Question: Please help with step 3. questions 1-5 on the case study Step 1: Please read the following: Making good estimates is the main purpose of
Please help with step 3. questions 1-5 on the case study 




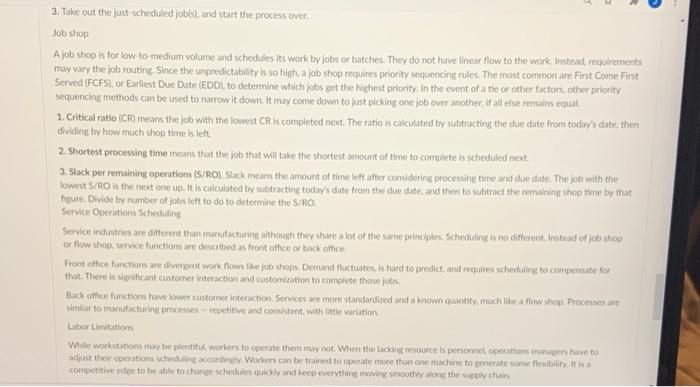
Step 1: Please read the following: Making good estimates is the main purpose of forecasting. Every chay, operation managers make decisions with uncertain outcomes. No one can see the future to know what sales will be, what will break, what new equipment will be needed, or what investments will yield. Yet those decisions need to be made and executed to move the firm forward, What is Forecasting? Forecasting is the art and science of predicting what will happen in the future. Sometimes that is determined by a mathematical method sometimes it is based on the intuition of the operations manager. Most forecasts and end decisions are a combination of both, Forecasting is conducted by what are referred to as time horizons 1. Short range forecast. While it can be up to one year, this forecast is usually used for three months or less. It is used for planning purchases, hiring. job assignments, production levels, and the like. 2. Medium range forecast. This is generally three months to three years. Medium range forecasts are used for sales and production planning budgeting and analysis of different operating plans 3. Long range forecast Generally three years or more in tirnie spon, it Wised for new products, capital expenditures, facilly exparoskon, colocation, and research and development Medium and long range forecasts differ from short ryge forecasts by other characteristics as well 1. Medium and long range forecasts are more comprehensive in nature. They support and guide management decisions in plorining products processes and plants. A new plant can take seven or eight years from the time it is thought of, until it is ready to move into and become functional, 2. Short term forecasts use different methodologies than the others. Most short term forecasts are quantitative in nature and use existing data in mathematical formulas to anticipate immediate future needs and impacts. 3. Short term forecasts are more accurate than medium or long range forecasts. A lot can change in three months, a year, three years and longer Factors that could influence those forecasts change every day, Short term forecasts need to be updated regularly to maintain their effectiveness. Types of Forecasts There are three major types of forecasting, regardless of time horizon, that are used by organizations. 1. Economic forecasts address the business cycle. They predict housing starts, inflation rates, money supplies, and other indicators 2. Technological forecasts monitor rates of technological progress. This keeps organizations abreast of trends and can result in exciting new products New products may require new facilities and equipment, which must be planned for in the appropriate time frame. 3. Demand forecasts deal with the company's products and estimate consumer demand. These are also referred to as sales forecasts, which have multiple purposes. In addition to driving scheduling, production, and capacity, they are also inputs to financial, personnel, and marketing future plans Strategic Importance of Forecasts Operation managers have two tools at their disposal by which to make decisions: actual data and forecasts. The importance of forecasting cannot be underestimated. Take a product forecast and the functions of human resources, capacity and supply chain management, The workforce is based on demand. This includes hiring, training, and lay-off of workers. If a large demand is suddenly thrust upon the organization, training declines and the quality of the product could suffer When the capacity cannot keep up to the demand, the result is independable delivery, loss of customers, and maybe loss of market share. Yet. excess capacity can skyrocket costs Last minute shipping moans high cost. Asking for parts last minute can raise the cost. Most proht margins are slim, which means either of those scenarios can wipe out a profit margin and have an organization operating at cost or at a loss These scenarios are why forecasting is important to an organization. Good operations managers learn how to forecast, to trust the numbers, and to trust their instincts to make the right decisions for their firm. Forecasting System These seven steps can generate forecasts. 1. Determine what the forecast is for 2. Select the items for the forecast. 3. Select the time horizon 4. Select the forecast model type, 5. Gather data to be input into the model 6. Make the forecast 7. Verity and implement the results, Routinely repeat these steps, regardless of the time horizon, to stay abreast of changes in regard to internal and external factors, Forecasting Approaches There are two predominant approaches to forecasting qualitative approach and quantitative analysis. A qualitative approach uses factors such as experience, instinct and emotion while the quantitative analysis relies heavily on mathematics, historical data and casual variables Qualitative methods include: 1. Jury of executive opinion. This is based on the inputs and decisions of high-level experts or management 2. Delphi method. Decision makers, staff, and respondents al meet to develop the forecast Every shareholder in the process provides input. 3. Salesforce composite. Each sales person provides an individual estimate which is reviewed for realism by Mancement, and then combined for a Dit picture view 4. Consumer market survey. This is surveying the prospective customer se to determine demand for existing products and can be used for new products As these methods are based mostly on instinct experience and human input, be cautious of excessive optimism. Quantitative methods are in two categories. Time-series models predict by assuming the future is a function of the pist. Associative models tres Similar historical data inputs and then includes other external variables such as advertising budget, housing, competitor's prices and more Time Series Models Associative Model Naive method Linear regression Moving averages Exponuntial smoothing Trend projection Service Sector Service sector industries have other unique factors to incorporate into their forecasts. Local events can increase the need for hotel stays food, 0% and more. Holidays will have an act. It can