Question: Please note!! This is only one question, I explained the question in the detailed formated with instructions and example, you only have to edit the
Please note!! This is only one question, I explained the question in the detailed formated with instructions and example, you only have to edit the given code to get the similar output in the example. Please answer it in step by step format. Thank you!!
edgelist: Loading, representing, and printing an undirected unweighted graph. A basic kind of graph is an undirected, unweighted graph, meaning that the edges are not directional, and each edge doesn't have any additional properties. Here is an example of an undirected, unweighted graph G=(V,E), V={0,1,2,3}, E={(0,1),(0,2),(0,3),(1,3)} of four nodes and four edges:
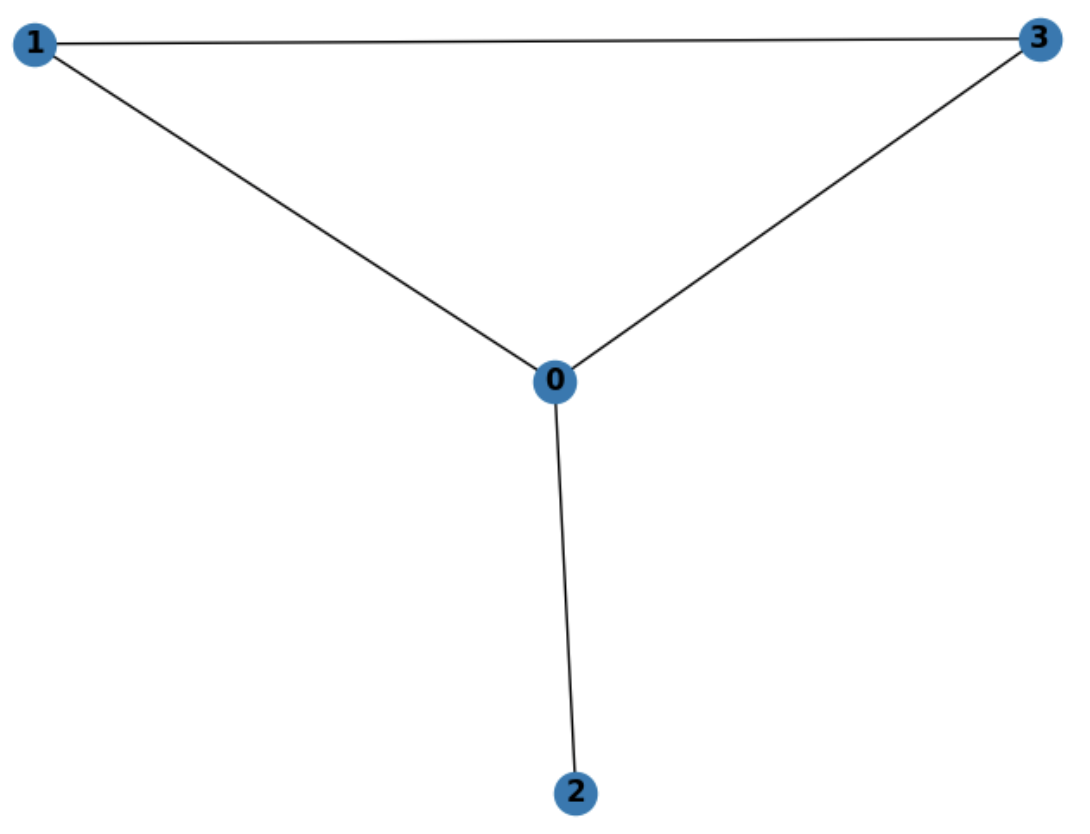
The first graph representation is an adjacency matrixLinks to an external site.. The adjacency matrix of the above graph is:
0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0
The second graph representation is an adjacency listLinks to an external site.. For a graph consisting of N nodes, the adjacency list data structure is an array of N separate linked lists for each node p, where each link in the linked list records a node q if the edge (p,q) exists. For example, the adjacency list representation of the above graph is:
0->1->2->3->/ 1->0->3->/ 2->0->/ 3->0->1->/
The ->/ indicates a null pointer terminating the linked list.
