Question: Please help with this question in 1.5 hours max please. Course is AFA717 Canadian Income Taxation Question 1 (110 Minutes;65 Marks) Penelope Jones is a


Please help with this question in 1.5 hours max please.
Course is AFA717 Canadian Income Taxation
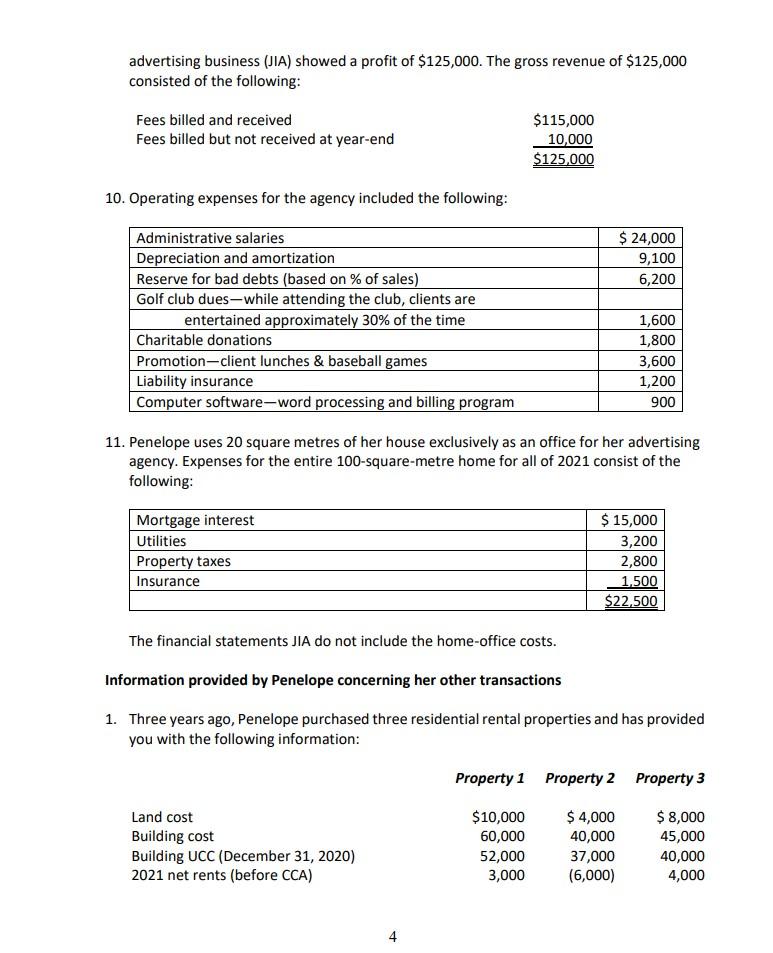
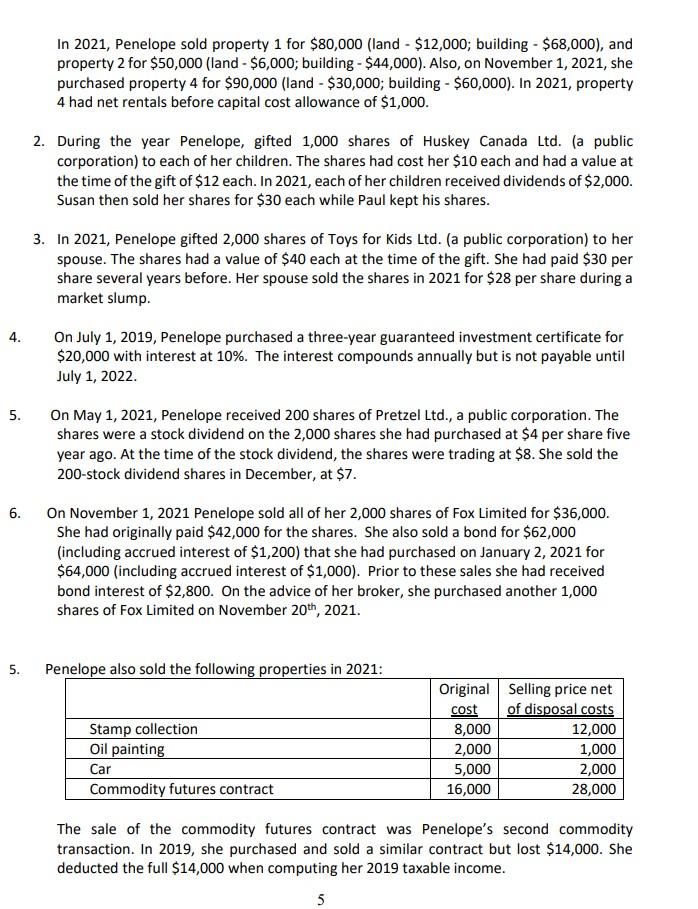
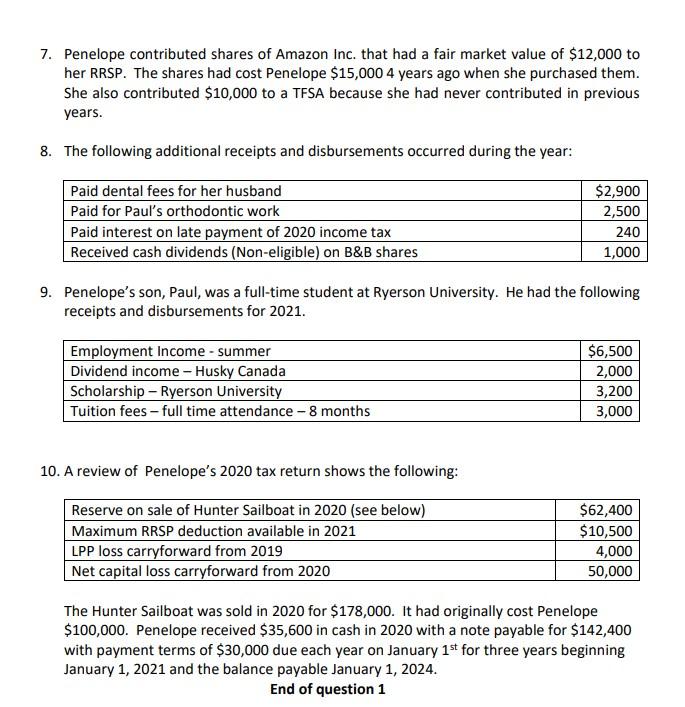
Question 1 (110 Minutes;65 Marks) Penelope Jones is a good friend of yours from high school. She is the mother of two children, a daughter, Susan, aged 16 and a son, Paul, aged 20. Her husband is a successful lawyer with an annual salary of $150,000 per year. Penelope has been very successful in her career as well. She has been able to save and invest her money over the years. Penelope has worked for Better and Best Limited (B&B), a Canadian controlled private corporation, for the last 10 years. She feels that she has learned all she can from the agency and as a result, on July 1, 2021 she started her own advertising agency, Jones Innovative Advertising (JIA), as a sole proprietor from an office in her home. JIA has a December 31, 2021 year end. At a recent dinner, Penelope asked you, her best friend, to help her with the preparation of her 2021 income tax return. Although she usually prepared her own return, she feels that there are enough complications to require the help of her accountant friend. She has done a number of transactions and is not certain how she should account for them for tax purposes. She knows that you have completed a tax course so is asking for your assistance. After your evening discussion with Penelope you asked her to summarize all of her transactions. She has prepared the following information provided after the required. Required: a. Based on the information that Penelope has provided determine Penelope's net income for tax purposes in accordance with the aggregating formula of Section 3 of the Income Tax Act and her taxable income for the 2021 taxation year. Based on your answer to part (a), calculate Penelope's federal income tax for the 2021 taxation year. b. Information Provided by Penelope re: Work and her Business (JAI) 1. Penelope's salary to June 30th from B&B was $85,000. He employer contributed $3,000 to the company pension plan in her name. Penelope made an equal contribution of $3,000. From this, B&B deducted El and CPP of $4,056 (includes CPP enhanced contributions of $290), income tax of $13,000, and $400 for Penelope's portion of the private group medical insurance premium. An additional premium of $400 was paid by B&B. Also, B&B paid the $800 premium for Penelope's group term life insurance coverage of $100,000. 2. Until the day of her leaving the company, Penelope had the use of a company car. She returned the car on June 30th when she left the company. The car cost $35,000, and the undepreciated capital cost on B&B's records was $18,000. B&B also paid the operating costs for the car, which amounted to $2,100. Penelope drove her car 12,000 km over the period of use, of which 7,800 were for employment purposes. 3. Penelope traveled extensively for B&B. In May, Penelope and her spouse used some of the travel points she had accumulated from this travel to attend his mother's funeral in Winnipeg. As a result, she saved the normal airfare of $850 per person. 