Question: please help with 2 and 7. also did i do 6 correct? 2. Price controls in the apple market The following graph depicts the market
please help with 2 and 7. also did i do 6 correct?
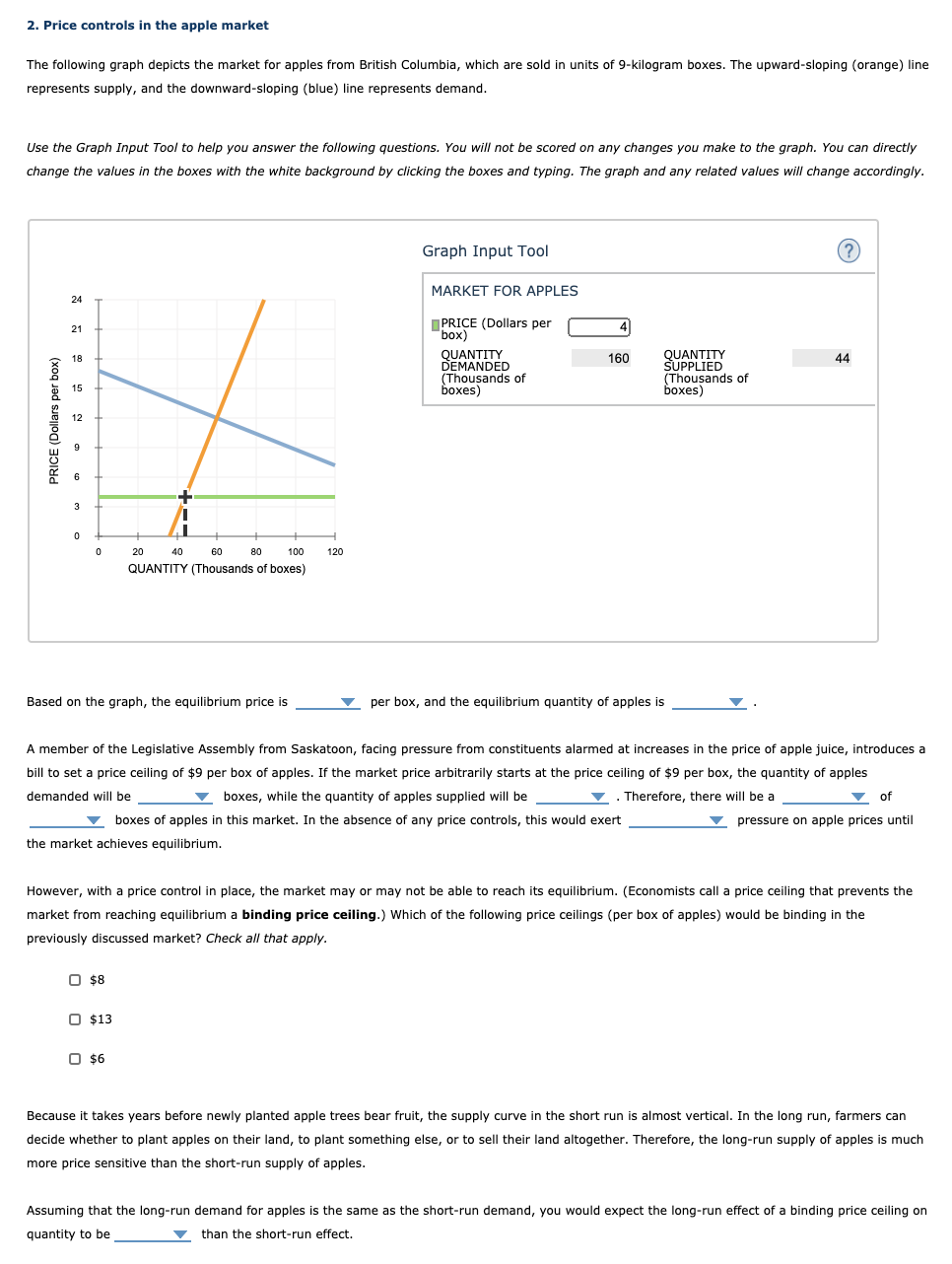
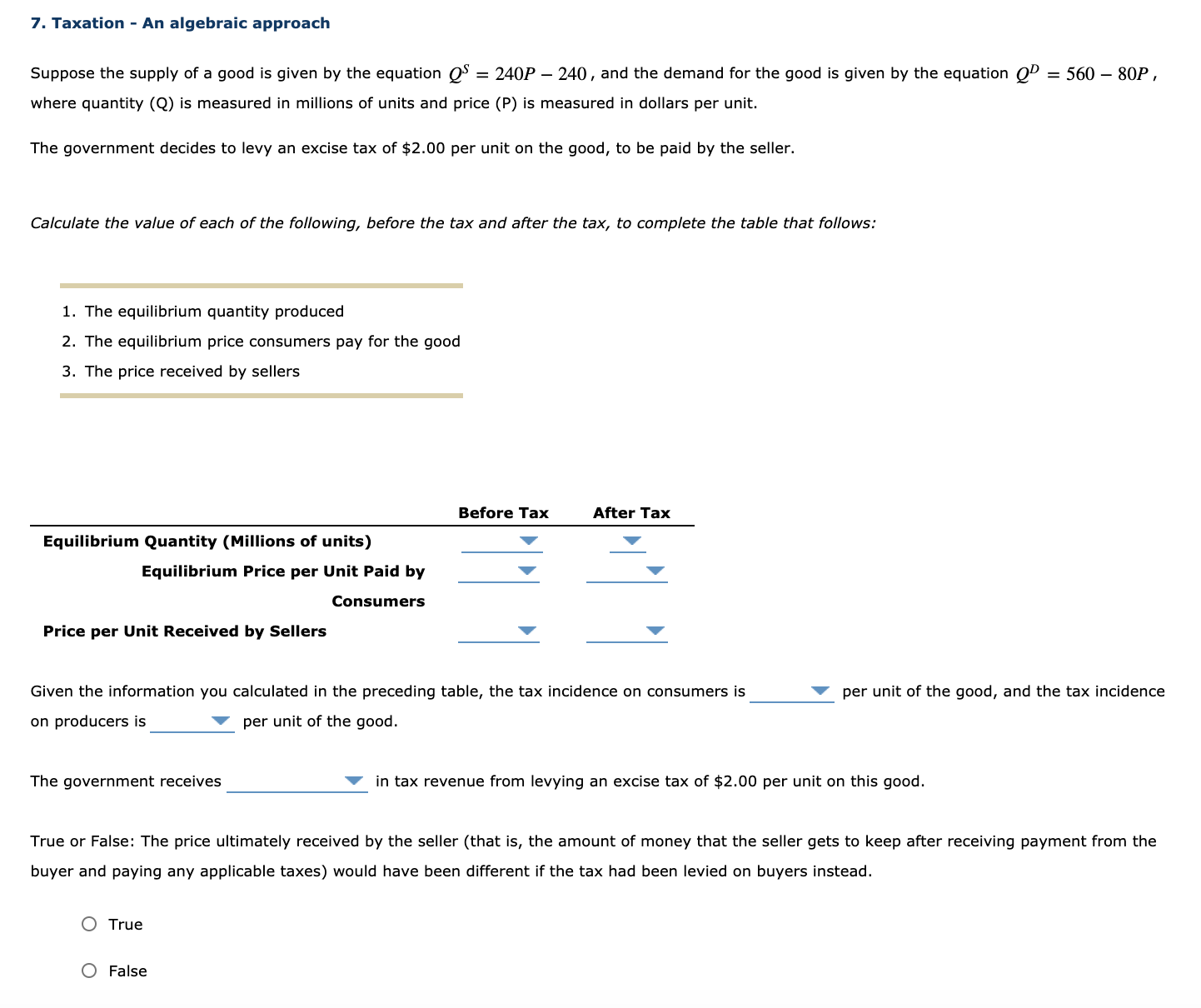
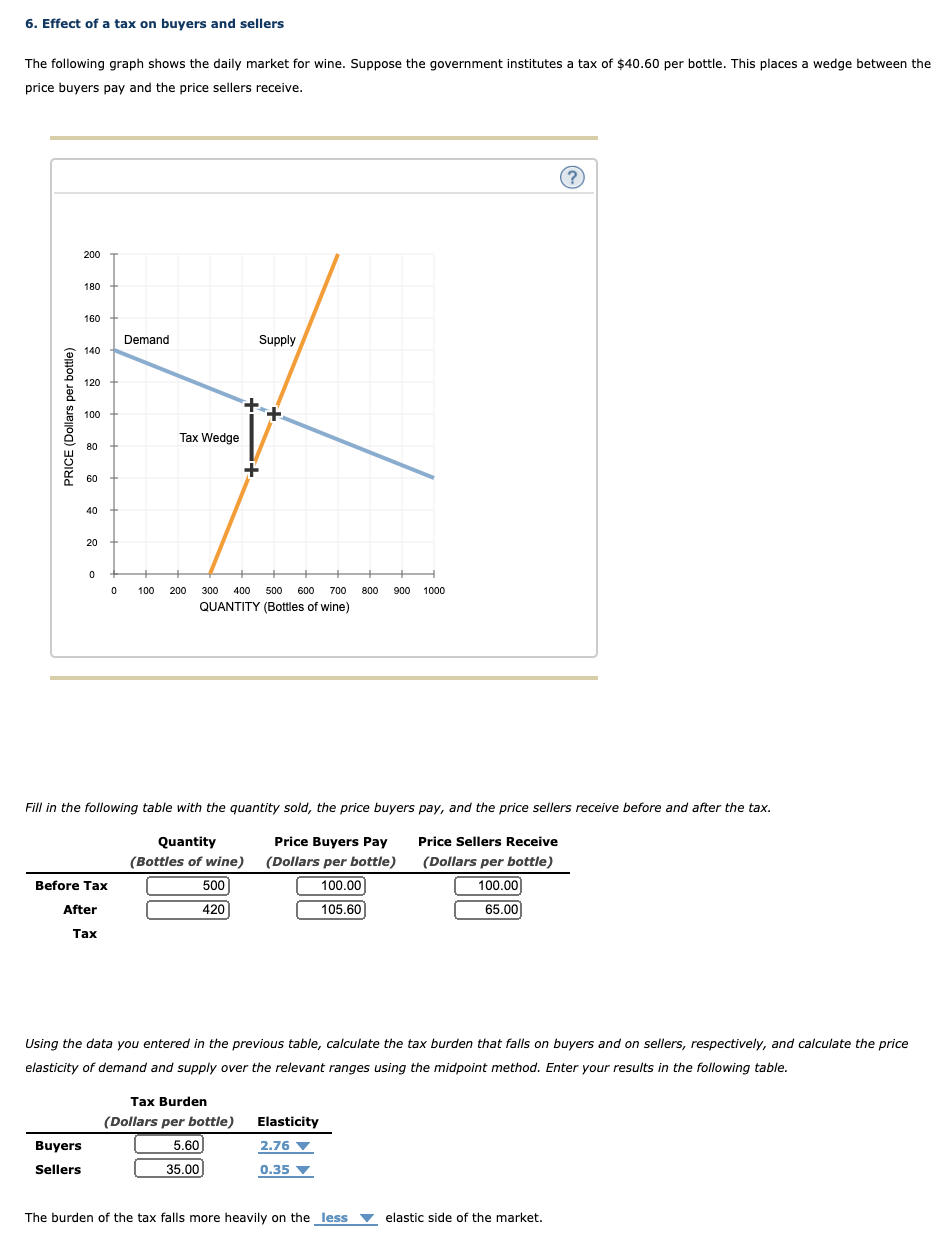
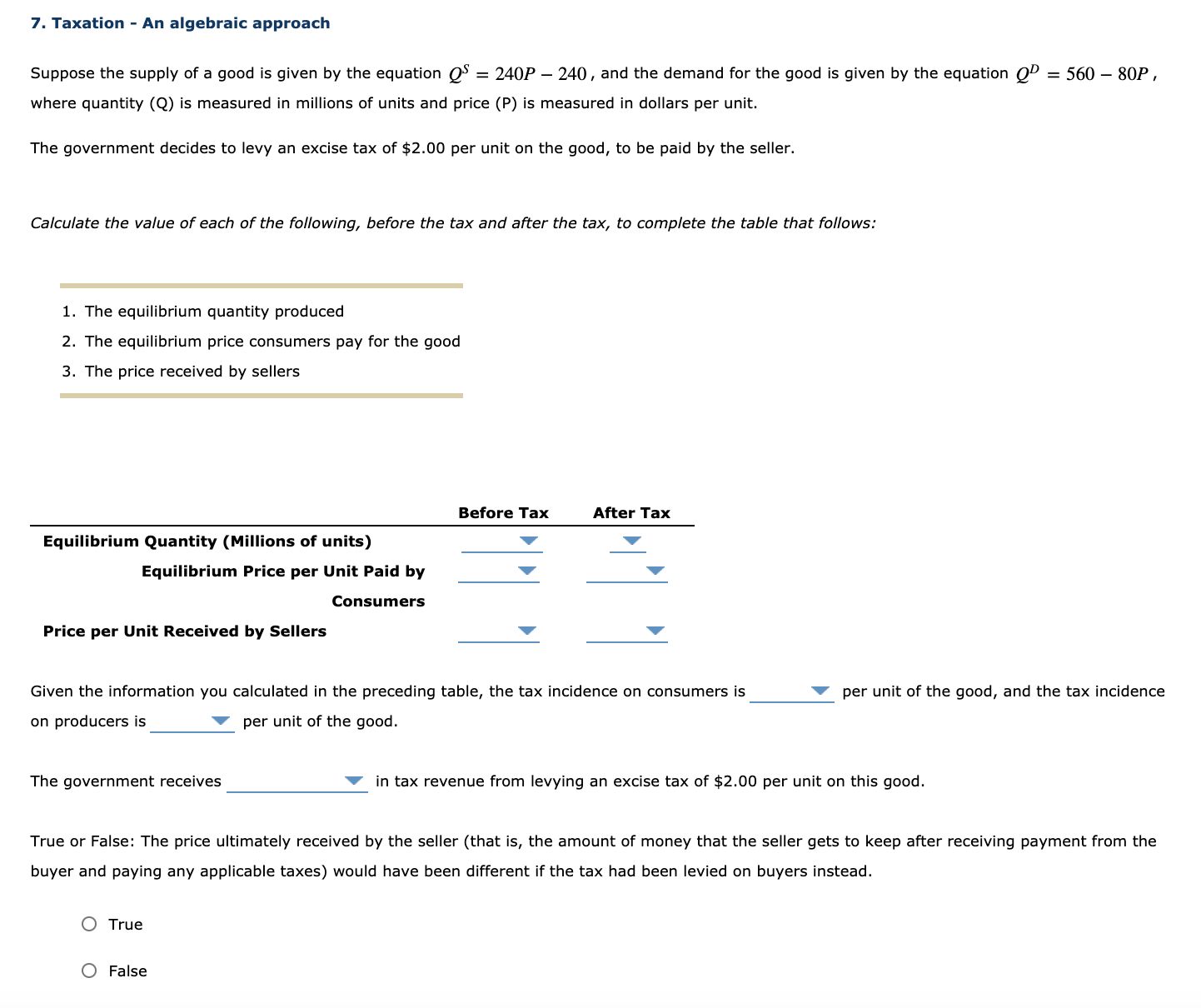
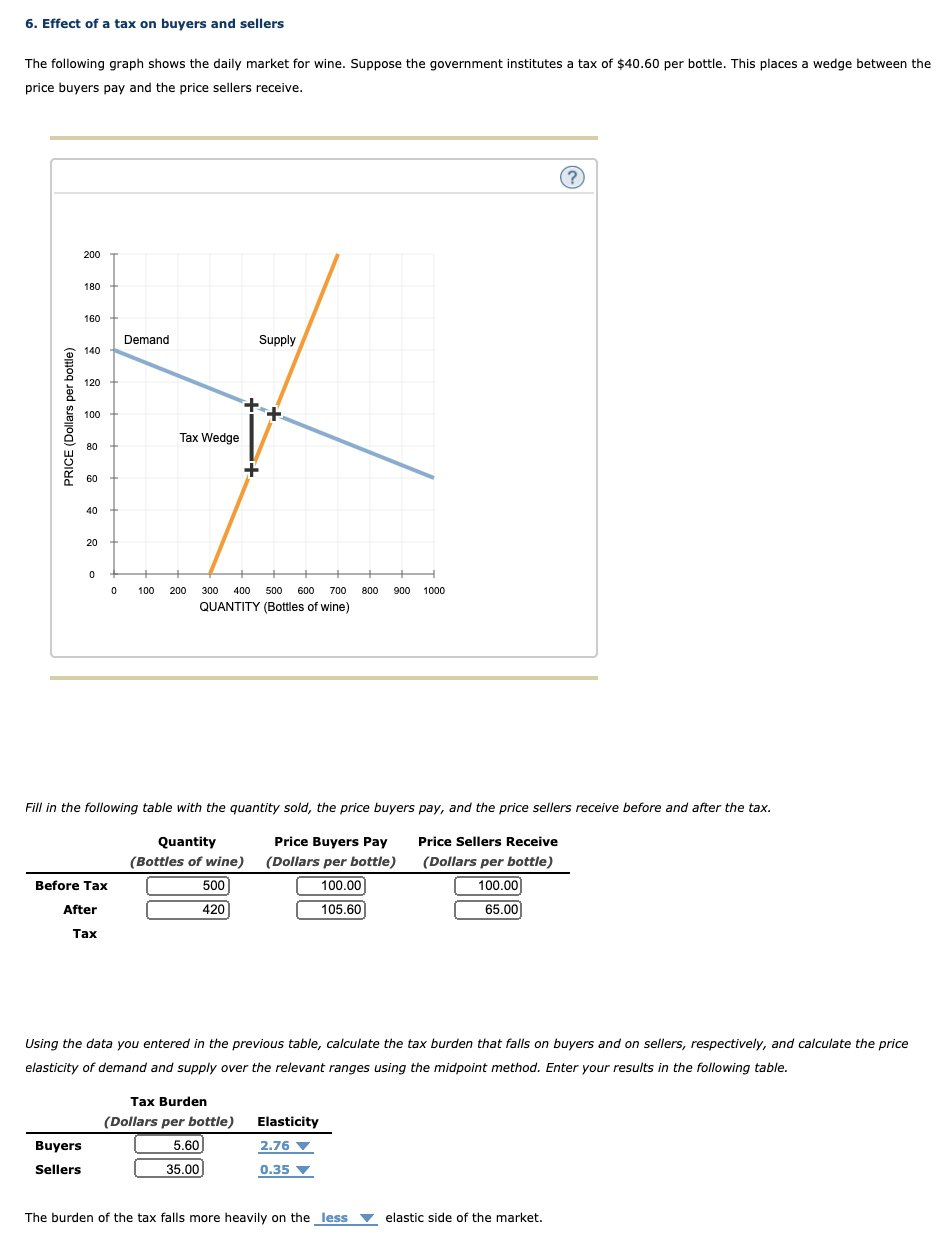
2. Price controls in the apple market The following graph depicts the market for apples from British Columbia, which are sold in units of 9-kilogram boxes. The upward-sloping (orange) line represents supply, and the downward-sloping (blue) line represents demand. Use the Graph Input Tool to help you answer the following questions. You will not be scored on any changes you make to the graph. You can directly change the values in the boxes with the white