Question: Please IMPLEMENT IN JAVA. In section 11.5, 1. implment the insertion operation of (2,4) tree, reappear the example of Figure 11.25. 2. implment the deletion
Please IMPLEMENT IN JAVA.
In section 11.5, 1. implment the insertion operation of (2,4) tree, reappear the example of Figure 11.25. 2. implment the deletion ooperation of (2,4) tree, reappear the example of Figure 11.27 and 11.28. Your program should print out all the trees in Figure 11.25, 11.27 and 11.28.
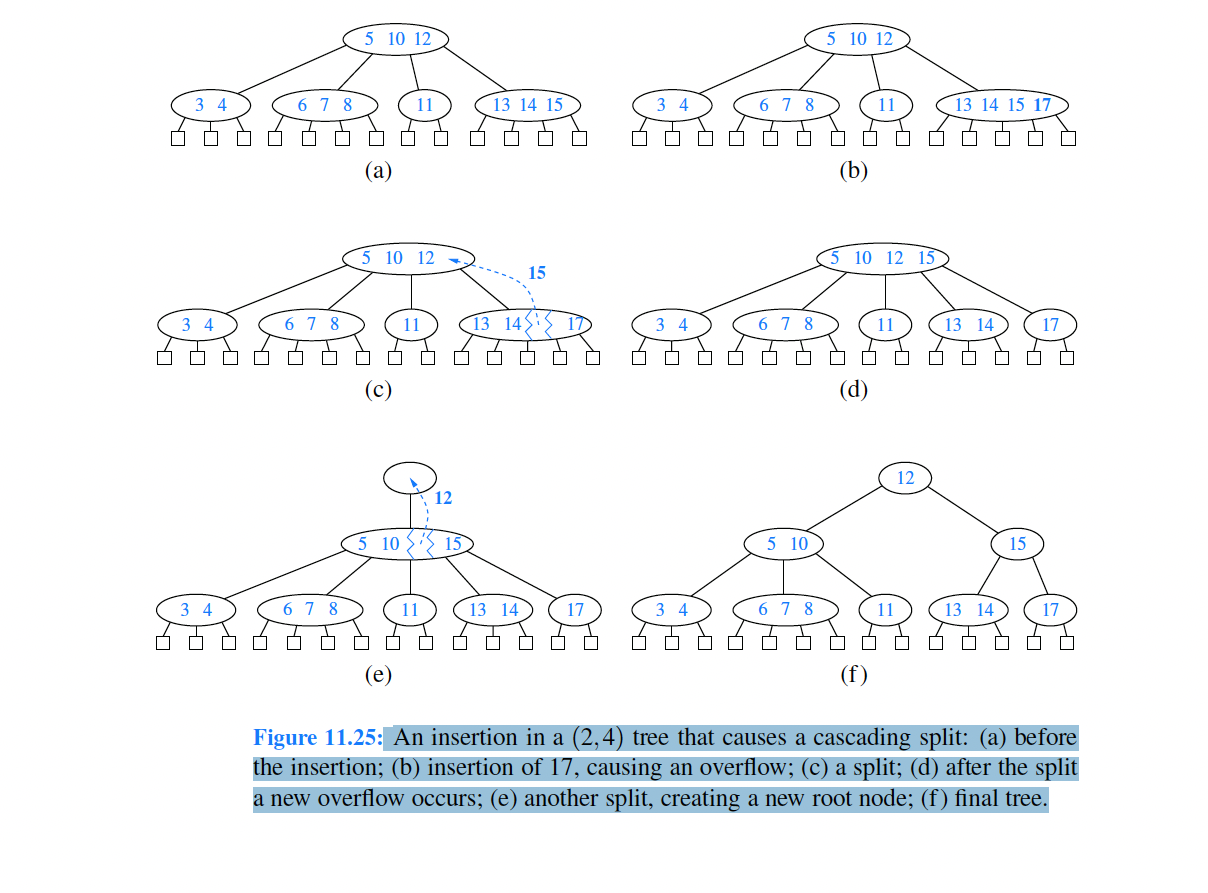
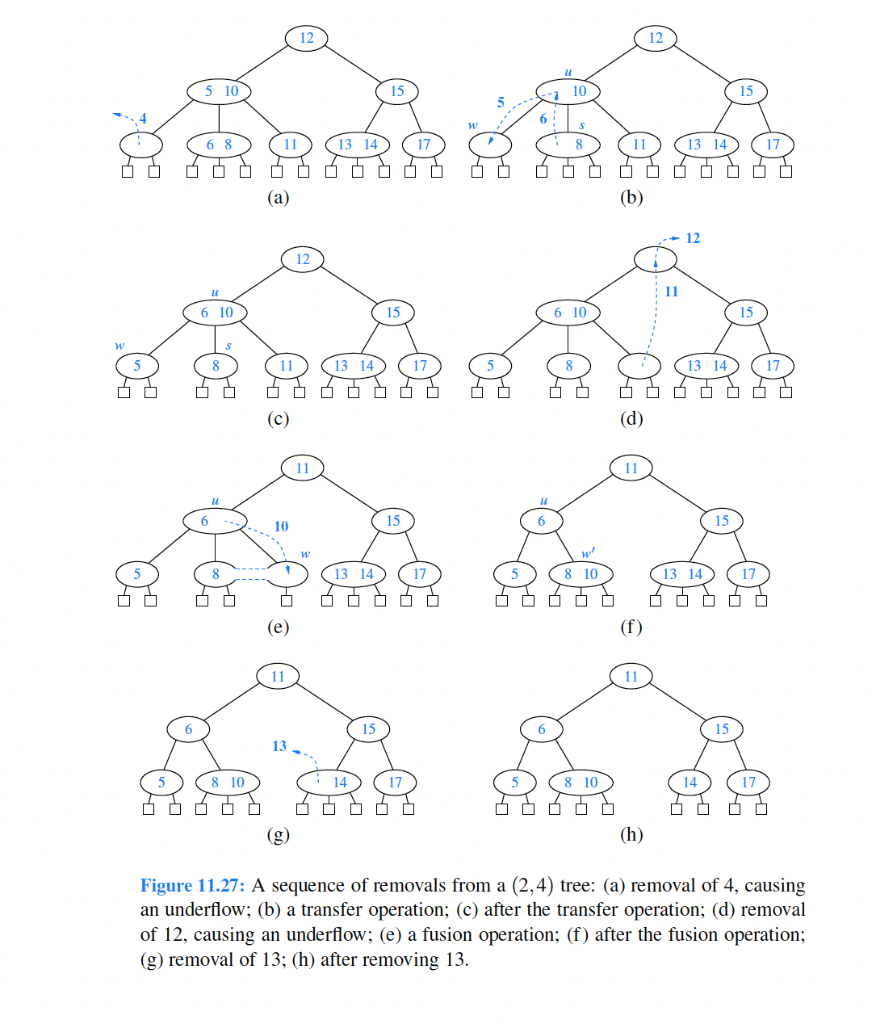
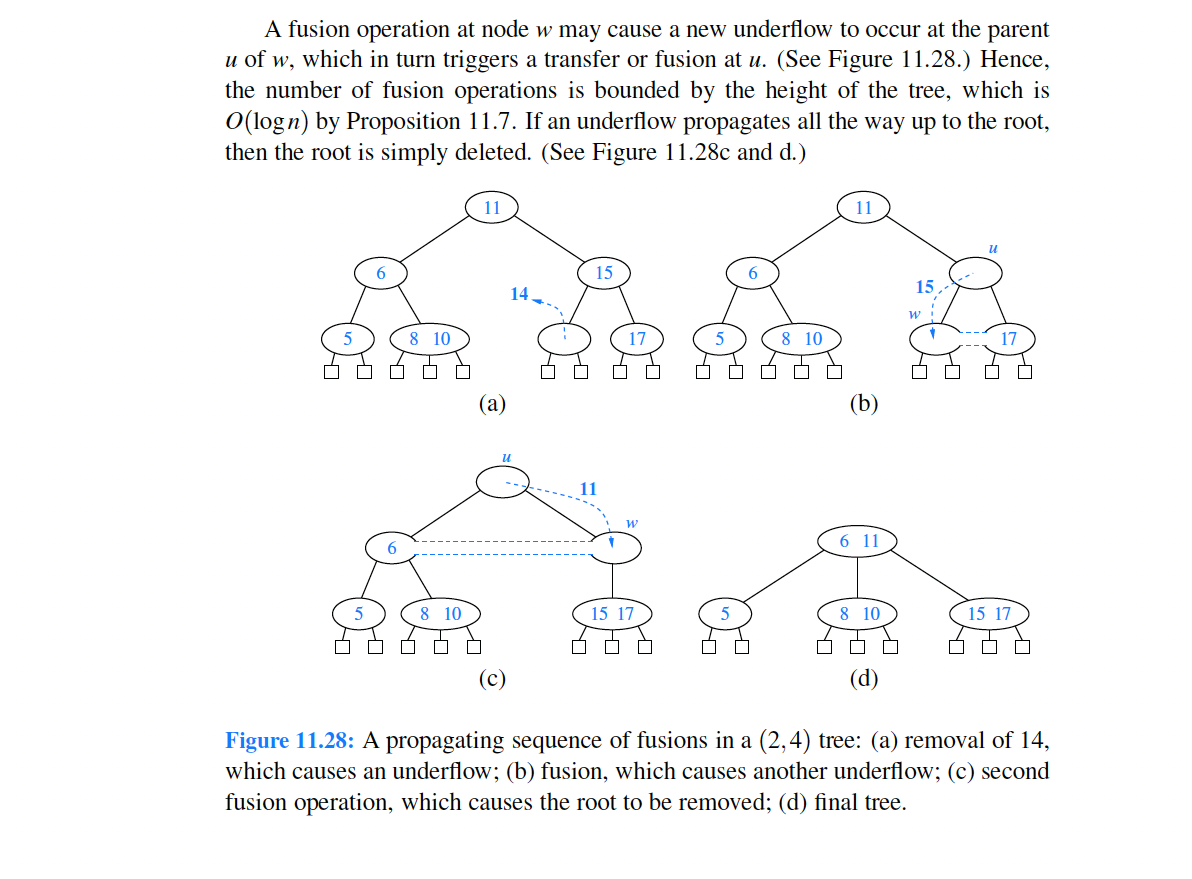
Figure 11.25: An insertion in a (2,4) tree that causes a cascading split: (a) before the insertion; (b) insertion of 17, causing an overflow; (c) a split; (d) after the split a new overflow occurs; (e) another split, creating a new root node; (f) final tree. (a) (I) Figure 11.27: A sequence of removals from a (2,4) tree: (a) removal of 4, causing an underflow; (b) a transfer operation; (c) after the transfer operation; (d) removal of 12, causing an underflow; (e) a fusion operation; (f) after the fusion operation; (g) removal of 13 ; (h) after removing 13. A fusion operation at node w may cause a new underflow to occur at the parent u of w, which in turn triggers a transfer or fusion at u. (See Figure 11.28.) Hence, the number of fusion operations is bounded by the height of the tree, which is O(logn) by Proposition 11.7. If an underflow propagates all the way up to the root, then the root is simply deleted. (See Figure 11.28c and d.) (a) Figure 11.28: A propagating sequence of fusions in a (2,4) tree: (a) removal of 14, which causes an underflow; (b) fusion, which causes another underflow; (c) second fusion operation, which causes the root to be removed; (d) final tree
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


