Question: please help me with my test ! complete a-n using Beard, Marianna J numbers . it is due on the 27th Microsoft Word - C...
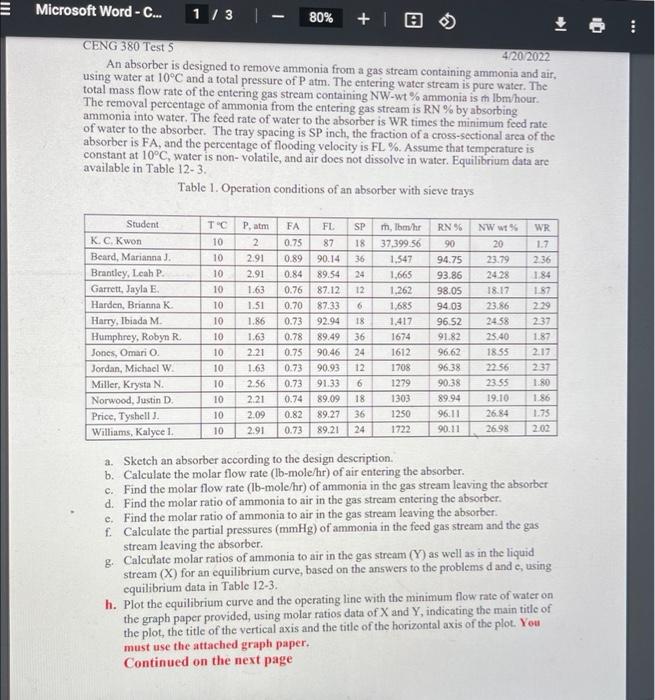
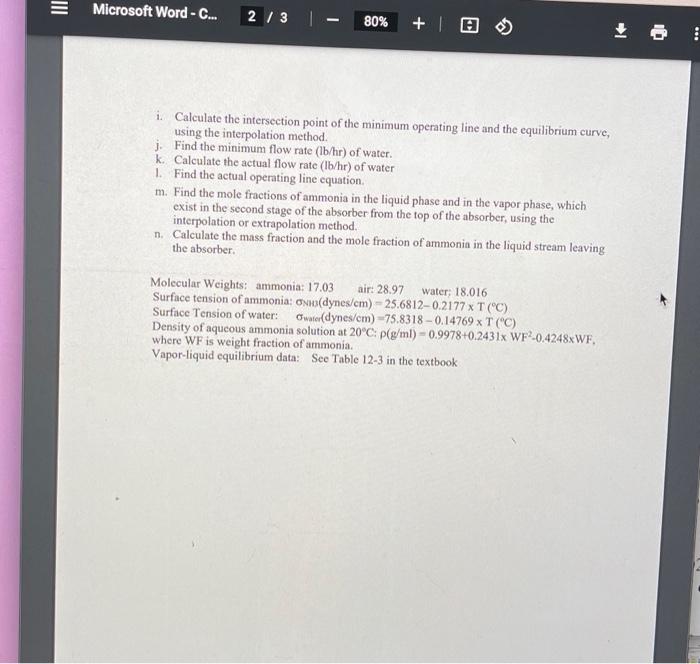
Microsoft Word - C... 1/3 80% + 10 . CENG 380 Test 5 4202022 An absorber is designed to remove ammonia from a gas stream containing ammonia and air, using water at 10C and a total pressure of Patm. The entering water stream is pure water. The total mass flow rate of the entering gas stream containing NW-wt% ammonia is h Ibm/hour. The removal percentage of ammonia from the entering gas stream is RN % by absorbing ammonia into water. The feed rate of water to the absorber is WR times the minimum feed rate of water to the absorber. The tray spacing is SP inch, the fraction of a cross-sectional area of the absorber is FA, and the percentage of flooding velocity is FL %. Assume that temperature is constant at 10C, water is non-volatile, and air does not dissolve in water. Equilibrium data are available in Table 12-3. Table 1. Operation conditions of an absorber with sieve trays Patm S- T' 10 10 10 SP 18 36 24 12 10 6 Student KC Kwon Beard, Marianna J. Brantley, Leah P. Garrett, Jayla E Harden, Brianna K Harry, Ibiada M. Humphrey, Robyn R Jones, Omario Jordan, Michael W Miller, Krysta N. Norwood, Justin D Price, Tyshell. Williams, Kalye 1 ololololololololols 10 10 10 2 2.91 2.91 1.63 1.51 1.86 1.63 2.21 1.63 2.56 2.21 2.09 2.91 FA 0.75 0.89 0.84 0.76 0.70 0.73 0.78 0.75 0.73 0.73 0.74 0.82 0.73 FL 87 90.14 89.54 87.12 87.33 92.94 89.49 90.46 90.93 91.33 89.09 89.27 89.21 18 36 24 12 m, Thehr 37,399.56 1.547 1,665 1.262 1,685 1,417 1674 1612 1708 1279 1303 1250 1722 RN 96 90 94.75 93.86 98.05 94.03 96.52 91.82 96.62 96.38 90.38 89.94 96,11 90.11 NW W 20 23.79 24.28 18.17 23.86 2458 25.40 1855 22.56 23.55 19.10 26.84 26.98 WR 1.7 236 1.84 157 2.29 237 1.87 2.17 237 1.80 1 86 1.75 2.02 10 10 10 10 6 18 36 24 10 10 a. Sketch an absorber according to the design description b. Calculate the molar flow rate (lb-mole/hr) of air entering the absorber. c. Find the molar flow rate (lb-mole/hr) of ammonia in the gas stream leaving the absorber d. Find the molar ratio of ammonia to air in the gas stream entering the absorber. e. Find the molar ratio of ammonia to air in the gas stream leaving the absorber. f. Calculate the partial pressures (mmHg) of ammonin in the feed gas stream and the gas stream leaving the absorber. g. Calculate molar ratios of ammonia to air in the gas stream (Y) as well as in the liquid stream (X) for an equilibrium curve, based on the answers to the problems and c, using equilibrium data in Table 12-3. h. Plot the equilibrium curve and the operating line with the minimum flow rate of water on the graph paper provided, using molar ratios data of X and Y, indicating the main title of the plot, the title of the vertical axis and the title of the horizontal axis of the plot. You must use the attached graph paper. Continued on the next page Microsoft Word - C... 2 / 3 80% +1 i. Calculate the intersection point of the minimum operating line and the equilibrium curve, using the interpolation method. j. Find the minimum flow rate (1b/hr) of water. k. Calculate the actual flow rate (lb/hr) of water 1. Find the actual operating line equation m. Find the mole fractions of ammonia in the liquid phase and in the vapor phase, which exist in the second stage of the absorber from the top of the absorber, using the interpolation or extrapolation method. n. Calculate the mass fraction and the mole fraction of ammonin in the liquid stream leaving the absorber Molecular Weights: ammonia: 17.03 air: 28.97 water: 18.016 Surface tension of ammonia: oniodynes/cm) - 25.6812-0.2177 x T (C). Surface Tension of water: Owedynes/cm) -75.8318 -0.14769x T (C) Density of aqueous ammonia solution at 20C: p(g/ml) - 0.9978+0.2431x WF2-0.4248xWF, where WF is weight fraction of ammonia Vapor-liquid equilibrium data: See Table 12-3 in the textbook
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