background by clicking the boxes and typing. The graph and any related values will change accordingly. Graph Input Tool ? MARKET FOR APPLES PRICE (Dollars per "box) PRICE (Dollars per box) QUANTITY DEMANDED 160 QUANTITY (Thousands of SUPPLIED 44 boxes (Thousands of boxes) w 20 40 60 80 100 120 QUANTITY (Thousands of boxes) Based on the graph, the equilibrium price is Vper box, and the equilibrium quantity of apples is A member of the Legislative Assembly from Saskatoon, facing pressure from constituents alarmed at increases in the price of apple juice, introduces a bill to set a price ceiling of $9 per box of apples. If the market price arbitrarily starts at the price ceiling of $9 per box, the quantity of apples demanded will be V boxes, while the quantity of apples supplied will be V . Therefore, there will be a of boxes of apples in this market. In the absence of any price controls, this would exert pressure on apple prices until the market achieves equilibrium. However, with a price control in place, the market may or may not be able to reach its equilibrium. (Economists call a price ceiling that prevents the market from reaching equilibrium a binding price ceiling.) Which of the following price ceilings (per box of apples) would be binding in the previously discussed market? Check all that apply. O $8 O $13 O $6 Because it takes years before newly planted apple trees bear fruit, the supply curve in the short run is almost vertical. In the long run, farmers can decide whether to plant apples on their land, to plant something else, or to sell their land altogether. Therefore, the long-run supply of apples is much more price sensitive than the short-run supply of apples. Assuming