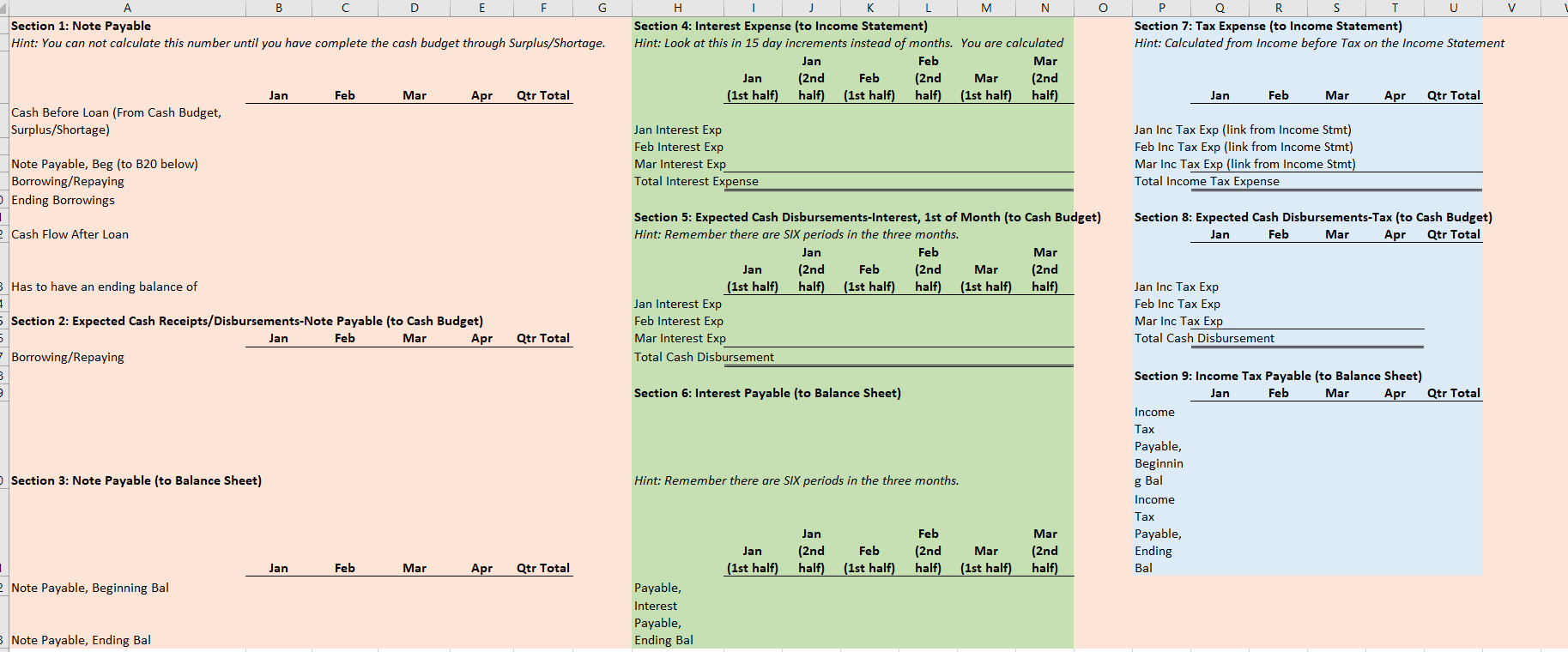
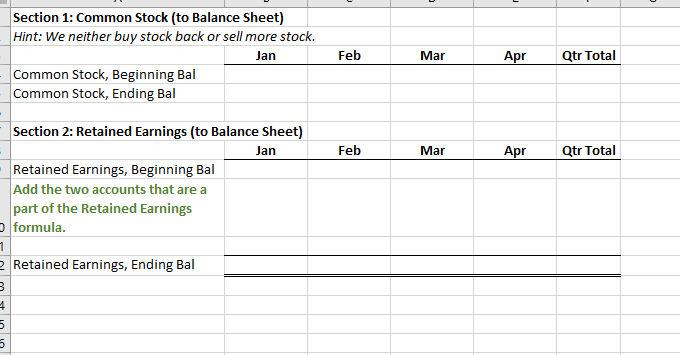
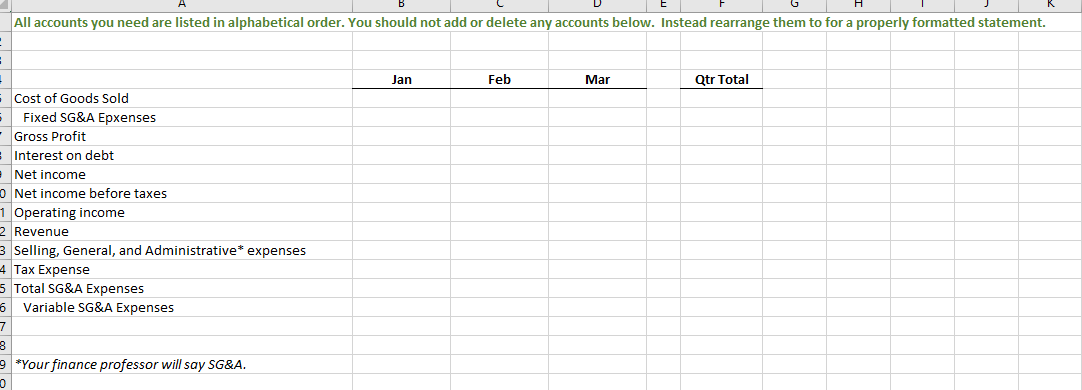
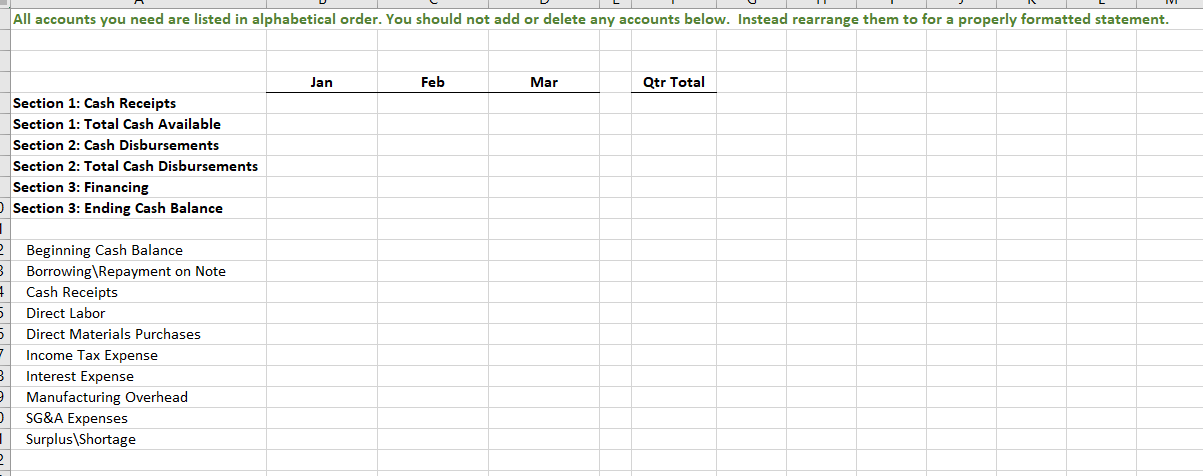
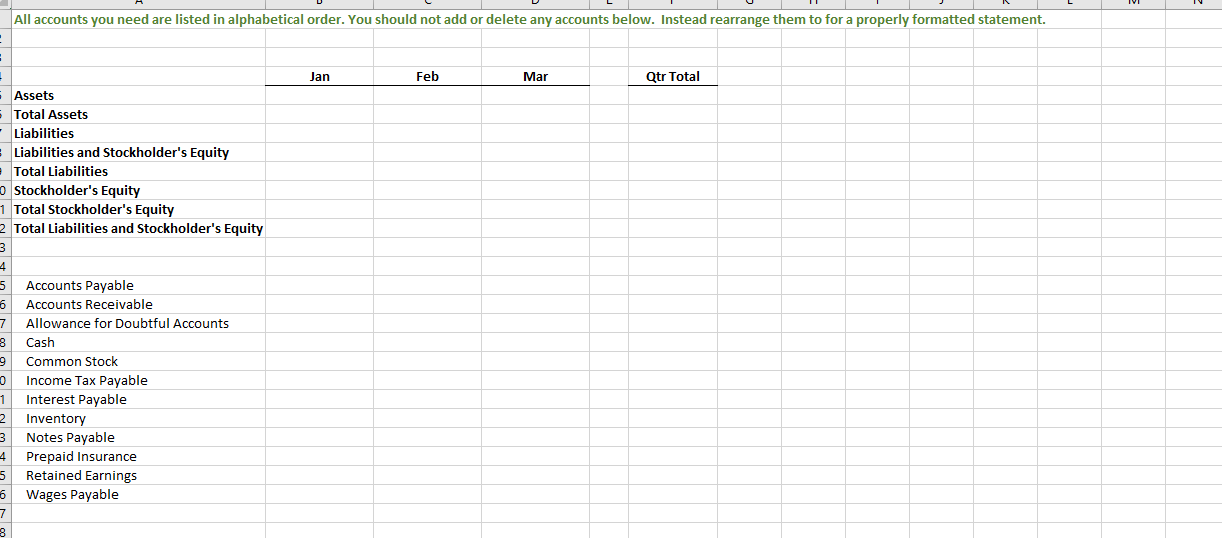
Section 1: Projected Sales (to Income Statement) Jan Feb Mar Apr May Qtr Total Budget Sales, in Units 1,584 1,849 2,114 2,379 2,644 5,547 Sales Price, in $ (constant each month) $ 831.00 $ 831.00 $ 831.00 $ 831.00 S 831 $ 831 I automated the first line but I am not sure where other lines are calculated form this sheet needs to be automated Budgeted Sales, in $ $ 1,316,700 $ 1,536,981 $ 1,757,263 $ 1,977,544 $ 2,197,825 $ 4,610,944 Section 2: Expected Cash Collection (to Cash Budget) Jan Feb Mar Apr May Qtr Total Bad Debt Expense (to SG&A Exp) I Monthly Sales Check January Sales, in $ $ 500,346 $ 500,346 $ 263,340 $. $ 1,264,032 52,668 $ 447,678 February Sales, in $ 584,053 584,053 307,396 $ - $ 1,168,106 61,479 $ 1,022,920 March Sales, in $ S - $ - 667,760 667,760 351,453 $ 667,760 70,291 S 1,444,862 Total Cash Collection, in $ $ 500,346 $ 1,084,399 $ 1,515,153 $ 975,156 $ 351,453 $3,099,898 $184,438 $2,915,460 Section 3: Accounts Receivable (to Balance Sheet) Jan Feb Mar Apr May Qtr Total Accounts Receivable, Beginning Balance, in $ $ - $ 763,686 $ 1,154,789 $ - 5 - Accounts Receivable, Ending Balance, in $ 763,686 $ 1,154,789 $ 1,326,609 $- $ 1,326,609Note: Use ONLY "D" in the instructions for this tab. Production=FINISHED Inventory Section 1: Production Budget (Have to complete this BEFORE the Direct Material Schedule) Jan Feb Mar Apr May Qtr Total Budgeted Sales, in Units (from Sales) 1,584 1,849 2,114 2,379 2,644 5,547 + Desired Ending Inventory, Units 555 634 714 793 873 1,903 Total Productions Needs, Units 2,139 2,483 2,828 3,172 3,517 7,450 - Less Beginning Inventory, Units 555 634 714 793 1,189 0 Required Production, Units 2,139 1,929 2,194 2,459 2,724 6.261 2 3 Section 2: Inventory-Finished (to Balance Sheet) 4 Jan Feb Mar Apr May Qtr Total 5 Inventory-Finished, Beginning Balance, in $ 184,160 210,554 236,948 263,342 394,715 6 Inventory-Finished, Ending Balance, in $ 184,160 210,554 236,948 263,342 289,736 631,663 7 8 Finished Inventory Value, PER Unit (use this number