Question: please help me summarize this chapter summarize this chapter please g) whes din indring woont of ochgeful in s tem pai . 4 buy per

please help me summarize this chapter

summarize this chapter please
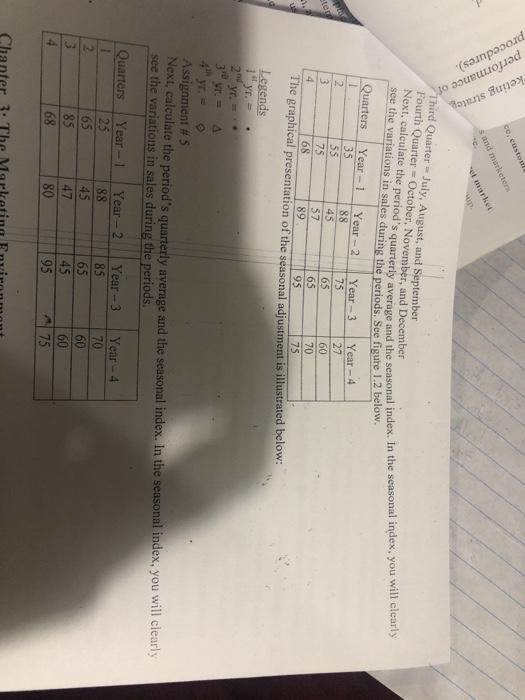
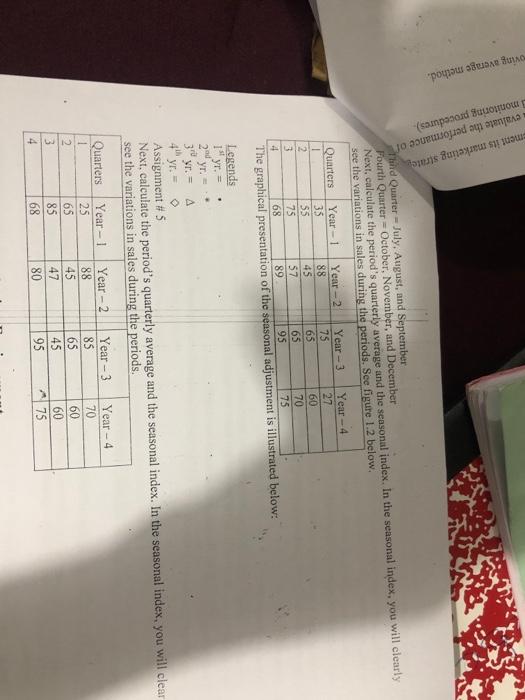
g) whes din indring woont of ochgeful in s tem pai . 4 buy per 2 Puneing. Implementing and Evaluating Marketing Strategies e marketing management is the process of planning, implementing and evaluating the performance The will goal of strategie marketing management is to facilitate desirable customer relationships 1. The Strategie Planning Process. The process of strategie planning helps a firm establishin national mission and formulate goals, a corporate strategy, marketing objectives, and a marketing The process beans with the establishment or revision of an organization's mission and goals The corporation and individual business units then develop strategies to achieve these goals The company then analyses its strengths and weaknesses and identifies opportunities and threats within the external marketing environment Fach functional area of the organization establishes its own objetives and develop strategies to achieve them, which must support the organization's overall goals and mission and should be focused on market orientation Establishing Organizational Mission Statements and Goals The goal of any organisation derive from its mission statement, a long-term view or vision of what the organization wants to become. An organization's mission really awwers two questions Who are our customers What is our core competency? A company's mission, goals, and objectives must be properly implemented to achieve and communicate the desired corporate Identity a company's unique symbols, personalities, and philosophies An organization's goals and objectives, derived from its mission statement, guide its planning efforts Goals focus on the end results sought by the organization Developing Corporate and Business-Unit Strategies Strategic planning often begins at the corporate level and proceeds downward to the business-unit and marketing levels. However, organizations are increasingly developing strategies and conducting strategic planning that moves in both directions to seek expertise from multiple levels Corporate strategy should be developed with the organization's overall mission in mind, business-unit Strategy should be consistent with corporate strategy, and marketing strategy should be consistent with both. Corporate Strategies Corporate strategy determines the means for utilizing resources in the functional areas of marketing, production, finance, research and development (R&D), and human resources to achieve the organization's Corporate strategy planners are concerned with broad issues such as organizational culture, competition differentiation, diversification, interrelationships among business units, and environmental and social issues They attempt to match the resources of the organization with the opportunities and threats in the environment Business-init Strategies Pg. 9 owned die made who An UNGEN Sweety Mb A strategic business unit (SBU) is a division, product line, or other profiteer within the parent Stegle planners should recognize the performance capabilities of each SBU and carefully Resources among the division A market is a group of individuals and/or organizations that have needs for products in a products and have the ability, willingness, and authority to purchase those products. The percentage of a market that actually buys a specific product from a particular company is referred to as that products for business unit's market share The market wil market share matrix, developed by the Boston Consulting Group (BCG).is philosophy that a products market growth rate and its market share are important considerations in determining its marketing strategy All the organization's SBUs and products are integrated into a single matrix and compared and evaluated to determine appropriate strategies for individual products and overall portfolio strategies Mange this model to determine and classify each product's expected future can contribution and future cash out The CG analytical approach is more of a diagnostic tool than a guide for making to press This model is an organization's products into four basic types. Stars have a dominant share of the market and good prospects for prowth, they were cash they De to finance growth, add capacity, and ince market share Cash-cows have a dominant share of the market but low prospects for growth, they wypically more caththa is required to maintain market share. Example Procter & Gamble's Bounty Paper Dogs have a chordinate share of the market and low prospects for growth, the products wished markets Example: Panasonie's cathode ray tube television Question marks, sometimes called "problem children." have small share of a growing red may require a large amount of cash to build market share The long-term health of an organisation depends on having a range of products, so that and provide aceptable prota) and others that we coupon Competitive Growth Strategies Based on analyses of each product or business unit, afirmay choose one or more competitive Market penetration is a strategy of increasing sales in current markets with current products Market development is a strategy of increasing sales of current products in new markets Market developmental curs when a company leoduce its products into interminal markets for the line Product development is a strategy of increasing sales by improving pecvent products or developing new products for current markets (eg automotive industry) Diversification is a strategy of developing tww products to be sold in new markets. Diversification allows finns to make bene and wider use of their managerial, technological and financial resources Divcnification also offers some advantages over single business Suns because it allows firms to spread their risk across a number of markets. Assessing Organizational Resources and Opportunities The stupid planning process begins with an analysis of the marketing environment, which can influence ar organization's goals, resources, and opportunities. Strategic planning must assess an organization's available financial and human resources and capabilities ad how these resources are likely to change over time pg. 10 compar can includer setion and loyalty Reputation in names Core competencies, things a femdoes extremely well sometimes so well that they can give the company an advantage over its competition Analysis of the marketing environment also includes identifying opportunities in the marketplace, which requires a solid understanding of the company's industry, A market opportunity exists when the right combination of circumstances and timing permits an organization to take action to reach a particular target market Strategie windows are temporary periods of optimal fit between the key requirements of a market and the particular capabilities of a firm competing in that market A company is said to have a competitive advantage when it matches a core competency to opportunities has discovered in the marketplace SWOT Analysis A SWOT analysis is one tool marketers uses to assess an organization's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Strengths and weaknesses are internal factors that can influence an organization's ability to satisfy its target markets Strengths refer to competitive advantages or core competencies that give the organization an advantage in meeting the needs of its target markets. Weaknesses are internal limitations a company faces in developing or implementing a marketing strategy Both strengths and weaknesses should be examined from a customer perspective, Opportunities