The third graph representation is by listing the edges of the graph. For example, the edge list of the above graph is:
0 2 0 3 0 1 1 3
Write a C program that:
1. Loads an adjacency matrix representation of an undirected unweighted graph,
2. Holds that graph representation as a adjacency list data structure,
3. Prints out the edge list representation of the graph.
header file: graphutils.h
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
typedef size_t graphNode_t;
typedef struct AdjacencyListNode AdjacencyListNode;
struct AdjacencyListNode {
graphNode_t graphNode; // the destination graph node
double weight; // a weight, if weighted graph, otherwise will be 1.0
AdjacencyListNode* next; // pointer to next linked list node
};
bool almostEqual (double a, double b)
{
return fabs(a - b)
}
// READ INPUT FILE TO CREATE GRAPH ADJACENCY LIST
// Reads adjacency matrices for both undirected and directed graphs.
// Reads adjacency matrices for both unweighted and weighted graphs.
// Returns the number of nodes in the graph; returns 0 if reading failed.
size_t adjMatrixToList (
const char* filename, // path to input file containing adjacency matrix
AdjacencyListNode** adjacencyList
) {
FILE* fp = fopen(filename, "r");
if (!fp) {
perror("fopen failed");
return 0;
}
// first, read the graphNodeCount
size_t graphNodeCount;
fscanf(fp, "%ld", &graphNodeCount);
// next, allocate the linked list heads
*adjacencyList = calloc( graphNodeCount, sizeof(AdjacencyListNode) );
// finally, read the adjacency matrix and allocate linked list nodes
for (size_t adjMatrixRow=0; adjMatrixRow (*adjacencyList)[adjMatrixRow].graphNode = adjMatrixRow; // A note indicating source graph node (*adjacencyList)[adjMatrixRow].next = NULL; for (size_t adjMatrixCol=0; adjMatrixCol double weight; fscanf(fp, "%lf", &weight); if ( !almostEqual(weight,0.0) ) { // if not almost zero, indicating an edge exists AdjacencyListNode* newTop = calloc(1,sizeof(AdjacencyListNode)); newTop->graphNode = adjMatrixCol; newTop->weight = weight; newTop->next = (*adjacencyList)[adjMatrixRow].next; (*adjacencyList)[adjMatrixRow].next = newTop; } } } fclose(fp); return graphNodeCount; } // TRAVERSE AND FREE THE LINKED LISTS, AND FREE THE ADJACENCY LIST void freeAdjList ( size_t graphNodeCount, AdjacencyListNode* adjacencyList ) { // example of how to traverse the graph adjacency list for (size_t source=0; source AdjacencyListNode* dest = adjacencyList[source].next; // list iterator while (dest) { AdjacencyListNode* temp = dest; dest = dest->next; // iterator moves to next free(temp); } } free(adjacencyList); } Edit the code given below: #include "../graphutils.h" // header for functions to load and free adjacencyList // A program to print the edge list of a graph given the adjacency matrix int main ( int argc, char* argv[] ) { // FIRST, READ THE ADJACENCY MATRIX FILE AdjacencyListNode* adjacencyList = NULL; size_t numNodes = adjMatrixToList ( argv[1], &adjacencyList ); // NEXT, TRAVERSE THE ADJACENCY LIST AND PRINT EACH EDGE, REPRESENTED AS A PAIR OF NODES // Example of traversing the adjacency list is in the freeAdjList() function in graphutils.h for (size_t source=0; source AdjacencyListNode* dest = adjacencyList[source].next; while(dest) { graphNode_t destNodeName = (*dest).graphNode; printf("%ld %ld ", source, destNodeName); dest = dest->next; } } // NOW, BE SURE TO FREE THE ADJACENCY LIST freeAdjList ( numNodes, adjacencyList ); return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