to change Section 1 units to $ in Section 2) $ 332 332 $ 332 $ 332 332 9 20 Sales price inclused cost plus additional 150% of cost 2 sales price =$831 per unit 3 Let the cost price be $100 14 Sale price = 100+150 = 250 15 cost per unit = 831/250*100=332.4Note: Use ONLY "E" in the instructions for this tab. Raw Material=Packet 2 3 Section 1: Raw Materials Budget Jan Feb Mar Qtr Total 6 Required Production, Units (From Production) 2,139 1,929 2,194 6.262 7 Packets Needed (Ratio of packet need per unit) 8 Required Raw Material Units 2,139 1,929 2,194 6,262 9 + Desired Ending Inventory, Units 1,929 2,194 2.459 5.582 10 Total Needs, Units 4,067 4,122 4,652 12,844 11 - Less Beginning Inventory, Units 2,305 1,929 2,194 6,428 12 Packets to Purchase, Units 1,762 2,194 2,459 6,416 13 Packet Cost PER Unit S 140 140 S 140 $ 420 14 Total Packet Cost to Purchase, in $ 246,708 $ 307,090 344,190 S 898,240 15 16 Section 2: Expected Cash Disbursements (to Cash Budget) 17 Jan Feb Mar Qtr Total 18 December purchases, in $ $ 322,700 $322,700 19 January purchases, in $ $ 246,708 $246,708 20 February purchases, in $ $ 307,090 $307,090 21 March purchases, in $ SO 22 Total Cash Disbursements, in $ $ 322,700 $ 246,708 $ 307,090 $876,498 23 24 Section 3: Accounts Payable (to Balance Sheet) 25 Jan Feb Mar Qtr Total 26 Accounts Payable, Beginning Balance, in $ $ 322,700 $ 246,708 $ 307,090 876,498 27 Accounts Payable, Ending Balance, in $ $ 246,708 $ 307,090 $ 344,190 897,988 28 29 Section 4: Inventory-Raw (to Balance Sheet) 30 Jan Feb Mar Qtr Total 31 Inventory-Raw, Beginning Balance, in $ $ 322,700 $ 269,990 $ 307,090 899,780 32 Inventory-Raw, Ending Balance, in $ $ 269,990 $ 307,090 $ 344,190 921,270 33 34 Raw Inventory Value, PER Unit (use this number to change Section 1 units to $ in Section 4) $ 140.00 $ 140.00 $ 140.00 35 36 e. Direct Materials Tab only: At the start of each month, management plans to have enough packets of raw materials on hand to cover the nex 37 38 30A B C D F G H Section 1: Direct Labor Budget 2 Jan Feb Mar Qtr Total 3 Required Production, Units (From Production) 2,139 1,929 2,194 6,261 4 Labor Hours, Per Unit 5 5 5 15 5 Total Labor Hours 10,694 9,643 10,968 31,304 Labor