Question: Please help with A. creating a horizontal analysis of John Doe's case from accounts information provided. B. what does a horizontal analysis reveals (please show
Please help with
A. creating a horizontal analysis of John Doe's case from accounts information provided.
B. what does a horizontal analysis reveals (please show the formulas and calculations)
C. recommendation on which financial accounts John should reevaluate
After 20 years of service at his prior job, John was burned out and considering a change. While Christmas shopping, he was talking with a retail owner at a local mall and was informed that most retail stores mark up their prices 200%. John decided to quit his job and purchase and operate a retail toys and hobby shop. So, after finding the right opportunity, in January of year 1, he purchased a small store and inventory of toys / games for $300,000. He financed the purchase through the local bank, which loaned him 80% of the money at 7% for 10 years and required John to personally finance the other 20%. Since he is the owner of a small business, he has been operating it as a sole proprietor and not issued any stock. He is not paid a salary, but draws money out as needed. He has a full-time bookkeeper who handles all his books and accounting functions. There are two full-time sales clerks that work in the store and stock inventory in storage or on the shelves as it is delivered. All three of these employees have worked for him since he opened his business. John started each of them out at about $25,000 per year and has given each of them raises every year (approximately 3% per year). Additionally, if the company has a good year (net income), he rewards the employees by paying each of them a bonus of 3% of the net income amount. The bonuses are paid in the following year (February).