that the long-run demand for apples is the same as the short-run demand, you would expect the long-run effect of a binding price ceiling on quantity to be than the short-run effect.7. Taxation - An algebraic approach Suppose the supply of a good is given by the equation Q5 = 2,40P 240 , and the demand for the good is given by the equation Q\" = 560 SOP , where quantity (Q) is measured in millions of units and price (P) is measured in dollars per unit. The government decides to levy an excise tax of $2.00 per unit on the good, to be paid by the seller. Calcufate the value of each of the foowing, before the tax and after the tax, to compiete the table that foows: 1. The equilibrium quantity produced 2. The equilibrium price consumers pay for the good 3. The price received by sellers Before Tax After Tax Equilibrium Quantity (Millions of units) '7 '7 Equilibrium Price per Unit Paid by 'I' '7 Consumers Price per Unit Received by Sellers '7 V Given the information you calculated in the preceding table, the tax incidence on consumers is '7 per unit of the good, and the tax incidence on producers is Y per unit of the good. The government receives Y in tax revenue from levying an excise tax of $2.00 per unit on this good. True or False: The price ultimately received by the seller (that is, the amount of money that the seller gets to keep after receiving payment from the buyer and paying any applicable taxes) would have been different if the tax had been levied on buyers instead. 0 True 0 False 6. Effect of a tax all buyers and sellers The following graph shows the daily market for wine. Suppose the government institutes a tax of $40.60 per bottle. This places a wedge between the price buyers pailr and the price sellers receive. E i 5 a g E olnomoauowosuosuomauomolmn QUANTITY (Bottles oi wine} Fill in the following table with the quantity sold, the price buyers pay, and the price sellers receive before and alter the tax. Quantity Price Buyers Pay Price Sellers Receive (Bottles of wine) (Dollars per bottle) (Dollars per bottle) mmm m Tax Using the data you entered in the previous table, calculate the tax burden that falls on buyers and on sellers, respectively, and calwiate the price elasticity of demand and supply over the relevant ranges using the midpoint method. Enter your results in the following table. Tax Burden (Dollars per bottle) Elasticity Buyers m 235 v Sellers 0.35 v The burden of the tax falls more heavily on the less V elastic side of the market
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