Cost, Per Hour S 22 $ 22 5 22 5 66 7 Total Labor Cost, in $ $ 235,257 $212,135 $241,285 S 688,677 9 10 Section 2: Expected Cash Disbursements (to Cash Budget) 11 Jan Feb Mar Qtr Total 12 Jan Direct Labor, in $ $ 117,629 $117,629 235,257 13 Feb Direct Labor, in $ $106,068 $106,068 212,135 14 Mar Direct Labor, in S $120,643 120,643 15 Total Cash Disbursements, in $ $ 117,629 $223,696 $226,710 568,035 16 17 Section 3: Wages Payable (to Balance Sheet) 18 Jan Feb Mar Qtr Total 19 Wages Payable, Beginning Balance, in $ $ $117,629 $106,068 $ 223,696.00 20 Wages Payable, Ending Balance, in S S 117,629 $106,068 $120,643 S 344,339 21 22A B C D F Section 1: Manufacturing Overhead Budget Jan Feb Mar Qtr Total Total Labor Cost, in $ (from Direct Labor) $ 235,257 $ 212,135 $ 241,285 S 688,677 of Direct Labor to MOH 75% 75% 75% Manufacturing Overhead, in $ $ 176,443 $ 159,101 $ 180,964 $ 516,508 Section 2: Expected Cash Disbursements (to Cash Budget) Jan Feb Mar Qtr Total Jan MOH, in S 70,577 $ 105,866 5 176,442.75 Feb MOH, in S 63,641 95,461 5 159,101.25 Mar MOH, in S 72,386 S 72,385.50 Total Cash Disbursement, in $ $ 70,577 $ 169,506 $ 167,846 S 407,930 Section 3: Accounts Payable (to Balance Sheet) Jan Feb Mar Qtr Total Accounts Payable, Beginning Balance, in $ $ 105,866 95,461 S 201,326 Accounts Payable, Ending Balance, in $ 5 105,866 S 95,461 5 108,578 S 309,905A B C D F 1 Note: All numbers below should be in $ and linked from a previous completed tab 2 3 Section 1: Cost of Goods Sold (to Income Statement) 4 5 Jan Feb Mar Qtr Total 6 Beginning Raw Materials Inventory, in $ $ 322,700 $ 269,990 5 307,090 5 899,780 7 + Raw Materials Purchases, in $ 246,708 307,090 344,190 897,988 8 - Ending Raw Material Inventory, in $ 269,990 307.090 344,190 921,270 Raw Materials Used, in S 299,418 269,990 307,090 876,498 10 Labor, in $ 235,257 212,135 241,285 688.677 11 Overhead, in $ 176.443 159,101 180.964 516,508 12 Cost of Goods Manufactured, in $ 711 118 641, 226 729,339 2,081,683 13 + Beginning Finished Goods Inventory, in $ 0 184,160 210,554 394,715 14 - Ending Finished Goods Inventory, in $ 5 184,160 $ 210,554 $ 236,948 5 631,663 15 Cost of Goods Sold, in S $ 526,957 $ 614,832 $ 702,945 $1,844,734 18 