Question: Please help me answer these questions: 1. Circle all correct statements. 1 point B When building a classification tree, each feature can only be used
Please help me answer these questions:
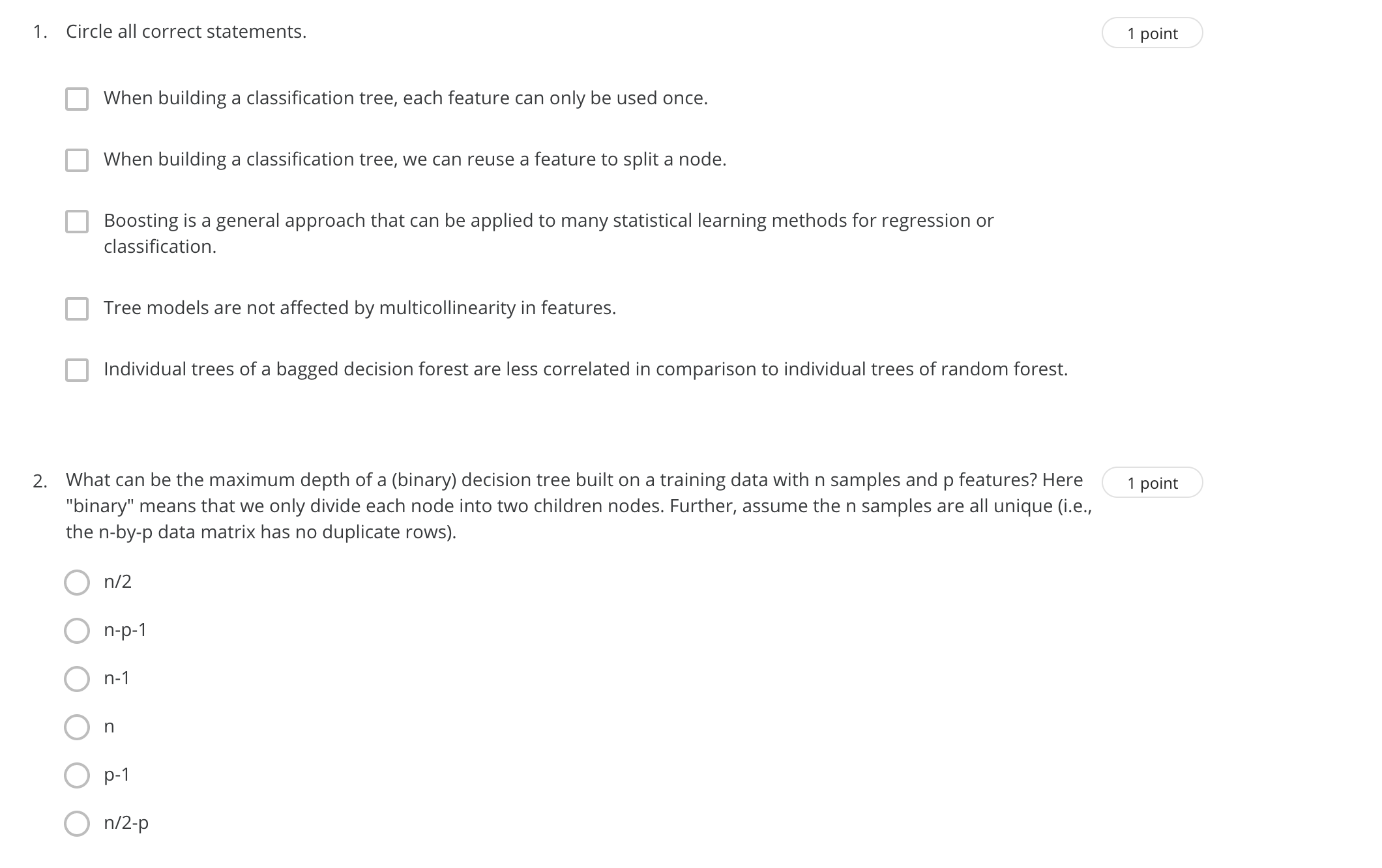


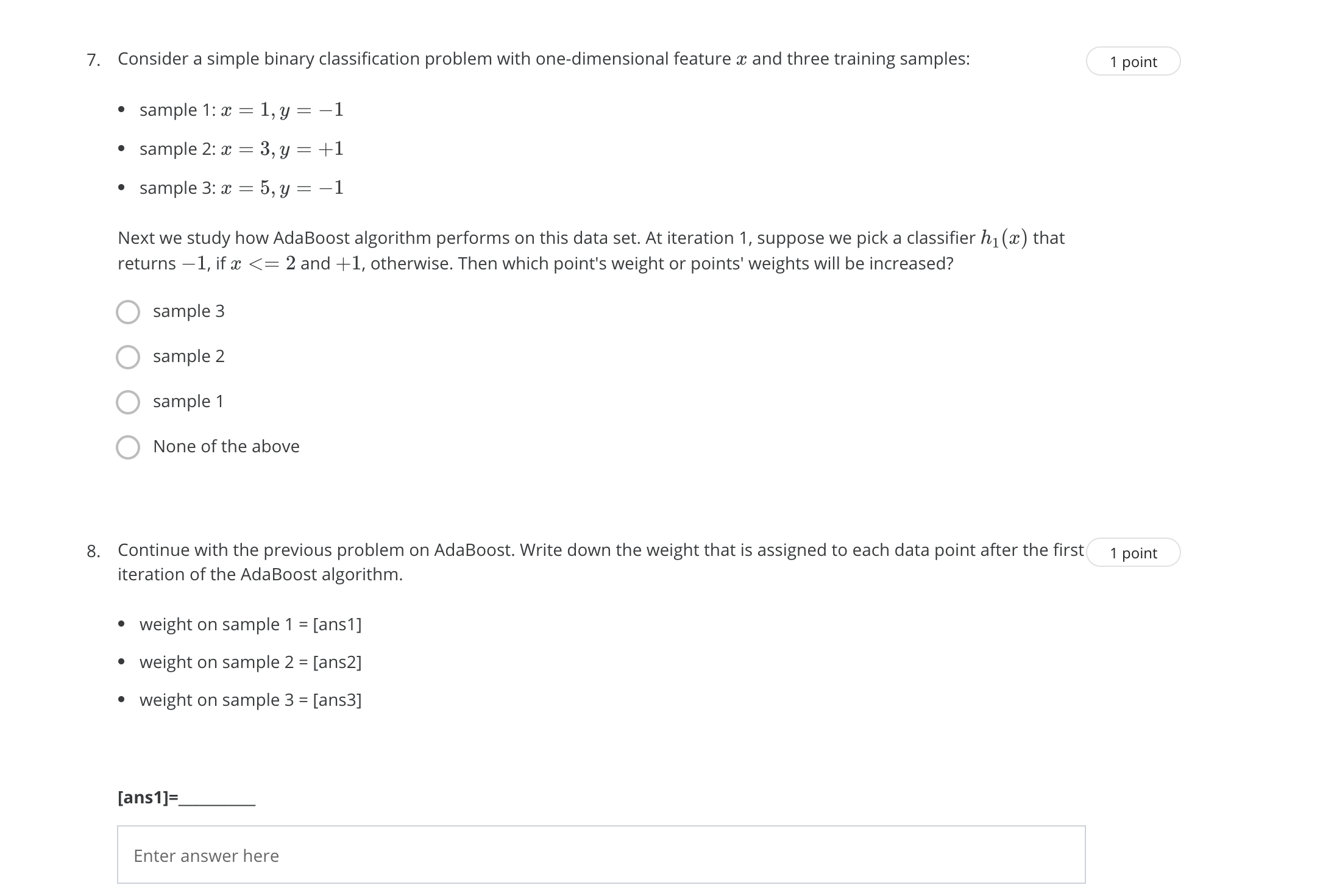
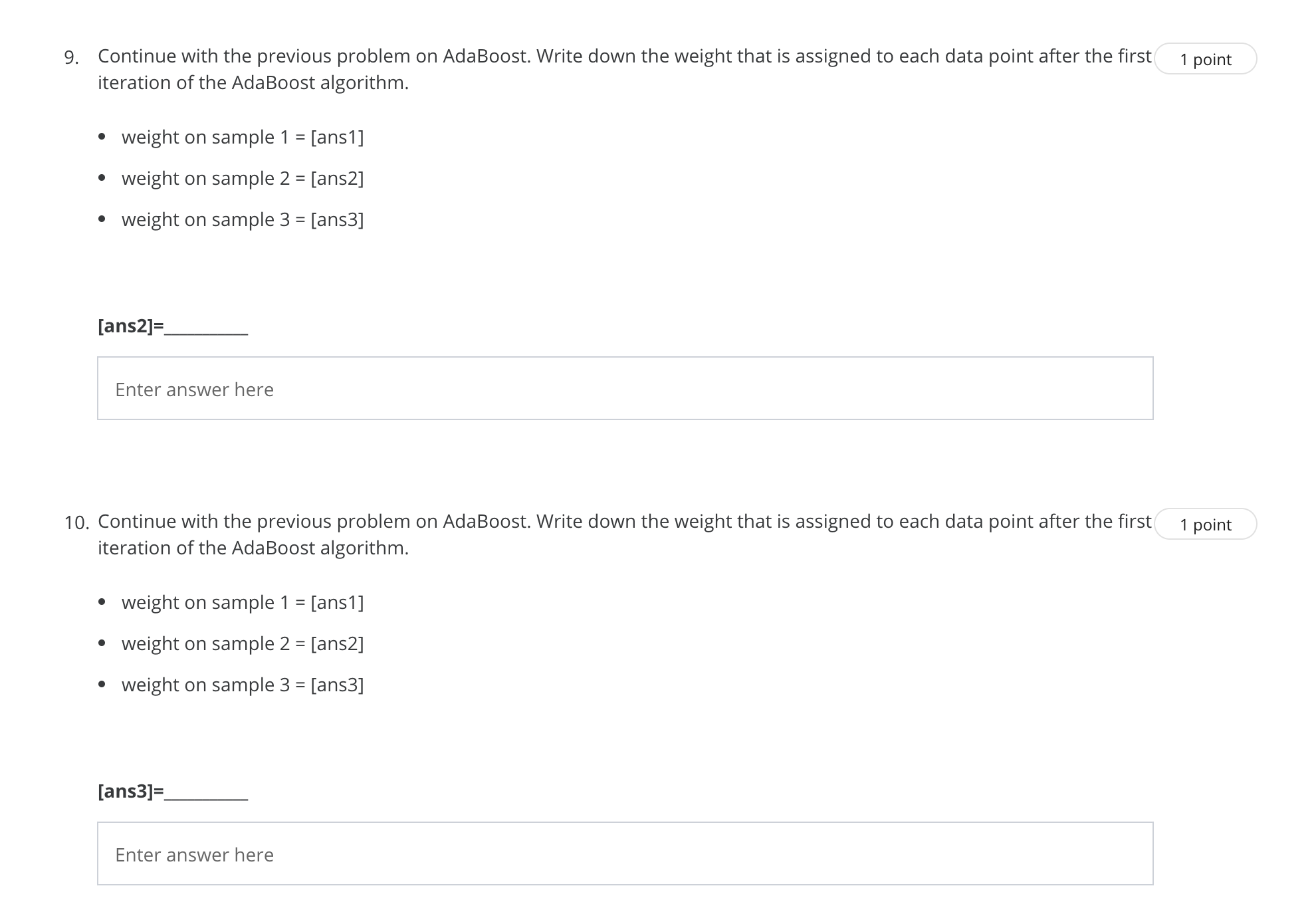
1. Circle all correct statements. 1 point B When building a classification tree, each feature can only be used once. B When building a classification tree, we can reuse a feature to split a node. B Boosting is a general approach that can be applied to many statistical learning methods for regression or classication. D Tree models are not affected by multicollinearity in features. D Individual trees ofa bagged decision forest are less correlated in comparison to individual trees of random forest. 2. What can be the maximum depth of a (binary) decision tree built on a training data with n samples and p features? Here 1 point "binary" means that we only divide each node into two children nodes. Further, assume the n samples are all unique (i.e., the n-by-p data matrix has no duplicate rows). 