be carrowed to hours in the day around popular meal times. Tools for forecasting in this regard include point of sale tracking that computes sales by the quarter hour to establish a pattern for scheduling of personnel for peak times and deliveries or other activities during slower periods Operations Schedulin Operation scheduling focuses on Jobs, Jobs are assigned to individuals for a period of time, or jobs are assigned to workstations for completion. A job in the objective being produced, either a good or a service Schedullrig to meet demand is a critical impect of the operations manager's function in the organization "Scheduling is the process of organizing choosing and trening resource usage to carry out all the activities necessary to produce the desired outputs at the desired times while satisfying a large number of time and relationship constraints among the activities and the resources (Morton and Pentico) There are many ways to schedule and sequence jobs Performance Measures Flow time is a performance measure that tracks the time a job is in the systern. Past due is a measure of by how much time a job missed its due date. These are basic and very general measures to determine how to schedule a job and its priority. There are more refined techniques to aid in that determination 1. Makespan is the total amount of time required to complete a group of jobs. It is calculated by subtracting the starting time of a job from the time of completion from the last job. This technique results in lower inventory and increased delivery speed 2. Total inventory is the total when one adds the scheduled receipts for items, plus the on-hand inventories for these items, and reduces inventory holding costs. 3. Utilization is measured as a ratio of average output rate to maxienum capacity, Maximizing utilization creates slack capachy These are all related somehow. For instance, by minimizing makeson, utilization is maximized. A combination of these techniques can be used to determine sequencint Sequencing There are two types of environments in manufacturing Jobshop and flow shop. The type of environment contributes to scheduling and secuencia decisions and methodology Allow shop uses continuous flow processes. These are most commonly found in medium to high volume production. All the jobs will have a similar flow pattern from workstation to work station. This shop benefits from the makespan technique. The group of jobs will be completed in the minimum amount of time, while maximizing utilization, Johnson's rule is a dominant factor in flow shop scheduling. It is a procedure that demonstrates, with all workstations being equat in capability all jobs should be given the same priority 1. Scan workstation processing times and find the shortest processing time of the jobs waiting processing 2. Schedule the job to the workstation with the shortest processing time. If it's the first workstation, do it as early as possible. It is a workstation further down the line schedule it as late as possible 3. Take out the just scheduled jobs, and start the process over Job shop A job shop is for low-to-medium volume and schedules its work by jobs or batches. They do not have lineat Now to the work. Instead, requirements may vary the job routing Since the unpredictability is so high, a job shop requires priority sequencing rules. The most common are First Come First Served (FCFS), or Earliest Due Date (EDD), to determine which jobs get the highest priority. In the event of a tie or other factors, other priority sequencing methods can be used to narrow it down. It may come down to just picking one job over another, it all else remainis equat 1. Critical ratio (CR) means the job with the lowest CR is completed next. The ratio is calculated by subtracting the due date from today's date, then dividing by how much shop time is left 2. Shortest processing time means that the job that will take the shortest amount of time to complete is scheduled next. 3. Slack per remaining operations (S/RO). Slack means the amount of time left after considering processing time and due date. The job with the lowest S/RO is the next one up. It is calculated by subtracting today's date from the due date, and then to subtract the remaining shop time by that figure Divide by number of jobs left to do to determine the S/RO Service Operations Scheduling Service industries are different than manufacturing although they share a lot or the same principles Scheduling is no different, instead of job shop or how shop, service functionare described as front otice or track office Front office functions are divergent work Nows like job shops Demand fluctuates, is hard to predict, and requires scheduling to compensate for that. There is significant customer interaction and customization to complete those jobs. Bach othce functions have lower antomer interaction Services are more standardized and a known quantity, much like a flow shod Processes are similar to manufacturing processes repetitive and consistent with little variation Labor Limitations While workstations may be plentiful workers to operate them may not When the lacking resource is personnel operations have to adjust their operations scheduling accordingly. Workers can be trained to operate more than one machine to generate some flexibility. It is a competitive edge to be able to change schedules quickly and keep everything moving smoothly for the supply chain Step 1: Read The Following Reno X Lite.com/courses/546/discussion_topics/1031 competitive edge to be able to change schedules quickly and keep everything moving smoothly along the supply chain, 1. Assign personnel to complete the job that has been in the system the longest. 2. Assign personnel to a workstation that has the most jobs waiting 3. Assign personnel to jobs with the earliest due date. 4. Assign personnel to workstations with the most standard work to run. Step 2: Review the discussion from Unit 1 on Retail Operations Management Step 3: For Wednesday, respond to the following discussion questions: 1. What type of forecasting would best work for retail operations management? Why? 2. How would this differ from forecasting done in manufacturing? 3. How would LEAN e principles apply? 4. Where would you go to learn more about forecasting? 5. How would forecasting help you with continuous improvement







Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