17Note: I have colored coded this tab to make it easier. All numbers are in $. Section 1: SG&A Budget (to Income Statement) Jan Feb Mar Apr Qtr Total Section 6: Expected Cash Disbursements-Other Admin Expense (to Section 14) Section 12: Expected Cash Disbursements-Admin Salaries/Benefits [to Section 14] Variable Jan Feb Mar Apr Qtr Tota Jan Mar Apr Qtr Total Sales Commission (from Sales) Jan Other Admin Jan Other Admin Bad Debt Expense (from Sales] Feb Other Admir Feb Other Admin Other Admin Expense (from Sales) Mar Other Admin Mar Other Admin Total Variable Total Cash Disbursements Total Cash Disbursements Fixed Section 7: Accounts Payable (to Section 16] Section 13: Wages Payable (to Section 15) Rent Expense Jan Feb Mar Apr Qtr Total Jan Feb Mar Apr Qtr Total Insurance Expense Accounts Payable, Beginning Bal Wages Payable, Beginning Bal Admin Salaries/Benefits Accounts Payable, Ending Bal Wages Payable, Ending Bal Total Fixed Total Selling and Administrative Section 14: TOTAL Cash Disbursements-SG&A Expenses from Section 2. 4. 6, 8. 10, 12 (to Cash Budget) Fixed Jan Feb Mar Apr Qtr Total Section 8: Expected Cash Disbursements-Rent Expense (to Section 14) TOTAL Cash Disbursement Jan Feb Mar Apr Qtr Total Variable Jan Rent Section 15: Wages Payable from Section 3 and 13 (to Balance Sheet) Section 2: Expected Cash Disbursements-Sales Commission (to Section 14) Feb Rent Jan Feb Mar Apr Qtr Total Jan Feb Mar Apr Qur Total Mar Rent Wages Payable, Beginning Bal Jan Sales Commission Total Cash Disbursements Wages Payable, Ending Bal Feb Sales Commission Mar Sales Commission Section 9: Accounts Payable (to Section 16) Section 16: Accounts Payable from Section 7 and 9 (to Balance Sheet) Total Cash Disbursements Jan Feb Mar Apr Qtr Total Jan Feb Mar Apr Qtr Total Accounts Payable, Beginning Bal Accounts Payable, Beginning Bal Section 3: Wages Payable (to Section 15) Accounts Payable, Ending Bal Accounts Payable, Ending Bal Jan Feb Mar Apr Qtr Total Wages Payable, Beginning Bal Section 10: Expected Cash Disbursements-Insurance (to Section 14) Wages Payable, Ending Bal Jan Feb Mar Apr Qur Total Jan Insurance Section 4: Expected Cash Disbursements-Bad Debt Expense (None] Feb Insurance Jan