For years 1 and 2, he had some external accountants prepare a compilation report. For years 3, 4, and 5, he had a different set of external accountants prepare the compilation reports. The compilation reports state that the books are kept on an accrual basis of accounting according to GAAP and that Property Equipment is capitalized at cost and depreciated using the straight-line method over the useful life of the property (Equipment 3 years, Furniture 5 years and Building 15 years).
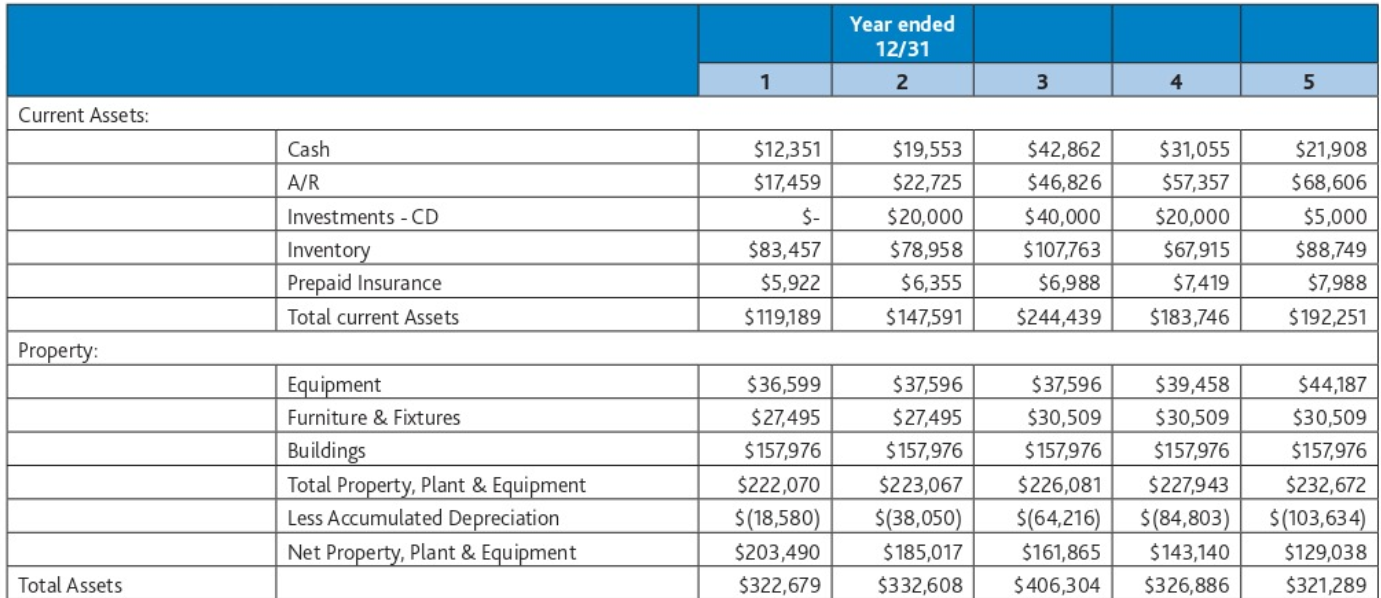
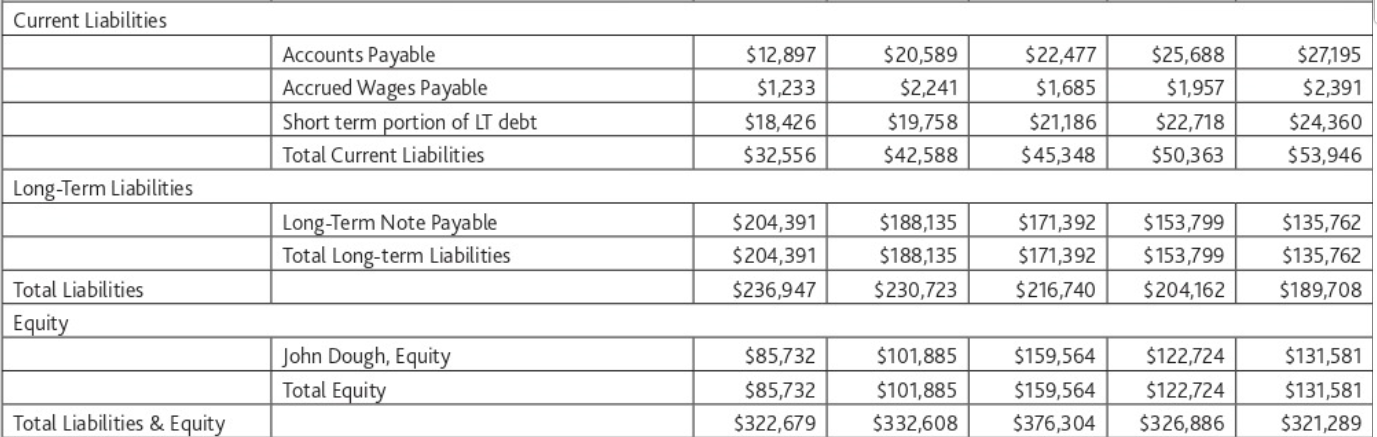
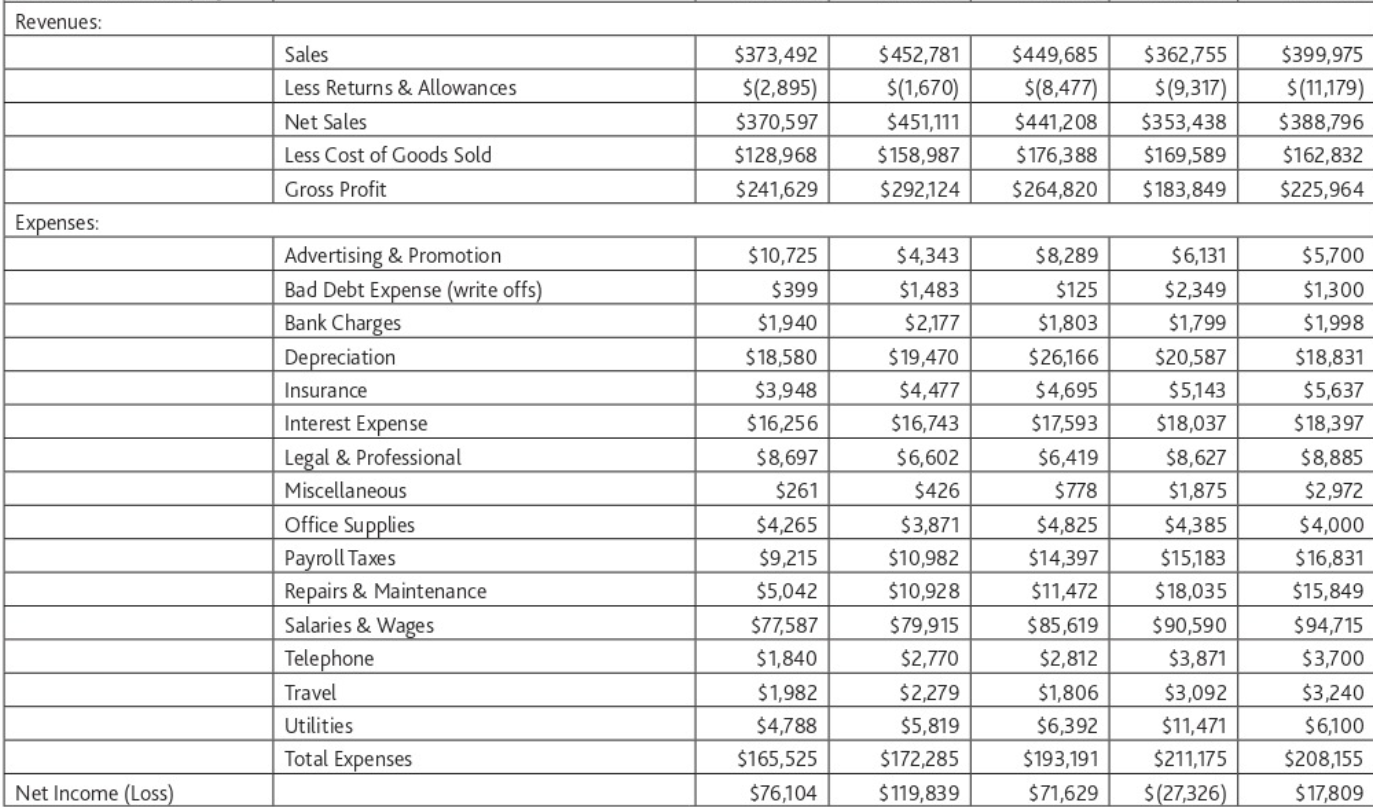
Current Assets: Property: Total Assets Cash A/R Investments - CD Inventory Prepaid Insurance Total current Assets Equipment Furniture & Fixtures Buildings Total Property, Plant & Equipment Less Accumulated Depreciation Net Property, Plant & Equipment 1 $12,351 $17,459 $- $83,457 $5,922 $119,189 $36,599 $27,495 $157,976 $222,070 $(18,580) $203,490 $322,679 Year ended 12/31 2 3 4 5 $19,553 $42,862 $31,055 $21,908 $22,725 $46,826 $57,357 $68,606 $20,000 $ 40,000 $20,000 $5,000 $78,958 $107,763 $67,915 $88,749 $6,355 $6,988 $7,419 $7,988 $147,591 $244,439 $183,746 $192,251 $37,596 $37,596 $39,458 $44,187 $27,495 $30,509 $30,509 $30,509 $157,976 $157,976 $157,976 $157,976 $223,067 $226,081 $227,943 $232,672 $(38,050) $(64,216) $(84,803) $(103,634) $161,865 $143,140 $129,038 $185,017 $332,608 $406,304 $326,886 $321,289 Current Liabilities Long-Term Liabilities Total Liabilities Equity Total Liabilities & Equity Accounts Payable Accrued Wages Payable Short term portion of LT debt Total Current Liabilities Long-Term Note Payable Total Long-term