and threats affect all organizations within an industry, market, or geographic region because they exist outside of and independently of the company Opportunities refer to favourable conditions in the environment that could produce rewards for the Organization if acted upon Threats refer to barriers that could prevent the organization from reaching its objectives When an organization matches internal strengths to extemal opportunities, it creates competitive advantages in meeting the needs of its customers. Companies should attempt to convert internal weaknesses into strengths and external threats into opportunities First-Mover and Late-Mover Advantage A first-mover advantage is the ability of an innovative company to achieve long-term competitive advantages by being the first to offer a certain product in the marketplace Benefits include building a reputation as a market leader, reducing competition, establishing brand loyalty and protecting trade secrets Risks?nclude high costs associated with creating and marketing a new product, slower than predicted sales growth. And the potential for product failure. Alate-mover advantage is the ability of later market entrants to achieve long-term competitive advantages by not being the first to offer a certain product in a marketplace. 02771 I. Matuleht is panirantamanna The Mag jewed Mr Sir podpredenti -: en WOT antes and with completo Ayshe en afstand the coming is that will me market Mathew Select the Tear Seneste pe may be the most importadocions company make the policial for regio There must be chosen before the nation can adaptarting mix to meet the ' ial ter When exploring target niks, marketing managers try to be how entry could affect the cast, and profiles Mariehold determine whether target market aligns with the company's overall bytes Merki should losses whether the company has the resources to develop the right marketing mixte the particular target market. The time and me of competitors is also a com Creating the Marketing Mises The madeininga maringonly as pood as the one's Understanding comes from carefis-depth into demons as well as need preferences and behavior with respect to product design ide distribution, and promotion Marketing mix decisies held be consistent with the best and corporate strategies well lexible enough to permit the centation to her the main response to changes in mu conditional competition, and customer needs Liding the marketing mix as a tools, a company can deltow it will coves sastable competitive data pe: 12 ulty in convincing 3 Strategies sustainable competitive advantage is one that the competition cannot copy in the foreseeable future III. Managing Marketing Implementation Marketing implementation is the process of putting marketing strategies into action Organizing the Marketing Unit The structure and relationships of a marketing unit, including establishing lines of authority and communication that connect and coordinate individuals, strongly affect marketing activities. Companies that truly adopt the marketing concept develop an organizational culture that is based on a shar set of beliefs that places the customer's needs at the center of decisions about strategy and operation Firms must decide whether operations should be centralized or decentralized, a choice that directly impacts marketing decision making and strategy In a centralized organization, top-level managers delegate little authority to lower levels. Most traditional organizations are highly centralized In a decentralized organization, decision-making authority is delegated as fur down the chain of command possible. Decentralized authority allows the company to adapt more rapidly to customer needs. Organizing marketing activities to align with the overall strategic marketing approach enhances Organizational efficiency and performance A marketing department should clearly outline the hierarchical relationships between personnel and who is responsible for performing certain activities and making decisions Coordinating and Communicating To achieve marketing objectives, marketing managers must coordinate actions within and across departments, firms, and external organizations to ensure that marketing activities align with other functions of the firm Marketing managers can improve coordination by making each employee aware of how his or her job relatos to others and how his or her actions contribute to the achievement of marketing objectives Marketing managers must be in clear communication with the firm's upper-level management to ensure that they are aware of the firm's goals and achievements and that marketing activities are consistent with the company's overall goals and strategies. Communication that flows upward from the frontlines of the organization to higher level marketing managers provides important information about the needs of customers and employees Training provides employees with a forum to learn and ask questions, and results in employees who are empowered and can be held accountable for their performance Information systems expedite communications within and between departments and support other activities. such as allocating scarce organizational resources, planning, budgeting, sales analyses, performance evaluations, and report preparation Managers must address their employees' needs and then develop motivational methods that will help employees satisfy those needs. Employee rewards should be tied to organizational goals. A firm can motivate its workers by directly linking pay with performance, informing workers how their performance affects department and corporate results, following through with appropriate and competitive compensation, implementing a flexible benefits program, and adopting a participative management approsch Manage should also use a variety of other tools, including nonfinancial rewards such as prestige on recognition, job autonomy, skill variety, task significance, increased feedback, or even a more relaxed dos Pg. 13 Marketing Cost Analys Marketing costs marketing efforts By pinpointing exactly unprofitable customers, accounts Supernatud marketing implementation requires that employous know the specific activities for which responsible and the timetable for completing each activity Establishing an implementation timetable involves several steps Identifying the activities to be performed Determining the time required to complete each activity Separating the activities to be performed in sequence from those to be performed simultaneously Organizing the activities in the proper order Augning responsibility for completing each activity to one or more employees, teams, or managers Since scheduling can be a complicated task, some organizations use sophisticated computer programs to plan the timing of marketing activities IV. Evaluating Marketing Strategies Strategie performance evaluation consists of establishing performance standards, measuring actual performance, comparing actual performance with established standards, and modifying the marketing strategy, if needed Establishing Performance Standards performance standard is an expected level of performance against which actual performance can be compared, such as a reduction in customer complaints, a sales quota, or an increase in new customer Marketing objectives directly or indirectly set forth performance standards, usually in terms of sales, costs or communication dimensions Analyzing Actual Performance The principle means by which a marketer can gauge whether a marketing strategy has been effective in achieving objectives is by analyzing the actual performance of the marketing strategy Technology advancements have made it easier for firms to analyze actual performance Sales Analysis Sales analysis uses sales figures to evaluate a firm's