Feb Mar Apr Qtr Total Mar Insurance Bad Debt has nothing to do with cash. Total Cash Disbursements Section 5: Allow ance for Doubtful Accounts [DA] [to Balance Sheet] Section 11: Prepaid Insurance (to Balance Sheet) Jan Feb Mar Apr Qtr Total Jan Feb Mar Apr Qur Total Allow ance for DA, Beginning Bal Prepaid Insurance, Beginning Bal Allow ance for DA, Ending Bal Prepaid Insurance, Ending BalG H K N U V A B C D E M O P Q R S Section 7: Tax Expense (to Income Statement) Section 1: Note Payable Section 4: Interest Expense (to Income Statement) Hint: You can not calculate this number until you have complete the cash budget through Surplus/Shortage. Hint: Look at this in 15 day increments instead of months. You are calculated Hint: Calculated from Income before Tax on the Income Statement Jan Feb Mar Jan (2nd Feb (2nd Mar (2nd Jan Feb Mar Apr Qtr Total (1st half) half (1st half) half) (1st half) half Jan Feb Mar Apr Qtr Total Cash Before Loan (From Cash Budget, Jan Inc Tax Exp (link from Income Stmt) Surplus/Shortage) Jan Interest Exp Feb Interest Exp Feb Inc Tax Exp (link from Income Stmt) Note Payable, Beg (to B20 below) Mar Interest Exp Mar Inc Tax Exp (link from Income Stmt) Total Interest Expense Total Income Tax Expense Borrowing/Repaying Ending Borrowings Section 5: Expected Cash Disbursements-Interest, 1st of Month (to Cash Budget) Section 8: Expected Cash Disbursements-Tax (to Cash Budget) Jan Feb Mar Apr Qtr Total Cash Flow After Loan Hint: Remember there are SIX periods in the three months. Jan Feb Mar Jan (2nd Feb (2nd Mar (2nd Has to have an ending balance of (1st half) half) (1st half) half) (1st half) half) Jan Inc Tax Exp Jan Interest Exp Feb Inc Tax Exp Section 2: Expected Cash Receipts/Disbursements-Note Payable (to Cash Budget) Feb Interest Exp Mar Inc Tax Exp Feb Mar Apr Qtr Total Mar Interest Exp Total Cash Disbursement Jan Borrowing/Repaying Total Cash Disbursement Section 9: Income Tax Payable (to Balance Sheet) Section 6: Interest Payable (to Balance Sheet) Jan Feb Mar Apr Qtr Total Income Tax Payable, Beginnin Section 3: Note Payable (to Balance Sheet) Hint: Remember there are SIX periods in the three months. g Bal Income Tax Jan Feb Mar Payable, Jan (2nd Feb (2nd Mar (2nd Ending Jan Feb Mar Apr Qtr Total (1st half) half) (1st half) half) (1st half) half) Bal Note Payable, Beginning Bal Payable, Interest Payable, Note Payable, Ending Bal Ending BalSection 1: Common Stock (to Balance Sheet) Hint: We neither buy stock back or sell more stock. Jan Feb Mar Apr Qtr Total Common Stock, Beginning Bal Common Stock, Ending Bal Section 2: Retained Earnings (to Balance Sheet) Jan Feb Mar Apr Qtr Total Retained Earnings, Beginning Bal Add the two accounts that are a part of the Retained Earnings formula. Retained Earnings, Ending BalH K All accounts you need are listed in alphabetical order. You should not add or delete any accounts below. Instead rearrange them to for a properly formatted statement. Jan Feb Mar Qtr Total Cost of Goods Sold Fixed SG&A Epxenses Gross Profit Interest on debt Net income Net income before taxes Operating income Revenue Selling, General, and Administrative* expenses Tax Expense Total SG&A Expenses Variable SG&A Expenses *Your finance professor will say SG&A.All accounts you need are listed in alphabetical order. You should not add or delete any accounts below. Instead rearrange them to for a properly formatted statement. Jan Feb Mar Qtr Total Section 1: Cash Receipts Section 1: Total Cash Available Section 2: Cash Disbursements Section 2: Total Cash Disbursements Section 3: Financing Section 3: Ending Cash Balance Beginning Cash Balance Borrowing \\Repayment on Note Cash Receipts Direct Labor Direct Materials Purchases Income Tax Expense Interest Expense Manufacturing Overhead SG&A Expenses Surplus\\ShortageAll accounts you need are listed in alphabetical order. You should not add or delete any accounts below. Instead rearrange them to for a properly formatted statement. Jan Feb Mar Qtr Total Assets Total Assets Liabilities Liabilities and Stockholder's Equity Total Liabilities Stockholder's Equity Total Stockholder's Equity Total Liabilities and Stockholder's Equity Accounts Payable Accounts Receivable Allowance for Doubtful Accounts Cash Common Stock Income Tax Payable Interest Payable Inventory Notes Payable Prepaid Insurance Retained Earnings Wages Payable
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