4. In 2017, Penelope's employer had loaned her $60,000 so that she could purchase 5,000 shares of B&B under the stock option plan (see #6 below). She paid interest at 1% on the loan. Penelope repaid the loan and the interest due on June 30 when her employment ended. [Assume CRA's prescribed interest rate was 4% throughout 2021). 5. In February of 2021, Penelope attended a convention held in Montreal for eastern Canada advertising executives. She incurred costs of $1,500 which was the cost of the registration for the 2 day event as well as hotel costs and travel of $500. 6. Prior to leaving B&B, Penelope was required to sell to the controlling shareholder, the 5,000 shares of B&B that she had acquired in 2017, under the company's stock option plan. Penelope acquired them for $12 per share and at that time, the shares had a FMV of $15. Penelope sold them for $20 per share. 7. Penelope began her advertising agency business on July 1, 2021. In July, she purchased furniture for her home office for $10,000, a computer and systems software for $4,200 and a customer list from a competitor that was retiring from the business in the amount of $32,000 8. In order to be able to meet with clients, Penelope purchased a car on July 1, for $35,000 (net of GST). For the remainder of the year, Penelope traveled 6,000 kms for business out of the 10,000 kms she put on the car. 9. For the six months ended December 31, 2021, the financial statements of Penelope's advertising business (JIA) showed a profit of $125,000. The gross revenue of $125,000 consisted of the following: Fees billed and received Fees billed but not received at year-end $115,000 10,000 $125,000 10. Operating expenses for the agency included the following: $ 24,000 9,100 6,200 Administrative salaries Depreciation and amortization Reserve for bad debts (based on % of sales) Golf club dues-while attending the club, clients are entertained approximately 30% of the time Charitable donations Promotion-client lunches & baseball games Liability insurance Computer software-word processing and billing program 1,600 1,800 3,600 1,200 900 11. Penelope uses 20 square metres of her house exclusively as an office for her advertising agency. Expenses for the entire 100-square-metre home for all of 2021 consist of the following: Mortgage interest Utilities Property taxes Insurance $ 15,000 3,200 2,800 1,500 $22,500 The financial statements JIA do not include the home office costs. Information provided by Penelope concerning her other transactions 1. Three years ago, Penelope purchased three residential rental properties and has provided you with the following information: Property 1 Property 2 Property 3 Land cost Building cost Building UCC (December 31, 2020) 2021 net rents (before CCA) $10,000 60,000 52,000 3,000 $ 4,000 40,000 37,000 (6,000) $ 8,000 45,000 40,000 4,000 4 In 2021, Penelope sold property 1 for $80,000 (land - $12,000; building - $68,000), and property 2 for $50,000 (land - $6,000; building - $44,000). Also, on November 1, 2021, she purchased property 4 for $90,000 (land - $30,000; building - $60,000). In 2021, property 4 had net rentals before capital cost allowance of $1,000. 