current performance Sales analysis is a common method of evaluation because sales data are readily available and can reflect the target market's reactions to a marketing mix To be useful, marketers must compare current sales data with forecasted sales, industry sales, specitic competitors' sales, and the cost incurred from marketing efforts to achieve the sales volume. The basic unit of measurement is the sales transaction, which includes the quantity, terms, the salesperson or sales team, and the date Firms frequently use dollar volume in their sales analysis because the dollar is a common denominator of sales, costs, and profits. A marketing manager who uses dollar volume analysis should factor out the effects of price changes, which can skew the numbers by making it seem that more or fewer sales have been made than is the actual case Market share analysis lets a company compare its marketing strategy with competitors' strategies and estimate whether sales changes have resulted from the firm's marketing strategy or from uncontrollable environmental forces. However, the results must be interpreted carefully. or which by poly where a company in this form of analysis can help loop -lem profitable customers, product, oggi company that understand and its contes appropriately has competitive and.com One way to make costa is by comparing company's come with indoney very bowever.com Corts can be categorized into fixed lita (always the same over time) sont peu, s well as variables aftet by mules or production me) och is the cou to produce products. They can become by whether they can be linked to a specific business function Comparing Actual Performance with Performance Standards and Making Cheapes. If needed Comparing actual performance with established perfomance standards can result in actual performance seeding performance standards or actual performance most performance standards la important to find out why particular strategy in atfective or ineffective so that it can be improved. Marketers may have to alter the working objective to make it more reali Y. Cresting the Marketing Plan The strategic planning process ultimately yields a mange that is the trum plan a written document that specifies the marketing activities to be performed to me and eve the cat's marketing strategies provides a wifom marketing vision for the firm and is the basis for internal communication employees Il delineate marketing responsibilities and to outlines schedules for implemen At presents objectives and specifies how resources are to be allocated to achieve these objectives It helps marketing managers monitor and evaluate the performance of a marketing strategy A company may develop multiple marketing plans, with each relating to a specific brand or product Orgmizations use many different formats, and it is important to make sure that it ligns with corpore business-unit itrategies and is shared with all key employees Marketing planning and implementation are closely linked in successful companies The marketing plan provides a framework to stimulate thinking and provide strategie direction Implementation is an adaptive response to day-to-day issues, opportunities, and anticipated situations that can be incorponited into marketing plans The major components of a marketing plan include: The executive summary is a one-to two-page synopsis of the entire farketing plan The environmental analysis provides information about the company's current situation with respect to the marketing environment, the target market, and the firm's current objectives and performance The SWOT analysis assesses the organization's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats The my being objectives, a specifiontion of the company's marketing objectives that include qualitative le mears of what is to be accomplished. The man eting strategies, which outlines how the company will achieve its objectives (identifies the targes marks and marketing mix). PR 1 02 - ly Nestas th Qanun Ye Ye Year The tinimplementation section outlines how the company will implementit mark The performance in section, which explains how the company will evaluate the perform implemented plot includes performance Standards, finicial control, and monitoring procedure PORECASTING IN MARKETING From the below Forectale for the quarter using the moving average method Q You Year 2 55 12 35 50 Mon 0001 W OF QUARTER WITH SALE NOTE: Forecasting model attempts to predict future circumstances based on pastdata. A tools EXPONUNTIAL SMOOTHING METHOD is another method of forecasting sales in its simple for it consist of taking the last cu made for the quarter just ended and added to that forecast, a proportin of the difference between what actually happened quarter forecast. In mathematical om TO 0.1 (AS - TOP White NOF representa Next quarter forecast As - Actual Sale.. represents constant which symbolizes 100% and TTQ this quarter forecast From the below ales data, cast sale for the quarter using the moving average method Q Year1 Year 2 os 45 78 Forcall for the quarter using exponential smoothing method assuming that actual sales for the were SOLUTION FOTOF+OTAS - TOP Forecids for the quarter using exponential smoothing method assuming that actual les for the quatre SOLUTION NFO - TOF01 CASTOF) Variance in sales reporting is the actual difference between a proposal and actual result in sales for period. In calin variance in terms of amount ind percent, there are formulas associated cha calculation Prebelow For Anot- Atual sales This quarter forecast (AS - TOP) For that of percentuale. This cancer forecast X 100 or AS - TOEX 100 This quote Forecast TOF SEASONAL ADJUSTMENT Seasonal Adjustments other form of feeding that assist salesmamarketing managen under vantion in sales in partiolar fimmy Fothoroughly understand this method, it is won the year into four distinct quarians with the months in each quarter First Quarter January February, und March Second Quarter - April May, and lune oving average method. a monitoring procedures). evaluate the performance of ement its marketing strate and Quarter July August, and September Fourth Quarter October, November, and December Next, calculate the period's quarterly average and the seasonal index. In the seasonal index, you will clearly see the variations in sales during the periods. See figure 1.2 below, Quarters Year-1 Year-2 Year-3 Year-4 35 88 75 27 2 55 45 65 60 3 75 57 65 70 4 68 89 95 75 The graphical presentation of the seasonal adjustment is illustrated below: Legends YT 20 30 15 YT. Yr. yr. A Assignment #5 Next, calculate the period's quarterly average and the seasonal index. In the seasonal index, you will clear see the variations in sales during the periods. Quarters 1 2 3 4 Year-1 25 65 85 68 Year - 2 88 45 47 80 Year - 3 85 65 45 95 Year - 4 70 60 60 75 chase s on the lling (3) marketing en ck, first, the piering, Implementing, and Evaluating Marketing Strategies Sie marketing management is the process of planning, implementing and evaluating the performance of marketing activities and strategies, both effectively and efficiently reduce costs The overall goal of strategic marketing management is to facilitate desirable customer relationships arul II. The Strategie Planning Process: The process of strategie planning helps a firm establish an organizational mission and formulate goals, a corporate strategy, marketing objectives, and a marketing strategy The process begins with the establishment or revision of an organization's mission and goals The corporation and individual business units then develop strategies to achieve these goals The company then analyzes its strengths and weaknesses and identifies opportunities and threats within the external marketing environment. Each functional area of the organization