0 NZ OOOOO 3, Given 1000 observations, minimum number of observations required to split a node equals 200 and minimum leafsize 1 point equals 300, then what could be the maximum depth of a decision tree? (The depth for a tree withjust the root node is 0, and the depth for a tree with one split is 1.) 4. In random forest, what's randomly selected? 1 point 0 For each tree in the forest, we randomly select a set of features as the split candidates from the full set of p features. Q We randomly select the number oftrees in the forest. 0 For each node, we randomly select a set of features as the split candidates from the full set of p features. 0 For each node, we randomly select a feature from the full set of p features to split, 5. Which of the following statements are correct about gom parameters? 1 point "n.trees" should be inversely proportional to "shrinkage", that is, if decreasing "shrinkage", we should increase "n.trees" when tuning the parameters. "shrinkage" can be any non-negative number. "bag.fraction" should be between 0 and 1. "n.trees" can be equal to 1. 6. Suppose we are applying adaboosting and randomforest on a classification problem. Below, "error" refers to the ordinary 1 point miclassification rate (number of misclassified samples divided by the total sample size) using all trees. When the number of trees increases, The training error of randomforest decreases. O The test error of randomforest decreases. The training error of adaboosting decreases. O None of the above. O The test error of adaboosting decreases.7. Consider a simple binary classification problem with one-dimensional feature a and three training samples: 1 point . sample 1:x = 1, y = -1 . sample 2: x = 3, y = +1 . sample 3: x = 5, y = -1 Next we study how AdaBoost algorithm performs on this data set. At iteration 1, suppose we pick a classifier h1 (a) that returns -1, if x
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


