Question: PLEASE NOTE!!!! I need help figuring out how they want the IF statements input. Everything that is inserted is correct, hopefully someone who has used
PLEASE NOTE!!!! I need help figuring out how they want the IF statements input. Everything that is inserted is correct, hopefully someone who has used this program is familiar with exactly how they are wanting the formulas entered.
I can't simply write favorable or unfavorable, it must be an if statement in excel. I do need help with the other unanswered portions.

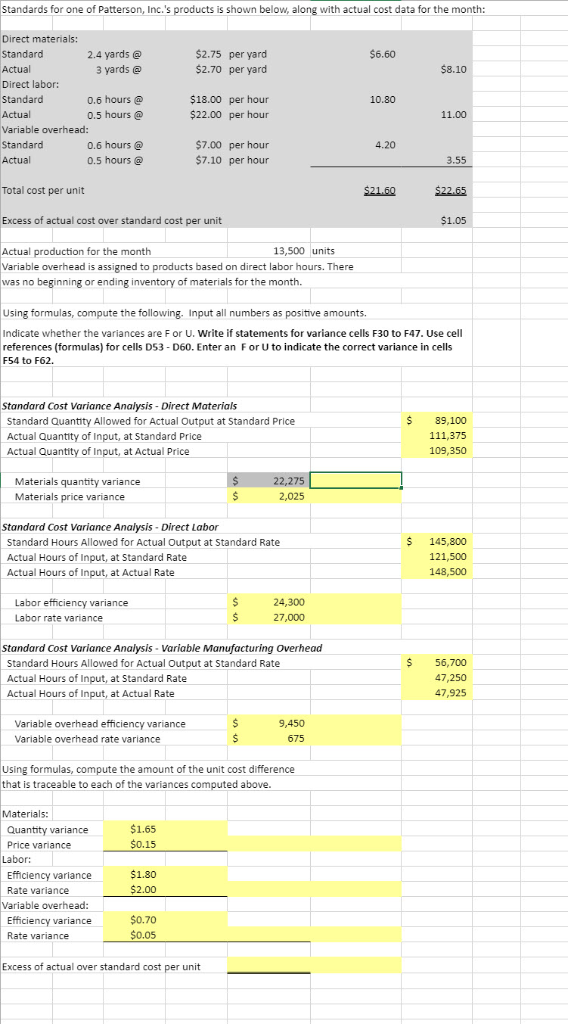
Patterson, Inc. has provided details of its actual cost data for the month. The Controller has asked you to compute the basic variances and the impact of those variances on unit costs. Use Cell Reference: Allows you to refer to data from another cell in the worksheet From the Excel Simulation below, if in a blank cell,-D4" was entered, the formula would output the result from cell D4, or 2.75 in this example . Basic Math functions: Allows you to use the basic math symbols to perform mathematical functions. You can use the following keys: +(plus sign to add), (minus sign to subtract), (asterisk sign to multiply), and (forward slash to divide). From the Excel Simulation below, if in a blank cell"-F4+G5" was entered, the formula would add the values from those cells and output the result, or 14.70 in this example lf using the other math symbols the result would output an appropriate answer for its function. in a blank cell-SUM(D4,D5) was entered, the formula would output the result of adding those two separate cells, or 5.45 in this example. Similarly, if in a blank cell-SUM(D4:D5) was entered, the formula would output the same result of adding those cells, except they are expressed as a range in the formula, and the result would be 5.45 in this example Allows you to return the absolute value of a number or calculation. You can reference any cell to display its absolute value, or surround another formula with the ABS function, to return the final result as an absolute value. From the Excel Simulation below, if in a blank cell you entered-ABS(F7-G8) Excel will first calculate the subtraction of F7-G8 that results in -0.20. Then, the ABS portion of the formula returms the absolute value of the subtraction result, which would be 0.20 in this example IF function: Allows you to test a condition and return a specific value is the result is true and different value if the result is false. The syntax of the IF function is -IF(test_condition, value if true,value_if false) and specific considerations need to be made when using this function. The test condition argument is an evaluation of the status of a cell, such as if the value of a cell is greater than, less than, or equal to another number or cell. The value if true and value if false arguments will return any specific result for each option, such as another cell reference, a value, or text. Throughout the entire equation, if text is being used in the test condition, value if true, or value_ if false arguments then the text itself should be entered in quotations so that Excel will recognize the text as a 'string of text" instead of another function. From the Excel Simulation below, if in a blank cell -IF(F13 20, Total Cost Per Unit is good Total Cost Per Unit is bad") was entered, the formula would output the result of the value if true since the test condition would be result as true, or in this case the text "Total Cost Per Unit is good. Excel processes the IF function by separating it out into separate parts. First the test condition Excel thinks, find cell F13 and Standards for one of Patterson, Inc.'s products is shown below, along with actual cost data for the month: Direct materials: Standard Actual Direct labor: Standard Actual Variable overhead: Standard Actual 2.4 yards @ 3 yards @ $2.75 per yard $2.70 per yard $6.60 $8.10 0.6 hours @ 0.5 hours @ $18.00 per hour $22.00 per hour 10.80 11.00 0.6 hours@ 0.5 hours@ $7.00 per hour $7.10 per hour 4.20 3.55 Total cost per unit $21,60 $22.65 Excess of actual cost over standard cost per unit $1.05 Actual production for the month Variable overhead is assigned to products based on direct labor hours. There was no beginning or ending inventory of materials for the month. 13,500 units Using formulas, compute the following. Input all numbers as positive amounts Indicate whether the variances are F or U. Write if statements for variance cells F30 to F47. Use cell references (formulas) for cells DS3 D60. Enter an For U to indicate the correct variance in cells F54 to F62 Standard Cost Variance Analysis- Direct Materials Standard Quantity Allowed for Actual Output at Standard Price Actual Quantity of Input, at Standard Price Actual Quantity of Input, at Actual Price $89,100 111,375 109,350 Materials quantity variance Materials price variance 275 2,025 Standard Cost Variance Analysis- Direct Labor Standard Hours Allowed for Actual Output at Standard Rate Actual Hours of Input, at Standard Rate Actual Hours of Input, at Actual Rate 145,800 121,500 148,500 Labor efficiency variance Labor rate variance 24,300 27,000 Standard Cost Variance Analysis-Variable Manufacturing Overhead Standard Hours Allowed for Actual Output at Standard Rate Actual Hours of Input, at Standard Rate Actual Hours of Input, at Actual Rate $ 56,700 47,250 47,925 Variable overhead efficiency variance Variable overhead rate variance 9,450 675 Using formulas, compute the amount of the unit cost difference that is traceable to each of the variances computed above. Materials: Quantity variance Price variance $1.65 $0.15 Labor: Efficiency variance Rate variance 1.80 2.00 Variable overhead Efficiency variance Rate variance $0.70 05 Excess of actual over standard cost per unit Patterson, Inc. has provided details of its actual cost data for the month. The Controller has asked you to compute the basic variances and the impact of those variances on unit costs. Use Cell Reference: Allows you to refer to data from another cell in the worksheet From the Excel Simulation below, if in a blank cell,-D4" was entered, the formula would output the result from cell D4, or 2.75 in this example . Basic Math functions: Allows you to use the basic math symbols to perform mathematical functions. You can use the following keys: +(plus sign to add), (minus sign to subtract), (asterisk sign to multiply), and (forward slash to divide). From the Excel Simulation below, if in a blank cell"-F4+G5" was entered, the formula would add the values from those cells and output the result, or 14.70 in this example lf using the other math symbols the result would output an appropriate answer for its function. in a blank cell-SUM(D4,D5) was entered, the formula would output the result of adding those two separate cells, or 5.45 in this example. Similarly, if in a blank cell-SUM(D4:D5) was entered, the formula would output the same result of adding those cells, except they are expressed as a range in the formula, and the result would be 5.45 in this example Allows you to return the absolute value of a number or calculation. You can reference any cell to display its absolute value, or surround another formula with the ABS function, to return the final result as an absolute value. From the Excel Simulation below, if in a blank cell you entered-ABS(F7-G8) Excel will first calculate the subtraction of F7-G8 that results in -0.20. Then, the ABS portion of the formula returms the absolute value of the subtraction result, which would be 0.20 in this example IF function: Allows you to test a condition and return a specific value is the result is true and different value if the result is false. The syntax of the IF function is -IF(test_condition, value if true,value_if false) and specific considerations need to be made when using this function. The test condition argument is an evaluation of the status of a cell, such as if the value of a cell is greater than, less than, or equal to another number or cell. The value if true and value if false arguments will return any specific result for each option, such as another cell reference, a value, or text. Throughout the entire equation, if text is being used in the test condition, value if true, or value_ if false arguments then the text itself should be entered in quotations so that Excel will recognize the text as a 'string of text" instead of another function. From the Excel Simulation below, if in a blank cell -IF(F13 20, Total Cost Per Unit is good Total Cost Per Unit is bad") was entered, the formula would output the result of the value if true since the test condition would be result as true, or in this case the text "Total Cost Per Unit is good. Excel processes the IF function by separating it out into separate parts. First the test condition Excel thinks, find cell F13 and Standards for one of Patterson, Inc.'s products is shown below, along with actual cost data for the month: Direct materials: Standard Actual Direct labor: Standard Actual Variable overhead: Standard Actual 2.4 yards @ 3 yards @ $2.75 per yard $2.70 per yard $6.60 $8.10 0.6 hours @ 0.5 hours @ $18.00 per hour $22.00 per hour 10.80 11.00 0.6 hours@ 0.5 hours@ $7.00 per hour $7.10 per hour 4.20 3.55 Total cost per unit $21,60 $22.65 Excess of actual cost over standard cost per unit $1.05 Actual production for the month Variable overhead is assigned to products based on direct labor hours. There was no beginning or ending inventory of materials for the month. 13,500 units Using formulas, compute the following. Input all numbers as positive amounts Indicate whether the variances are F or U. Write if statements for variance cells F30 to F47. Use cell references (formulas) for cells DS3 D60. Enter an For U to indicate the correct variance in cells F54 to F62 Standard Cost Variance Analysis- Direct Materials Standard Quantity Allowed for Actual Output at Standard Price Actual Quantity of Input, at Standard Price Actual Quantity of Input, at Actual Price $89,100 111,375 109,350 Materials quantity variance Materials price variance 275 2,025 Standard Cost Variance Analysis- Direct Labor Standard Hours Allowed for Actual Output at Standard Rate Actual Hours of Input, at Standard Rate Actual Hours of Input, at Actual Rate 145,800 121,500 148,500 Labor efficiency variance Labor rate variance 24,300 27,000 Standard Cost Variance Analysis-Variable Manufacturing Overhead Standard Hours Allowed for Actual Output at Standard Rate Actual Hours of Input, at Standard Rate Actual Hours of Input, at Actual Rate $ 56,700 47,250 47,925 Variable overhead efficiency variance Variable overhead rate variance 9,450 675 Using formulas, compute the amount of the unit cost difference that is traceable to each of the variances computed above. Materials: Quantity variance Price variance $1.65 $0.15 Labor: Efficiency variance Rate variance 1.80 2.00 Variable overhead Efficiency variance Rate variance $0.70 05 Excess of actual over standard cost per unit
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