establishes its own objectives and develops strategies to achieve them, which must support the organization's overall goals and mission and should be focused on market orientation Establishing Organizational Mission Statements and Goals The goals of any organization derive from its mission statement, a long-term view or vision of what the organization wants to become. An organization's mission really answers two questions: Who are our customers? What is our core competency? A company's mission, goals, and objectives must be properly implemented to achieve and communicate the desired corporate identity a company's unique symbols, personalities, and philosophies An organization's goals and objectives, derived from its mission statement, guide its planning efforts. Goals focus on the end results sought by the organization. Developing Corporate and Business-Unit Strategies Strategic planning often begins at the corporate level and proceeds downward to the business-unit and marketing levels. However, organizations are increasingly developing strategies and conducting strategie planning that moves in both directions to seek expertise from multiple levels. Corporate strategy should be developed with the organization's overall mission in mind, business-unit strategy should be consistent with corporate strategy, and marketing strategy should be consistent with both Corporate Strategies Corporate strategy determines the means for utilizing resources in the functional areas of marketing production, finance, research and development (R&D), and human resources to achieve the organization's goals. Corporate strategy planners are concemed with broad issues such as organizational culture, competition, differentiation, diversification, interrelationships among business units, and environmental and social issues They attempt to match the resources of the organization with the opportunities and threats in the environment. Business-Unit Strategies courees cast Customer sati Reputation Goodwill Core competencies, Brand names advantage over.com Anal A strategic business unit (SBU) is a division, product line, or other profit center within the parent com Strategic planners should recognize the performance capabilities of each SBU and carefully allocate resources among the divisions A market is a group of individuals and/or organizations that have needs for products in a product class and have the ability, willingness, and authority to purchase those products. The percentage of a market that actually buys a specific product from a particular company is referred to as that product's (or business unit's) market share. The market-growtlvmarket share matrix, developed by the Boston Consulting Group (BCG), is based on the philosophy that product's market growth rate and its market share are important considerations in determining its marketing strategy All the organization's SBUs and products are integrated into a single matrix atid compared and evaluated to determine appropriate strategies for individual products and overall portfolio strategies. Manager use this model to determine and classify cach product's expected future cash contribution and future cash requirements The BCO analytical approach is more of a diagnostic tool than a guide for making strategy prescription This model classifies an organization's products into four basic types Stars have a dominant share of the market and good prospects for growth, they use more cash than they generate to finance growth, add capacity, and increase market share. Cash-cows have a dominant share of the market but low prospects for growth; they typically generate more cash than is required to maintain market share. Example: Procter & Gamble's Bounty paper towels Dou have a subordinate share of the market and low prospects for growth; these products are often found in established markets. Example: Panasonic's cathode ray tube televisions Question marks, sometimes called "problem children," have a small share of a growing market and generally require a large amount of cash to build market share The long-term health of an organisation depends on having a range of products, some that generate cash and provide acceptable profits) and others that use cash to support growth Competitive Growth Strategies Based on alyses of each product or business unit, a firm may choose one or more competitive strategies Market penetration is a strategy of increasing sales in current markets with current products. Market development is a strategy of increasing sales of current products in new markets. Market development also occurs when a company introduces its products into international markets for the liest time Product development is a strategy of increasing sales by improving present products or developing new products for current markets (e.g. automotive industry), Diversification is a strategy of developing new products to be sold in new markets. Diversification allows firms to make better and wider use of their managerial, technological, and financial resources. Diversification also offers some advantages over single-business firms because it allows firms to spread their risk across a number of markets. Assessing Organizational Resources and Opportunities The straipgic planning process begins with an analysis of the marketing environment, which can influence an organization's goals, resources, and opportunities. Strategic planning must assess an organization's available financial and human resources and capabilities and how these resources are likely to change over time. Pg. 10 (or business arti ducts comp rear winclude: sction and loyalty Brand names Core competencies, things a firm does extremely well sometimes so well that they can give the company in indvantage over its competition Analysis of the marketing environnent also includes identifying opportunities in the marketplace, which requires a solid understanding of the company's industry, A market opportunity exists when the right combination of circumstances and timing permits a organization to take action to reach a particular target market Strategie windows are temporary periods of optimal fit between the key requirements of a market and the particular capabilities of a firm competing in that market A company is suid to have a competitive advantage when it matches a core competeney to opportunities in has discovered in the marketplace SWOT Analysis A SWOT analysis is one tool marketers uses to assess an organization's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Strengths and weaknesses are internal factors that can influence an organization's ability to satisfy its targel markets Strengths refer to competitive advantages or core competencies that give the organization an advantage in meeting the needs of its target markets. Weaknesses are internal limitations a company faces in developing or implementing a marketing strategy Both strengths and weaknesses should be examined from a customer perspective, Opportunities and threats affect all organizations within an industry, market, or geographic region because they exist outside of and independently of the company. Opportunities refer to favourable conditions in the environment that could produce rewards for the organization if acted upon. Threats refer to barriers that could prevent the organization from reaching its objectives When an organization matches internal strengths to external opportunities, it creates competitive advantages in meeting the needs of its customers. Companies should attempt to convert internal weaknesses into strengths and external threats into opportunities. First-Mover and Late-Mover Advantage A first-mover advantage is the ability of an innovative company to achieve long-term competitive advantages by being the first to offer a certain product