Question: Does ecological disturbance have an effect on plant species richness in an ecosystem? Species diversity can be measured by taking into account two (2)
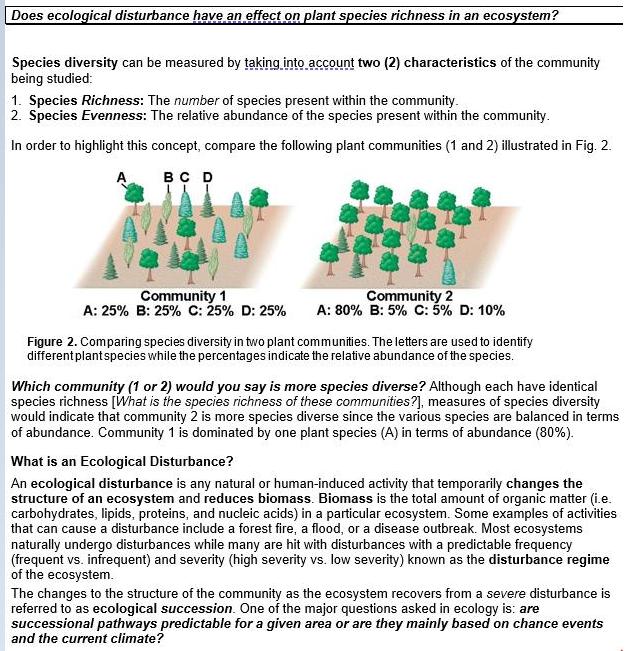
Does ecological disturbance have an effect on plant species richness in an ecosystem? Species diversity can be measured by taking into account two (2) characteristics of the community being studied: 1. Species Richness: The number of species present within the community. 2. Species Evenness: The relative abundance of the species present within the community. In order to highlight this concept, compare the following plant communities (1 and 2) illustrated in Fig. 2. A D Community 1 A: 25% B: 25% c: 25% D: 25% Community 2 A: 80% B: 5% C: 5% D: 10% Figure 2. Comparing species diversity in two plant communities. The letters are used to identify different plantspecies while the percentages indicate the relative abundance of the species. Which community (1 or 2) would you say is more species diverse? Although each have identical species richness [What is the species richness of these communities?], measures of species diversity would indicate that community 2 is more species diverse since the various species are balanced in terms of abundance. Community 1 is dominated by one plant species (A) in terms of abundance (80%). What is an Ecological Disturbance? An ecological disturbance is any natural or human-induced activity that temporarily changes the structure of an ecosystem and reduces biomass. Biomass is the total amount of organic matter (i.e. carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids) in a particular ecosystem. Some examples of activities that can cause a disturbance include a forest fire, a flood, or a disease outbreak. Most ecosystems naturally undergo disturbances while many are hit with disturbances with a predictable frequency (frequent vs. infrequent) and severity (high severity vs. low severity) known as the disturbance regime of the ecosystem. The changes to the structure of the community as the ecosystem recovers from a severe disturbance is referred to as ecological succession. One of the major questions asked in ecology is: are successional pathways predictable for a given area or are they mainly based on chance events and the current climate? Biodiversity and Ecosystem Stability Having multiple species present in a community can stabilize ecosystem processes if species vary in their responses to environmental fluctuations such that an increased abundance of one species can compensate for the decreased abundance of another. Biologically diverse communities are also more likely to contain species that help the ecosystem to be resilient to change, because as a community accumulates species, there is a higher chance of any one of them having traits that enable them to adapt to a changing environment. Such species could buffer the system against the loss of other species. Ecosystems with high biodiversity have many different species of organisms. Ecosystems with low biodiversity do not have many different species of organisms. The higher the biodiversity, the more stable the ecosystem (stable = stays the same). An ecosystem with high biodiversity does not change easily; it is stable. An ecosystem with low biodiversity is unstable. One small change could cause many species to die. MATERIALS AND METHODS MATERIALS Two outdoor plot (ecological zone) each five (5) meters in length that has not been mowed (cut) for several years (no disturbance; no biomass removed) and mowed areas (regular disturbance; biomass removed) Light intensity (Lux) meter app (must be downloaded ahead of time on a smart phone) Thermometer Does disturbance affect plant species richness in an ecosystem? 1. State your HYPOTHESIS: 2. Give a RATIONALE for your hypothesis: 3. Briefly describe your TREATMENTS/CONDITIONS and the results that you predict for each: A. EXPERIMENTAL Treatment/Condition: Result Predicted: B. CONTROL Treatment/Condition: Result Predicted: 4. Importance of a CONTROL treatment/condition in an experiment. a) In general, what is a control treatment/condition in an experiment? b) What information can be determined from the data obtained for this treatment/condition? c) Why is this information essential to know when analyzing the results of an experiment? 5. Describe the INDEPENDENT variable in this experiment? 6. Describe the DEPENDENT variable in this experiment? Is this variable qualitative or quantitative? 7. List 5 specific and distinct CONTROLLED variables (i.e. variables held constant between treatments/conditions) in your experiment. . . . D. E. 8. What is your UNIT of study? N.B. The easiest way to identify your unit of study is to think about your dependent variable. What is the specimen/subject used to make ONE independent measure of your dependent variable? 9. How many REPLICATES (number of these units) do you have in each group? Control Group: Experimental Group: 10. Importance of REPLICATION in an experiment. a) In general, what is replication in an experiment? b) What information can be determined from the data when replication is used in an experiment. c) Why is this information essential to know when analyzing the results of an experiment? Biodiversity and Ecosystem Stability Having multiple species present in a community can stabilize ecosystem processes if species vary in their responses to environmental fluctuations such that an increased abundance of one species can compensate for the decreased abundance of another. Biologically diverse communities are also more likely to contain species that help the ecosystem to be resilient to change, because as a community accumulates species, there is a higher chance of any one of them having traits that enable them to adapt to a changing environment. Such species could buffer the system against the loss of other species. Ecosystems with high biodiversity have many different species of organisms. Ecosystems with low biodiversity do not have many different species of organisms. The higher the biodiversity, the more stable the ecosystem (stable = stays the same). An ecosystem with high biodiversity does not change easily; it is stable. An ecosystem with low biodiversity is unstable. One small change could cause many species to die. MATERIALS AND METHODS MATERIALS Two outdoor plot (ecological zone) each five (5) meters in length that has not been mowed (cut) for several years (no disturbance; no biomass removed) and mowed areas (regular disturbance; biomass removed) Light intensity (Lux) meter app (must be downloaded ahead of time on a smart phone) Thermometer
Step by Step Solution
3.45 Rating (158 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Q 1 The soil in an area that has not been mowed for 5 years has a lower temperature than the one found in an area that is mowed regularly Q 2 An area ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts






