Question: Please help me code this in C + + for my data structures course: Natural merge sort overview The merge sort algorithm recursively divides the
Please help me code this in C for my data structures course:
Natural merge sort overview
The merge sort algorithm recursively divides the array in half until an array with one element is reached. A variant of merge sort, called natural merge sort, instead finds alreadysorted runs of elements and merges the runs together.
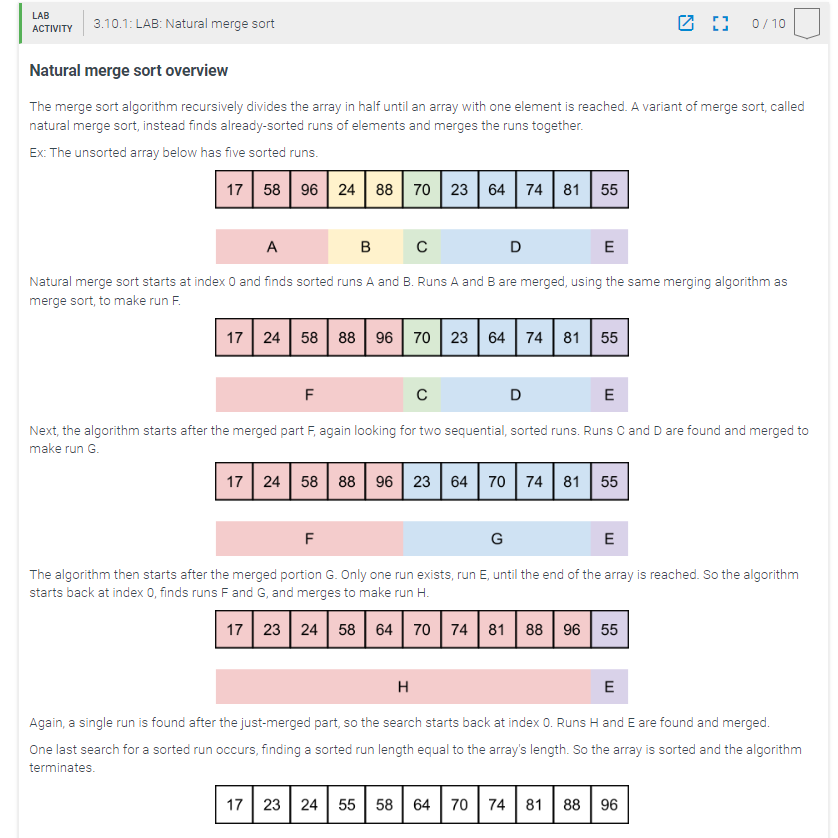
Ex: The unsorted array below has five sorted runs.
Natural merge sort starts at index and finds sorted runs A and B Runs A and B are merged, using the same merging algorithm asnmerge sort, to make run F
Next, the algorithm starts after the merged part F again looking for two sequential, sorted runs. Runs C and D are found and merged to
make run G
The algorithm then starts after the merged portion G Only one run exists, run E until the end of the array is reached. So the algorithm
starts back at index finds runs F and G and merges to make run H
Again, a single run is found after the justmerged part, so the search starts back at index Runs H and E are found and merged.
One last search for a sorted run occurs, finding a sorted run length equal to the array's length. So the array is sorted and the algorithm terminates.
Step : Implement the GetSortedRunLength member function
Implement the GetSortedRunLength member function in NaturalMergeSorter.h GetSortedRunLength has three parameters:
array: A pointer to an array of integers
arrayLength: An integer for the array's length
startIndex: An integer for the run's starting index
Return the number of array elements sorted in ascending order, starting at startIndex and ending either at the end of the sorted run, or the end of the array, whichever comes first. Return if startIndex is out of bounds.
File main.cpp has several test cases for GetSortedRunLength that can be run by clicking theRun button. One test case also exists for NaturalMergeSort but that can be ignored until step two is completed.
The program's output does not affect grading.
Submit for grading to ensure that the GetSortedRunLength unit tests pass before proceeding.
Step : Implement the NaturalMergeSort member function
Implement the NaturalMergeSort member function in NaturalMergeSorter.h NaturalMergeSort must:
Start at indexi
Get the length of the first sorted run, starting ati
Return if the first run's length equals the array lengthIf the first run ends at the array's end, reassigni and repeat step
Get the length of the second sorted run, starting immediately after the first
Merge the two runs with the provided Merge function
Reassigni with the first index after the second run, or if the second run ends at the array's end
Go to step Step : Implement the GetSortedRunLength member function
Implement the GetSortedRunLength member function in NaturalMergeSorter.h GetSortedRunLength has three parameters:
array: A pointer to an array of integers
arrayLength: An integer for the array's length
startIndex: An integer for the run's starting index
Return the number of array elements sorted in ascending order, starting at startIndex and ending either at the end of the sorted run, or the end of the array, whichever comes first. Return if startIndex is out of bounds.
File main.cpp has several test cases for GetSortedRunLength that can be run by clicking the Run button. One test case also exists for NaturalMergeSort but that can be ignored until step two is completed.
The program's output does not affect grading.
Submit for grading to ensure that the GetSortedRunLength unit tests pass before proceeding.
Step : Implement the NaturalMergeSort member function
Implement the NaturalMergeSort member function in NaturalMergeSorter.h NaturalMergeSort must:
Start at index i
Get the length of the first sorted run, starting at i
Return if the first run's length equals the array length
If the first run ends at the array's end, reassign i and repeat step
Get the length of the second sorted run, starting immediately after the first
Merge the two runs with the provided Merge function
Reassign i with the first index after the second run, or if the second run ends at the array's end
Go to step
Files main.cpp
C NaturalMergeSorter.h
RunLengthTestCase.h
Run
History
virtual void Mergeint numbers, int leftFirst, int leftLast,
int rightLast
int mergedSize rightLast leftFirst ;
int mergedNumbers new intmergedSize;
int mergePos ;
int leftPos leftFirst;
int rightPos leftLast ;
Add smallest element from left or right partition to merged numbers
while leftPos leftLast && rightPos rightLast
if numbersleftPos numbersrightPos
mergedNumbersmergePos numbersleftPos;
leftPos;
else
mergedNumbersmergePos numbersrightPos;
rightPos;
mergePos;
If left partition isn't empty, add remaining elements to mergedNumbers
while leftPos leftLast
mergedNumbersmergePos numbersleftPos;
If left partition isn't empty, add remaining elements to mergedNumbers
while leftPos leftL
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