2. During the year Penelope, gifted 1,000 shares of Huskey Canada Ltd. (a public corporation) to each of her children. The shares had cost her $10 each and had a value at the time of the gift of $12 each. In 2021, each of her children received dividends of $2,000. Susan then sold her shares for $30 each while Paul kept his shares. 3. In 2021, Penelope gifted 2,000 shares of Toys for Kids Ltd. (a public corporation) to her spouse. The shares had a value of $40 each at the time of the gift. She had paid $30 per share several years before. Her spouse sold the shares in 2021 for $28 per share during a market slump. 4. On July 1, 2019, Penelope purchased a three-year guaranteed investment certificate for $20,000 with interest at 10%. The interest compounds annually but is not payable until July 1, 2022. 5. 6. On May 1, 2021, Penelope received 200 shares of Pretzel Ltd., a public corporation. The shares were a stock dividend on the 2,000 shares she had purchased at $4 per share five year ago. At the time of the stock dividend, the shares were trading at $8. She sold the 200-stock dividend shares in December, at $7. On November 1, 2021 Penelope sold all of her 2,000 shares of Fox Limited for $36,000. She had originally paid $42,000 for the shares. She also sold a bond for $62,000 (including accrued interest of $1,200) that she had purchased on January 2, 2021 for $64,000 (including accrued interest of $1,000). Prior to these sales she had received bond interest of $2,800. On the advice of her broker, she purchased another 1,000 shares of Fox Limited on November 20th, 2021. . 5. Penelope also sold the following properties in 2021: Stamp collection Oil painting Original Selling price net cost of disposal costs 8,000 12,000 2,000 1,000 5,000 2,000 16,000 28,000 Car Commodity futures contract The sale of the commodity futures contract was Penelope's second commodity transaction. In 2019, she purchased and sold a similar contract but lost $14,000. She deducted the full $14,000 when computing her 2019 taxable income. 5 7. Penelope contributed shares of Amazon Inc. that had a fair market value of $12,000 to her RRSP. The shares had cost Penelope $15,000 4 years ago when she purchased them. She also contributed $10,000 to a TFSA because she had never contributed in previous years. 8. The following additional receipts and disbursements occurred during the year: Paid dental fees for her husband Paid for Paul's orthodontic work Paid interest on late payment of 2020 income tax Received cash dividends (Non-eligible) on B&B shares $2,900 2,500 240 1,000 9. Penelope's son, Paul, was a full-time student at Ryerson University. He had the following receipts and disbursements for 2021. Employment Income - summer Dividend income - Husky Canada Scholarship - Ryerson University Tuition fees - full time attendance - 8 months $6,500 2,000 3,200 3,000 10. A review of Penelope's 2020 tax return shows the following: Reserve on sale of Hunter Sailboat in 2020 (see below) Maximum RRSP deduction available in 2021 LPP loss carryforward from 2019 Net capital loss carryforward from 2020 $62,400 $10,500 4,000 50,000 The Hunter Sailboat was sold in 2020 for $178,000. It had originally cost Penelope $100,000. Penelope received $35,600 in cash in 2020 with a note payable for $142,400 with payment terms of $30,000 due each year on January 1st for three years beginning January 1, 2021 and the balance payable January 1, 2024. End of question 1 Question 1 (110 Minutes;65 Marks) Penelope Jones is a good friend of yours from high school. She is the mother of two children, a daughter, Susan, aged 16 and a son, Paul, aged 20. Her husband is a successful lawyer with an annual salary of $150,000 per year. Penelope has been very successful in her career as well. She has been able to save and invest her money over the years. Penelope has worked for Better and Best Limited (B&B), a Canadian controlled private corporation, for the last 10 years. She feels that she has learned all she can from the agency and as a result, on July 1, 2021 she started her own advertising agency, Jones Innovative Advertising (JIA), as a sole proprietor from an office in her home. JIA has a December 31, 2021 year end. At a recent dinner, Penelope asked you, her best friend, to help her with the preparation of her 2021 income tax return. Although she usually prepared her own return, she feels that there are enough complications to require the help of her accountant friend. She has done a number of transactions and is not certain how she should account for them for tax purposes. She knows that you have completed a tax course so is asking for your assistance. After your evening discussion with Penelope you asked her to summarize all of her transactions. She has prepared the following information provided after the required. Required: a. Based on the information that Penelope has provided determine Penelope's net income for tax purposes in accordance with the aggregating formula of Section 3 of the Income Tax Act and her taxable income for the 2021 taxation year. Based on your answer to part (a), calculate Penelope's federal income tax for the 2021 taxation year. b. Information Provided by Penelope re: Work and her Business (JAI) 1. Penelope's salary to June 30th from B&B was $85,000. He employer contributed $3,000 to the company pension plan in her name. Penelope made an equal contribution of $3,000. From this, B&B deducted El and CPP of $4,056 (includes CPP enhanced contributions of $290), income tax of $13,000, and $400 for Penelope's portion of the private group medical insurance premium. An additional premium of $400 was paid by B&B. Also, B&B paid the $800 premium for Penelope's group term life insurance coverage of $100,000. 2. Until the day of her leaving the company, Penelope had the use of a company car. She returned the car on June 30th when she left the company. The car cost $35,000, and the undepreciated capital cost on B&B's records was $18,000. B&B also paid the operating costs for the car, which amounted to $2,100. Penelope drove her car 12,000 km over the period of use, of which 7,800 were for employment purposes. 3. Penelope traveled extensively for B&B. In May, Penelope and her spouse used some of the travel points she had accumulated from this travel to attend his mother's funeral in Winnipeg. As a result, she saved the normal airfare of $850 per person. 