Question: please help solve and show work Interest rate risk and bond price changes Apex Corp. has two outstanding bond issues. One issue consists of 6%
please help solve and show work

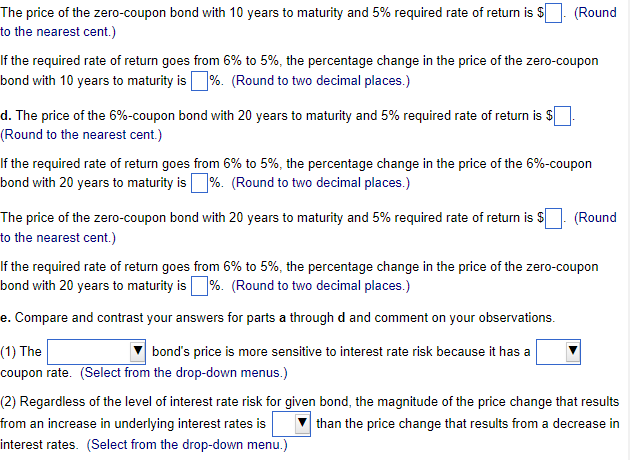
Interest rate risk and bond price changes Apex Corp. has two outstanding bond issues. One issue consists of 6% annual coupon bonds and the other issue consists of zero-coupon bonds. For each bond issue, calculate the bond prices and percentage change in prices when the required rate of return changes from 6% to 7%. a. Ten years to maturity and the required rate of return goes from 6% to 7%. b. Twenty years to maturity and the required rate of return goes from 6% to 7%. c. Ten years to maturity and the required rate of return goes from 6% to 5%. d. Twenty years to maturity and the required rate of return goes from 6% to 5%. e. Compare and contrast your answers for parts a through d and comment on your observations. a. The price of the 6%-coupon bond with 10 years to maturity and 6% required rate of return is $ (Round to the nearest cent.) The price of the 6%-coupon bond with 10 years to maturity and 7% required rate of return is $ (Round to the nearest cent.) If the required rate of return goes from 6% to 7%, the percentage change in the price of the 6%-coupon bond with 10 years to maturity is \%. (Round to two decimal places.) The price of the zero-coupon bond with 10 years to maturity and 6% required rate of return is $. (Round to the nearest cent.) The price of the zero-coupon bond with 10 years to maturity and 7% required rate of return is $. (Round to the nearest cent.) If the required rate of return goes from 6% to 7%, the percentage change in the price of the zero-coupon bond with 10 years to maturity is \%. (Round to two decimal places.) b. The price of the 6%-coupon bond with 20 years to maturity and 6% required rate of return is $ (Round to the nearest cent.) The price of the 6%-coupon bond with 20 years to maturity and 7% required rate of return is $ (Round to the nearest cent.) If the required rate of return goes from 6% to 7%, the percentage change in the price of the 6%-coupon bond with 20 years to maturity is %. (Round to two decimal places.) The price of the zero-coupon bond with 20 years to maturity and 6% required rate of return is $. (Round to the nearest cent.) The price of the zero-coupon bond with 20 years to maturity and 7% required rate of return is $. (Round to the nearest cent.) If the required rate of return goes from 6% to 7%, the percentage change in the price of the zero-coupon bond with 20 years to maturity is %. (Round to two decimal places.) c. The price of the 6%-coupon bond with 10 years to maturity and 5% required rate of return is $ (Round to the nearest cent.) The price of the zero-coupon bond with 10 years to maturity and 5% required rate of return is $. (Round to the nearest cent.) If the required rate of return goes from 6% to 5%, the percentage change in the price of the zero-coupon bond with 10 years to maturity is %. (Round to two decimal places.) d. The price of the 6%-coupon bond with 20 years to maturity and 5% required rate of return is $ (Round to the nearest cent.) If the required rate of return goes from 6% to 5%, the percentage change in the price of the 6\%-coupon bond with 20 years to maturity is \%. (Round to two decimal places.) The price of the zero-coupon bond with 20 years to maturity and 5% required rate of return is $. (Round to the nearest cent.) If the required rate of return goes from 6% to 5%, the percentage change in the price of the zero-coupon bond with 20 years to maturity is \%. (Round to two decimal places.) e. Compare and contrast your answers for parts a through d and comment on your observations. (1) The bond's price is more sensitive to interest rate risk because it has a coupon rate. (Select from the drop-down menus.) (2) Regardless of the level of interest rate risk for given bond, the magnitude of the price change that results from an increase in underlying interest rates is than the price change that results from a decrease in interest rates. (Select from the drop-down menu.)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