in the marketplace Benefits include building a reputation as a market leader, reducing competition, establishing brand loyalty, and protecting trade secrets. Risks include high costs associated with creating and marketing a new product, slower than predicted sales growth, and the potential for product failure. A late-mover advantage is the ability of later market entrants to achieve long-term competitive advantages by not being the first to offer a certain product in a marketplace. Pg. 11 100 Sube Com Book ustainable competitive adva ill. Mawaging Marketing Replies Marketing implementation in the poems per Organizing the Marketing Cat tantander Wher tion Benefits include learning from first-mover's mistakes, improved products and marketing strate initial investment costs, more market certainty, and more oducted buyers Risks include fiest-movers holding patents and other prgcections en products and difficulty in convincin consumers to change brands. The timing of entry to the market is erucinlund can determine the amount of ndvantage Developing Marketing Objectives and Marketing Strategies Marketing objective states what is to be accomplished through marketing activities Objectives can be given in terms of product introduction, product improvement or innovation, les volume profitability, market share.pricing. distribution, advertising, or employee training activities Objectives should be based on a careful study of the SWOT analysis, matching strengths to opportunities eliminating weaknesses, and minimizing threats Marketing objectives should: Be expressed in cler, simple terma De mearumble Speely a time frame for its accomplishment Be consistent with both business-unit and corporate strategies He achievable and use company resources effectively, and successful accomplishment should contribute the overall corporate strategy A marketing strategy is the selection of a target market and the creation of a marketing mix that will satisfy the needs of target market members Marketing strategies may need to be adapted as the environment changes. Selecting the Target Market Selecting an appropriate target market may be the most important decision a company makes in the strateji pinning process and is crucial for strategie success The target market must be chosen before the organization can adapt its marketing mix to meet the customer needs and preferences When exploring possible target markets, marketing managers try to evaluate how entry could affect the company's sales, costs, and profits. Micketers should determine whether a selected target market aligns with the company's overall mission and objectives Marketers should also assess whether the company has the resources to develop the right marketing mix to meet the needs of a particular target market. The size and number of competitors is also a concern Creating the Marketing Mixes The decisions made in creating a marketing mix are only as good as the organization's understandings of the target market APER Understanding comes from careful in-depth research into demographics as well as customer needs. preferences, and behavior with respect to product design, pricing, distribution, and promotion, Marketing mix decisions should be consistent with the business-unit and corporate strategies as well as flexible enough to permit the organization to alter the marketing mix in response to changes in marketing conditions, competition, and customer needs. Utilizing the marketing mix as a tool set, a company can detail how it will achieve a sustainable competitive advantage pg competitive advantage is one that the competition cannot copy in the foreseeable future Mg Marketing Implementation QUALITY PAPE ng implementation is the process of putting marketing strategies into action, Organising the Marketing Unit The sucture and relationships of a marketing unit, including establishing lines of authority and communication that connect and coordinate individually, strongly affect marketing activities Companies that truly adopt the marketing concept develop an organizational culture that is based on a must decide whether operation should be centralized or decentralized, choice that directly impacts marketing decision organizations are highly centralized, In a centralized organization, top-level managers delegate lite authority to lower levels. Most traditional In a decentralized organization, decision-making authority is delegated as far down the chain of commands possible Decentralized authority allows the company to adapt more rapidly to customer feeds. Organizing marketing activities to align with the overall strategia marketing approach enhances organizational efficiency and performance. A marketing department should clearly outline the hierarchical relationships between personnel and who is responsible for performing certain activities and making decisions Coordinating and Communicating To achieve marketing objectives, marketing managers must coordinate actions within and across departments, firms, and external organizations to ensure that marketing activities align with other functions of the firm Marketing managers can improve coordination by making each employee aware of how his or her job relates to others and how his or her actions contribute to the achievement of marketing objectives. Marketing managers must be in clear communication with the firm's upper-level management to ensure that they are aware of the firm's goals and achievements and that marketing activities are consistent with the company's overall goals and strategies Communication that flows upward from the frontlines of the organization to higher level marketing managers provides important information about the needs of customers and employees. Training provides employees with a forum to learn and ask questions, and results in employees who are empowered and can be held accountable for their performance Information systems expedite communications within and between departments and support other activities such as allocating scarce organizational resources, planning, budgeting, sales analyses, performance evaluations, and report preparation Managers must address their employees' needs and then develop motivational methods that will help employees satisfy those needs. Employee rewards should be tied to organizational goals A firm can motivate its workers by directly linking pay with performance, informing workers bow their performance affects department and corporate results, following through with appropriate and competitive compensation, implementing a flexible benefits program, and adopting a participative management approtich Manages should also use a variety of other tools, including nonfinancial rewards such as prestige or recognition job autonomy, skill variety, task significance, increased feedback, or even a more relaxed dress code Pg. 13 xer rketing Cost Amaya Marketing cost saya buat earketing eller By pinpointing and where profitable customers, modo Acompany that understand compete on price One way to Establishing a Timetable for Implementation Successful marketing implementation requires that employees know the specific activities for while responsible and the timetable for completing each activity Establishing an implementation timetable involves several steps: Identifying the activities to be performed Determining the time required to complete each activity Separating the activities to be performed in sequence from those to be performed simultaneously Organizing the activities in the proper order Assigning responsibility for completing each activity to one or more employees, Teams, or managers Since scheduling can be a complicated task, some organizations use sophisticated computer programs to plain the timing of marketing activities IV. Evaluating Marketing Strategies