4. In 2017, Penelope's employer had loaned her $60,000 so that she could purchase 5,000 shares of B&B under the stock option plan (see #6 below). She paid interest at 1% on the loan. Penelope repaid the loan and the interest due on June 30 when her employment ended. [Assume CRA's prescribed interest rate was 4% throughout 2021). 5. In February of 2021, Penelope attended a convention held in Montreal for eastern Canada advertising executives. She incurred costs of $1,500 which was the cost of the registration for the 2 day event as well as hotel costs and travel of $500. 6. Prior to leaving B&B, Penelope was required to sell to the controlling shareholder, the 5,000 shares of B&B that she had acquired in 2017, under the company's stock option plan. Penelope acquired them for $12 per share and at that time, the shares had a FMV of $15. Penelope sold them for $20 per share. 7. Penelope began her advertising agency business on July 1, 2021. In July, she purchased furniture for her home office for $10,000, a computer and systems software for $4,200 and a customer list from a competitor that was retiring from the business in the amount of $32,000 8. In order to be able to meet with clients, Penelope purchased a car on July 1, for $35,000 (net of GST). For the remainder of the year, Penelope traveled 6,000 kms for business out of the 10,000 kms she put on the car. 9. For the six months ended December 31, 2021, the financial statements of Penelope's advertising business (JIA) showed a profit of $125,000. The gross revenue of $125,000 consisted of the following: Fees billed and received Fees billed but not received at year-end $115,000 10,000 $125,000 10. Operating expenses for the agency included the following: $ 24,000 9,100 6,200 Administrative salaries Depreciation and amortization Reserve for bad debts (based on % of sales) Golf club dues-while attending the club, clients are entertained approximately 30% of the time Charitable donations Promotion-client lunches & baseball games Liability insurance Computer software-word processing and billing program 1,600 1,800 3,600 1,200 900 11. Penelope uses 20 square metres of her house exclusively as an office for her advertising agency. Expenses for the entire 100-square-metre home for all of 2021 consist of the following: Mortgage interest Utilities Property taxes Insurance $ 15,000 3,200 2,800 1,500 $22,500 The financial statements JIA do not include the home office costs. Information provided by Penelope concerning her other transactions 1. Three years ago, Penelope purchased three residential rental properties and has provided you with the following information: Property 1 Property 2 Property 3 Land cost Building cost Building UCC (December 31, 2020) 2021 net rents (before CCA) $10,000 60,000 52,000 3,000 $ 4,000 40,000 37,000 (6,000) $ 8,000 45,000 40,000 4,000 4 In 2021, Penelope sold property 1 for $80,000 (land - $12,000; building - $68,000), and property 2 for $50,000 (land - $6,000; building - $44,000). Also, on November 1, 2021, she purchased property 4 for $90,000 (land - $30,000; building - $60,000). In 2021, property 4 had net rentals before capital cost allowance of $1,000. 2. During the year Penelope, gifted 1,000 shares of Huskey Canada Ltd. (a public corporation) to each of her children. The shares had cost her $10 each and had a value at the time of the gift of $12 each. In 2021, each of her children received dividends of $2,000. Susan then sold her shares for $30 each while Paul kept his shares. 