Liabilities John Dough, Equity Total Equity $12,897 $1,233 $18,426 $32,556 $204,391 $204,391 $236,947 $85,732 $85,732 $322,679 $20,589 $2,241 $19,758 $42,588 $188,135 $188,135 $230,723 $101,885 $101,885 $332,608 $22,477 $25,688 $1,685 $1,957 $21,186 $22,718 $45,348 $50,363 $171,392 $153,799 $171,392 $153,799 $216,740 $204,162 $159,564 $122,724 $159,564 $122,724 $376,304 $326,886 $27,195 $2,391 $24,360 $53,946 $135,762 $135,762 $189,708 $131,581 $131,581 $321,289 Revenues: Expenses: Net Income (Loss) Sales Less Returns & Allowances Net Sales Less Cost of Goods Sold Gross Profit Advertising & Promotion Bad Debt Expense (write offs) Bank Charges Depreciation Insurance Interest Expense Legal & Professional Miscellaneous Office Supplies Payroll Taxes Repairs & Maintenance Salaries & Wages Telephone Travel Utilities Total Expenses $373,492 $(2,895) $370,597 $128,968 $241,629 $10,725 $399 $1,940 $18,580 $3,948 $16,256 $8,697 $261 $4,265 $9,215 $5,042 $77,587 $1,840 $1,982 $4,788 $165,525 $76,104 $452,781 $449,685 $362,755 $(8,477) $(9,317) $(1,670) $451,111 $ 158,987 $292,124 $4,343 $1,483 $2,177 $19,470 $4,477 $16,743 $6,602 $426 $3,871 $10,982 $10,928 $79,915 $2,770 $2,279 $5,819 $172,285 $119,839 $399,975 $(11,179) $441,208 $353,438 $388,796 $176,388 $169,589 $162,832 $264,820 $183,849 $225,964 $8,289 $6,131 $5,700 $125 $2,349 $1,300 $1,803 $1,799 $1,998 $26,166 $20,587 $18,831 $4,695 $5,143 $5,637 $17,593 $18,037 $18,397 $6,419 $8,627 $8,885 $778 $1,875 $2,972 $4,825 $4,385 $4,000 $14,397 $15,183 $16,831 $11,472 $18,035 $15,849 $85,619 $90,590 $94,715 $2,812 $3,871 $3,700 $1,806 $3,092 $3,240 $6,392 $11,471 $6,100 $193,191 $211,175 $208,155 $71,629 $(27,326) $17,809
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