Strategic performance evaluation consists of establishing performance standards, measuring actunl performance, comparing actual performance with established standards, and modifying the marketing strategy, if needed Establishing Performance Standards performance standard is an expected level of performance against which actual performance can be compared, such as a reduction in customer complaints, a sales quota, or an increase in new customer Marketing objectives directly or indirectly set forth performance standards, usually in terms of sales, costs. or communication dimensions Analyzing Actual Performance Achieving objectives is by analyzing the actual performance of the marketing strategy The principle means by which a marketer can gauge whether a marketing strategy has been effective in Technology advancements have made it easier for firms to analyze actual performance accounts Sales Analysis Sales analysis uses sales figures to evaluate a firm's current performance. Sales analysis is a common method of evaluation because sales duta are readily available and can reflect the target market's reactions to a marketing mix. To be useful, marketers must compare current sales data with forecasted sules, industry sales, specific competitors' sales, and the cost incurred from marketing efforts to achieve the sales volume The basic unit of measurement is the sales transaction, which includes the quantity, terms, the salesperson or sales team, and the date. Firms frequently use dollar volume in their sales analysis because the dollar is a common denominator of sales. costs, and profits. marketing manager who uses dollar-volume analysis should fuctor out the effects of price changes, which aan skew the numbers by making it seem that more or fewer sales have been made than is the actual ease. Market share analysis lets a company compare its marketing strategy with competitors' strategies and timate whether sales changes have resulted from the firm's marketing sirategy or from uncontrollable vironmental forces. However, the results must be interpreted carefully Making Con Analysis mating efforts Meeting cost analysis breaks down and classitles coste to determine which we weet watu weite By pinpointing exactly where a company incurs costs, this form of unnysicus help Isolate profitable or unprofitable customers, products, and geographie areas Acompany that understands and manages its cows appropriately has a competitive advantage and con compete on price. One way to analyze costs is by comparing a company's costs with industry averages however, a company should take into account its own unique situation Costs can be categorized into fixed costs (always the same over time) such as rent, as well as variable COM Caffected by sales or production volume) such as the cost to produce products. They can also be categorized by whether they can be linked to a specific business function. Comparing Aetual Performance with Performance Standards and Malding Changes, If Needed Comparing actual performance with established performance standards can result in actual performance exceeding performance standards or actual performance failing to meet performance standards. It is important to find out why a particular strategy is effective or ineffective so that it can be improved Marketers may have to alter the marketing objective to make it more realistic V. Creating the Marketing Plan The strategic planning process ultimately yields a marketing strategy that is the framework for a marketing plan, a written document that specifies the marketing activities to be performed to implement and evaluate the organization's marketing strategies. It provides a uniform marketing vision for the firm and is the basis for intemal communication among employees It delineates marketing responsibilities and tasks and outlines schedules for implementation. It presents objectives and specifies how resources are to be allocuted to achieve these objectives. It helps marketing managers monitor and evaluate the performance of a marketing strategy, A company may develop multiple marketing plans, with each relating to a specific brand or product Organizations use many different formats, and it is important to make sure that it aligns with corporate and business-unit strategies and is shared with all key employees. Marketing planning and implementation are closely linked in successful companies. The marketing plan provides a framework to stimulate thinking and provide strategic direction Implementation is an adaptive response to day-to-day issues, opportunities, and unanticipated situations that cannot be incorporated into marketing plans. The major components of a marketing plan include: The executive summary is a one-to two-page synopsis of the entire marketing plan. The environmental analysis provides information about the company's current situation with respect to the marketing environment, the target market, and the firm's current objectives and performance. The SWOT anglysis assesses the organization's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. The marketing objectives, a specification of the company's marketing objectives that include qualitative an quantitative measures of what is to be accomplished. The marketing strategies, which outlines how the company will achieve its objectives (identifies the target market(s) and marketing mix). PS The marketing implementation section outlines how the company will implement its marketing in The performance evaluation section, which explains how the company will evaluate the performance Implemented plan (Includes performance standards, financial controls, and monitoring procedures) hand Quarter Fourth Quarter Next, calculate the ce the var Quarter Year - 1 Year FORECASTING IN MARKETING From the below sales data, Forecast sale for the 4" quarter using the moving average method. 2 55 35 50 1 2 3 2 Moving average - QL-02-02 OF QUARTER WITH SALE NOTE: Forecasting model attempts to predict future circumstances based on past duta. A tool such as EXPONENTIAL SMOOTHING METHOD is another method of forecasting sales. In its simplest form, it one tonth of the difference between what actually happened it quarter forecast. In mathematical form.NO TT-01 (AS - TOF) where NOF represents Next quarter forecast, AS Actual Sale, 0.1 represents constant which symbolizes 100% and TFQ = this quarter forecast From the below sales data, Forecast sale for the 4 quarter using the moving average method. Quarter Year! Assignment Year - 2 1 2 3 4 65 45 75 Forecast sales for the 5 quarter were 98. quarter using exponential smoothing method assuming that actual sales for the 5" SOLUTION: NFQ-TQF +0.1 (AS - TOE) Assignment Forecast sales for the 5 quarter using exponential smoothing method assuming that actual sales for the quarter were 78 SOLUTION: NFO - TOF+0.1 (AS - TOF) Variance in sales reporting is the actual difference between a proposal and actual result in sales for a s period. In calculating variance in terms of amount and percent, there are formulas associated such calculations. Please see below. For Amount = Actual sales - This quarter forecast (AS - TOF) For that or percent - Actual sales - This quarter forecast X 100 or AS - TOF X 100 This quarter Forecast TOF SEASONAL ADJUSTMENT Seasonal Adjustment is another form of forecasting, that assist salesman marketing managers understand variation in sales in a particular firm or industry. To thoroughly understand this method, it is wise lo di the year into four distinct quarters with three months in each quarter. First Quarter - January February, and March Second Quarter - April May, and June De ce, custom and marketer procedures). performance of keting stratex et market Next, calculate the period's quarterly average and the seasonal index. In the seasonal index, you will clearly Third Quarter - July, August, and September , November, see the variations in sales during the periods. See figure 1.2 below. Quarters Year - 1 Year-2 Year - 3 Year - 4 35 88 75 55 45 65 3 75 57 65 70 68 89 95 75 The graphical presentation of the seasonal adjustment is illustrated below: Legends 1 yr. 2 27 te 60 4 2N yr. 3 yr. A Assignment #S Next, calculate the period's quarterly average and the seasonal index. In the seasonal index, you will clearly see the variations in sales during the periods. Quarters 1 2 3 4 Year - 25 65 85 68 Year - 2 88 45 47 80 Year - 3 85 65 45 95 Year - 4 70 60 60 75 3. The g) whes din indring woont of ochgeful in s tem pai . 