3. In 2021, Penelope gifted 2,000 shares of Toys for Kids Ltd. (a public corporation) to her spouse. The shares had a value of $40 each at the time of the gift. She had paid $30 per share several years before. Her spouse sold the shares in 2021 for $28 per share during a market slump. 4. On July 1, 2019, Penelope purchased a three-year guaranteed investment certificate for $20,000 with interest at 10%. The interest compounds annually but is not payable until July 1, 2022. 5. 6. On May 1, 2021, Penelope received 200 shares of Pretzel Ltd., a public corporation. The shares were a stock dividend on the 2,000 shares she had purchased at $4 per share five year ago. At the time of the stock dividend, the shares were trading at $8. She sold the 200-stock dividend shares in December, at $7. On November 1, 2021 Penelope sold all of her 2,000 shares of Fox Limited for $36,000. She had originally paid $42,000 for the shares. She also sold a bond for $62,000 (including accrued interest of $1,200) that she had purchased on January 2, 2021 for $64,000 (including accrued interest of $1,000). Prior to these sales she had received bond interest of $2,800. On the advice of her broker, she purchased another 1,000 shares of Fox Limited on November 20th, 2021. . 5. Penelope also sold the following properties in 2021: Stamp collection Oil painting Original Selling price net cost of disposal costs 8,000 12,000 2,000 1,000 5,000 2,000 16,000 28,000 Car Commodity futures contract The sale of the commodity futures contract was Penelope's second commodity transaction. In 2019, she purchased and sold a similar contract but lost $14,000. She deducted the full $14,000 when computing her 2019 taxable income. 5 7. Penelope contributed shares of Amazon Inc. that had a fair market value of $12,000 to her RRSP. The shares had cost Penelope $15,000 4 years ago when she purchased them. She also contributed $10,000 to a TFSA because she had never contributed in previous years. 8. The following additional receipts and disbursements occurred during the year: Paid dental fees for her husband Paid for Paul's orthodontic work Paid interest on late payment of 2020 income tax Received cash dividends (Non-eligible) on B&B shares $2,900 2,500 240 1,000 9. Penelope's son, Paul, was a full-time student at Ryerson University. He had the following receipts and disbursements for 2021. Employment Income - summer Dividend income - Husky Canada Scholarship - Ryerson University Tuition fees - full time attendance - 8 months $6,500 2,000 3,200 3,000 10. A review of Penelope's 2020 tax return shows the following: Reserve on sale of Hunter Sailboat in 2020 (see below) Maximum RRSP deduction available in 2021 LPP loss carryforward from 2019 Net capital loss carryforward from 2020 $62,400 $10,500 4,000 50,000 The Hunter Sailboat was sold in 2020 for $178,000. It had originally cost Penelope $100,000. Penelope received $35,600 in cash in 2020 with a note payable for $142,400 with payment terms of $30,000 due each year on January 1st for three years beginning January 1, 2021 and the balance payable January 1, 2024. End of question 1
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


