Question: Please help me with this math problem involving Euler's method. 5. We have seen that the error in approximating the solution to an initial value
Please help me with this math problem involving Euler's method.

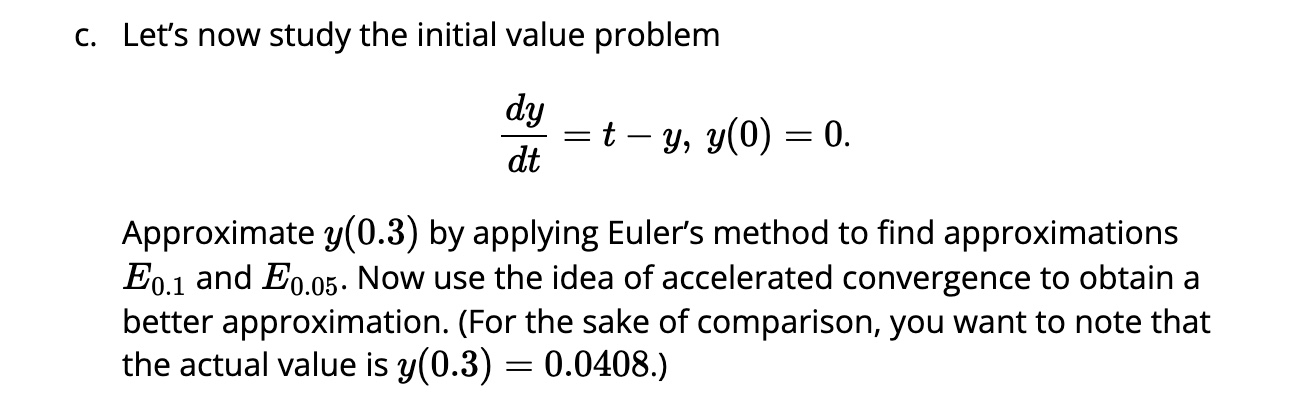
5. We have seen that the error in approximating the solution to an initial value problem is proportional to At. That is, if Ea; is the Euler's method approximation to the solution to an initial value problem at , then for some constant of proportionality K. In this problem, we will see how to use this fact to improve our estimates, using an idea called accelerated convergence. a. We will create a new approximation by assuming the error is exactly proportional to At, according to the formula y(t) Ear = KAt Using our earlier results from the initial value problem dy/dt = y and y(0) = 1 with At = 0.2 and At = 0.1, we have y(1) 2.4883 = 0.2K y(1) 2.5937 = 0.1K. This is a system of two linear equations in the unknowns y(1) and K. Solve this system to find a new approximation for y(1). (You may remember that the exact value is y(1) = e = 2.71828... ) b. Use the other data, Eq g5 = 2.6533 and Ej go5 = 2.6851 to do similar work as in (a) to obtain another approximation. Which gives the better approximation? Why do you think this is? c. Let's now study the initial value problem dy =1- 0) =0. Approximate y(0.3) by applying Euler's method to find approximations Ey1 and Ejg5. Now use the idea of accelerated convergence to obtain a better approximation. (For the sake of comparison, you want to note that the actual value is y(0.3) = 0.0408.)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