4 buy per 2 Puneing. Implementing and Evaluating Marketing Strategies e marketing management is the process of planning, implementing and evaluating the performance The will goal of strategie marketing management is to facilitate desirable customer relationships 1. The Strategie Planning Process. The process of strategie planning helps a firm establishin national mission and formulate goals, a corporate strategy, marketing objectives, and a marketing The process beans with the establishment or revision of an organization's mission and goals The corporation and individual business units then develop strategies to achieve these goals The company then analyses its strengths and weaknesses and identifies opportunities and threats within the external marketing environment Fach functional area of the organization establishes its own objetives and develop strategies to achieve them, which must support the organization's overall goals and mission and should be focused on market orientation Establishing Organizational Mission Statements and Goals The goal of any organisation derive from its mission statement, a long-term view or vision of what the organization wants to become. An organization's mission really awwers two questions Who are our customers What is our core competency? A company's mission, goals, and objectives must be properly implemented to achieve and communicate the desired corporate Identity a company's unique symbols, personalities, and philosophies An organization's goals and objectives, derived from its mission statement, guide its planning efforts Goals focus on the end results sought by the organization Developing Corporate and Business-Unit Strategies Strategic planning often begins at the corporate level and proceeds downward to the business-unit and marketing levels. However, organizations are increasingly developing strategies and conducting strategic planning that moves in both directions to seek expertise from multiple levels Corporate strategy should be developed with the organization's overall mission in mind, business-unit Strategy should be consistent with corporate strategy, and marketing strategy should be consistent with both. Corporate Strategies Corporate strategy determines the means for utilizing resources in the functional areas of marketing, production, finance, research and development (R&D), and human resources to achieve the organization's Corporate strategy planners are concerned with broad issues such as organizational culture, competition differentiation, diversification, interrelationships among business units, and environmental and social issues They attempt to match the resources of the organization with the opportunities and threats in the environment Business-init Strategies Pg. 9 owned die made who An UNGEN Sweety Mb A strategic business unit (SBU) is a division, product line, or other profiteer within the parent Stegle planners should recognize the performance capabilities of each SBU and carefully Resources among the division A market is a group of individuals and/or organizations that have needs for products in a products and have the ability, willingness, and authority to purchase those products. The percentage of a market that actually buys a specific product from a particular company is referred to as that products for business unit's market share The market wil market share matrix, developed by the Boston Consulting Group (BCG).is philosophy that a products market growth rate and its market share are important considerations in determining its marketing strategy All the organization's SBUs and products are integrated into a single matrix and compared and evaluated to determine appropriate strategies for individual products and overall portfolio strategies Mange this model to determine and classify each product's expected future can contribution and future cash out The CG analytical approach is more of a diagnostic tool than a guide for making to press This model is an organization's products into four basic types. Stars have a dominant share of the market and good prospects for prowth, they were cash they De to finance growth, add capacity, and ince market share Cash-cows have a dominant share of the market but low prospects for growth, they wypically more caththa is required to maintain market share. Example Procter & Gamble's Bounty Paper Dogs have a chordinate share of the market and low prospects for growth, the products wished markets Example: Panasonie's cathode ray tube television Question marks, sometimes called "problem children." have small share of a growing red may require a large amount of cash to build market share The long-term health of an organisation depends on having a range of products, so that and provide aceptable prota) and others that we coupon Competitive Growth Strategies Based on analyses of each product or business unit, afirmay choose one or more competitive Market penetration is a strategy of increasing sales in current markets with current products Market development is a strategy of increasing sales of current products in new markets Market developmental curs when a company leoduce its products into interminal markets for the line Product development is a strategy of increasing sales by improving pecvent products or developing new products for current markets (eg automotive industry) Diversification is a strategy of developing tww products to be sold in new markets. Diversification allows finns to make bene and wider use of their managerial, technological and financial resources Divcnification also offers some advantages over single business Suns because it allows firms to spread their risk across a number of markets. Assessing Organizational Resources and Opportunities The stupid planning process begins with an analysis of the marketing environment, which can influence ar organization's goals, resources, and opportunities. Strategic planning must assess an organization's available financial and human resources and capabilities ad how these resources are likely to change over time pg. 10 compar can includer setion and loyalty Reputation in names Core competencies, things a femdoes extremely well sometimes so well that they can give the company an advantage over its competition Analysis of the marketing environment also includes identifying opportunities in the marketplace, which requires a solid understanding of the company's industry, A market opportunity exists when the right combination of circumstances and timing permits an organization to take action to reach a particular target market Strategie windows are temporary periods of optimal fit between the key requirements of a market and the particular capabilities of a firm competing in that market A company is said to have a competitive advantage when it matches a core competency to opportunities has discovered in the marketplace SWOT Analysis A SWOT analysis is one tool marketers uses to assess an organization's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Strengths and weaknesses are internal factors that can influence an organization's ability to satisfy its target