Question: PLEASE HELP WITH THE CALCLULATIONS NOT THE CONCEPT! = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = =
PLEASE HELP WITH THE CALCLULATIONS NOT THE CONCEPT!
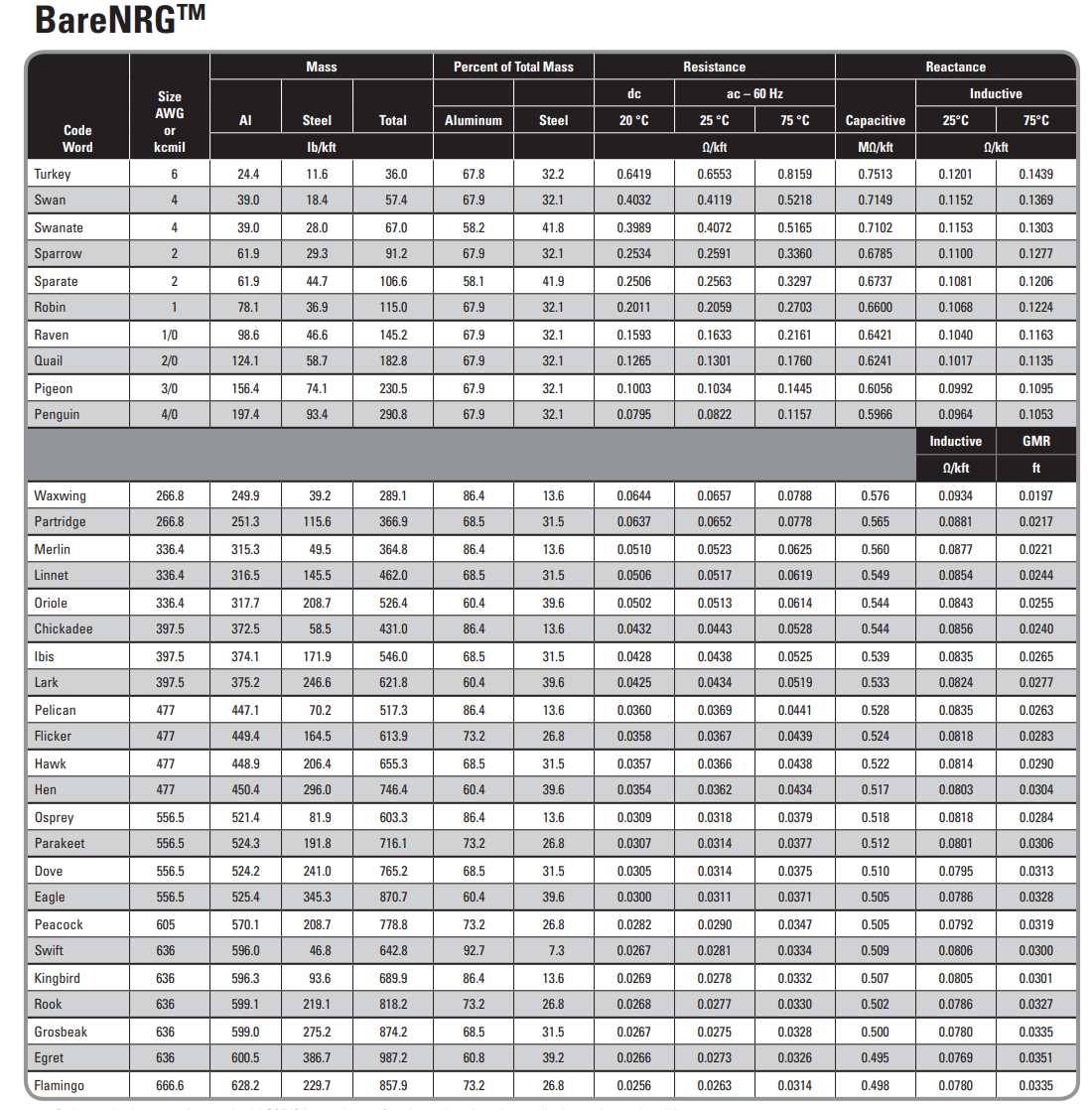
Assigned ACSR Conductor: DOVE
DOVE Weight lbKft
DOVE CDR
Conditions HEAVY Ice Thickness inch
Wind Pressure lbft
Temp degrees
K lbft
Span S ft
Ice loading lbfoot
Wind loading lbft
Find the maximum sag, tension, and length of the conductor of ACSR conductor your assigned conductor to be used in heavy loading districts.
Note : You will use the following specifications except the conductorspecific data that need to be obtained from the data sheet provided for your assigned conductor.
Specs:
Span S ft
Ice loading lbfoot
Wind loading lbft
K lbft
Note : Find the conductor weight from the datasheet and compute the total weight with ice and wind loading see example in slideset #
Weight, with ice and wind loading wT lbft
Horizontal tension rated initial, Hi lbs
Cross section total A in
Calculate from overall diameter of the conductor given in the datasheet
Breaking strength lb
Elastic modulus of the conductor Aluminum & Steel, combined x psi
Coefficient of thermal expansion Aluminum & Steel, combined x per oF
Note: Once you have all the data for your conductor follow the stepbystep process outlined in this sample to complete the problem.
Task: String the conductor applying the tension H and compute resulting sag D and the length L which will be used to determine the tower height to maintain the minimum ground clearance needed.
The sag D is computed for the following three scenarios:
Snow and wind loading
Maximum temperature
year creep
The worst sag longest is adapted. In this assignment you will do snow and wind loading only.
Problem: A conductor under tension would elongate, increasing the length of the conductor. Increase in L results in increase in D which in turn reduces the tension H
Fix: Find a combination of L D and H which would result in minimum change in tension H before and after stringing the conductor using an iterative technique.
Initialization:
Compute D using the given H and S
Compute L using D in and the given S
Compute ZTL at the normal temperature degrees
Compute ZTL at the maximum temperature degrees call it LHREF at
Compute D using ZTL in first and then use that D to compute Hi
Iterations:
Given the initial Hi compute the Li
Compute Di for Li in
Compute Hf for Li and Di from and
If the difference between Hi and Hf is minimal or less than lb stop. Else, repeat with a new initial Hi
New Hi could be the average of Hi and Hf
We need to do sagtension calculations for the conditions given below.
Snow and wind loading
This sample uses w lbft you need to calculate that for your assigned conductor. See the example of doing calculation in slides set
ZTL calculation
Compute D for a specific tension lb HREF.
Compute LREF for D in
Use LREF and HREF in ZTL calculation.
D wSHREF
LREF S DS
ZTL degree LH LHREFHHrefEcA
ZTL degree LT LTREF alphaAS x T TREF x ft
initial tension calculation
Compute D using ZTL degree
Compute Hi using D in
D SQRTSZTL S SQRT x
Hi wSD x x
Iterative Technique:
Using the tension, Hi compute L where HREF and LREF ZTL degree
Compute D for L in
L LREF Hi HREFEcA
D SQRTSLS
Iterative Technique continued:
Compute Hf for L and D from and
If the difference between Hi and Hf is minimal, stop. Else, repeat with a new initial Hi
New Hi could be the average of Hi and Hf
Hf w SD
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