markets Strengths refer to competitive advantages or core competencies that give the organization an advantage in meeting the needs of its target markets. Weaknesses are internal limitations a company faces in developing or implementing a marketing strategy Both strengths and weaknesses should be examined from a customer perspective, Opportunities and threats affect all organizations within an industry, market, or geographic region because they exist outside of and independently of the company Opportunities refer to favourable conditions in the environment that could produce rewards for the Organization if acted upon Threats refer to barriers that could prevent the organization from reaching its objectives When an organization matches internal strengths to extemal opportunities, it creates competitive advantages in meeting the needs of its customers. Companies should attempt to convert internal weaknesses into strengths and external threats into opportunities First-Mover and Late-Mover Advantage A first-mover advantage is the ability of an innovative company to achieve long-term competitive advantages by being the first to offer a certain product in the marketplace Benefits include building a reputation as a market leader, reducing competition, establishing brand loyalty and protecting trade secrets Risks?nclude high costs associated with creating and marketing a new product, slower than predicted sales growth. And the potential for product failure. Alate-mover advantage is the ability of later market entrants to achieve long-term competitive advantages by not being the first to offer a certain product in a marketplace. 02771 I. Matuleht is panirantamanna The Mag jewed Mr Sir podpredenti -: en WOT antes and with completo Ayshe en afstand the coming is that will me market Mathew Select the Tear Seneste pe may be the most importadocions company make the policial for regio There must be chosen before the nation can adaptarting mix to meet the ' ial ter When exploring target niks, marketing managers try to be how entry could affect the cast, and profiles Mariehold determine whether target market aligns with the company's overall bytes Merki should losses whether the company has the resources to develop the right marketing mixte the particular target market. The time and me of competitors is also a com Creating the Marketing Mises The madeininga maringonly as pood as the one's Understanding comes from carefis-depth into demons as well as need preferences and behavior with respect to product design ide distribution, and promotion Marketing mix decisies held be consistent with the best and corporate strategies well lexible enough to permit the centation to her the main response to changes in mu conditional competition, and customer needs Liding the marketing mix as a tools, a company can deltow it will coves sastable competitive data pe: 12 ulty in convincing 3 Strategies sustainable competitive advantage is one that the competition cannot copy in the foreseeable future III. Managing Marketing Implementation Marketing implementation is the process of putting marketing strategies into action Organizing the Marketing Unit The structure and relationships of a marketing unit, including establishing lines of authority and communication that connect and coordinate individuals, strongly affect marketing activities. Companies that truly adopt the marketing concept develop an organizational culture that is based on a shar set of beliefs that places the customer's needs at the center of decisions about strategy and operation Firms must decide whether operations should be centralized or decentralized, a choice that directly impacts marketing decision making and strategy In a centralized organization, top-level managers delegate little authority to lower levels. Most traditional organizations are highly centralized In a decentralized organization, decision-making authority is delegated as fur down the chain of command possible. Decentralized authority allows the company to adapt more rapidly to customer needs. Organizing marketing activities to align with the overall strategic marketing approach enhances Organizational efficiency and performance A marketing department should clearly outline the hierarchical relationships between personnel and who is responsible for performing certain activities and making decisions Coordinating and Communicating To achieve marketing objectives, marketing managers must coordinate actions within and across departments, firms, and external organizations to ensure that marketing activities align with other functions of the firm Marketing managers can improve coordination by making each employee aware of how his or her job relatos to others and how his or her actions contribute to the achievement of marketing objectives Marketing managers must be in clear communication with the firm's upper-level management to ensure that they are aware of the firm's goals and achievements and that marketing activities are consistent with the company's overall goals and strategies. Communication that flows upward from the frontlines of the organization to higher level marketing managers provides important information about the needs of customers and employees Training provides employees with a forum to learn and ask questions, and results in employees who are empowered and can be held accountable for their performance Information systems expedite communications within and between departments and support other activities. such as allocating scarce organizational resources, planning, budgeting, sales analyses, performance evaluations, and report preparation Managers must address their employees' needs and then develop motivational methods that will help employees satisfy those needs. Employee rewards should be tied to organizational goals. A firm can motivate its workers by directly linking pay with performance, informing workers how their performance affects department and corporate results, following through with appropriate and competitive compensation, implementing a flexible benefits program, and adopting a participative management approsch Manage should also use a variety of other tools, including nonfinancial rewards such as prestige on recognition, job autonomy, skill variety, task significance, increased feedback, or even a more relaxed dos Pg. 13 Marketing Cost Analys Marketing costs marketing efforts By pinpointing exactly unprofitable customers, accounts Supernatud marketing implementation requires that employous know the specific activities for which responsible and the timetable for completing each activity Establishing an implementation timetable involves several steps Identifying the activities to be performed Determining the time required to complete each activity Separating the activities to be performed in sequence from those to be performed simultaneously Organizing the activities in the proper order Augning responsibility for completing each activity to one or more employees, teams, or managers Since scheduling can be a complicated task, some organizations use sophisticated computer programs to plan the timing of marketing activities IV. Evaluating Marketing Strategies Strategie performance evaluation consists of establishing performance standards, measuring actual performance, comparing actual performance with established standards, and modifying the marketing strategy, if needed Establishing Performance Standards performance standard is an expected level of performance against which actual performance can be compared, such as a reduction in customer complaints, a sales quota, or an increase in new customer Marketing objectives di


 please help me summarize this chapter
please help me summarize this chapter 





 summarize this chapter please
summarize this chapter please