Question: Please read the attached article and write a reflection/ a brief summary of the article including: - What is the purpose of this document? -
Please read the attached article and write a reflection/ a brief summary of the article including:
- What is the purpose of this document?
- What are the key arguments and supporting evidence?
-Summarize the framework
-Summarize the case studies
- Your opinion of the article













ive updated the pictures with more clear images
clearer imaged have been added to clarify photos
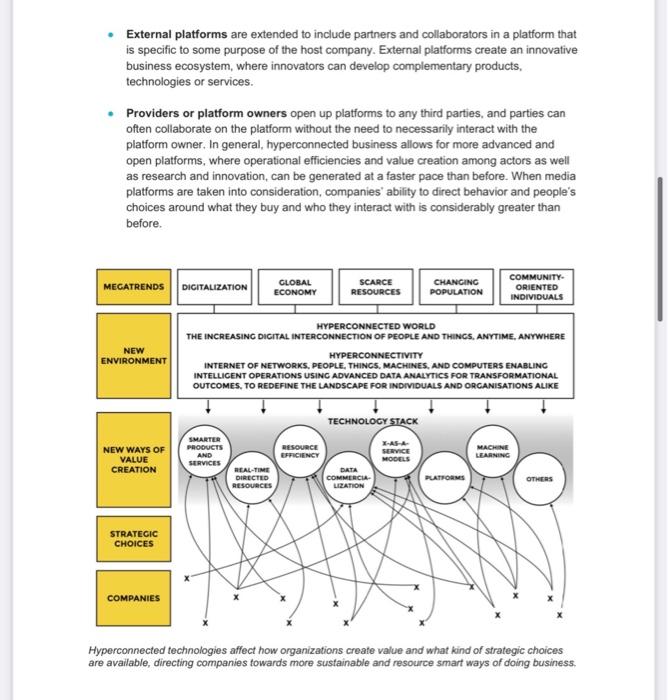
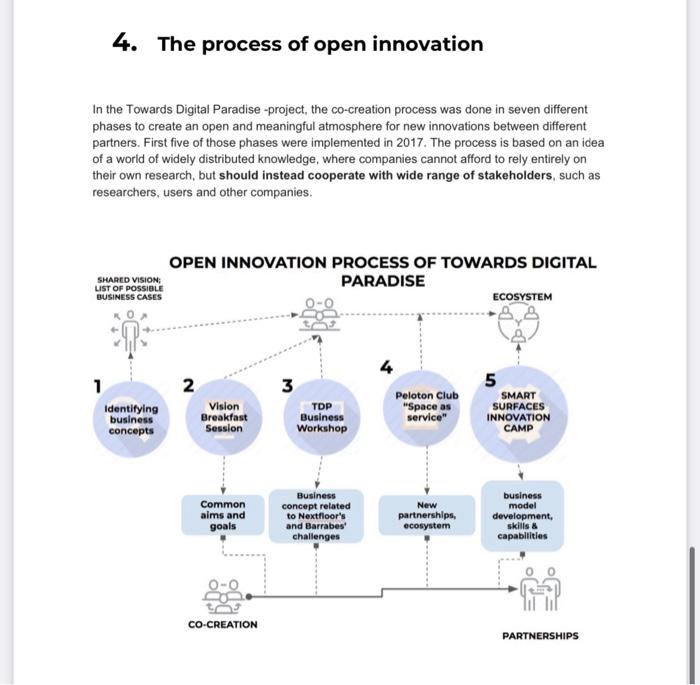
1. The world is becoming hyperconnected rytter og thaigal www HT- Ger pur tes www.es . 2. Six value creatlon models of hyperconnected business eatpar www2015 www.elem www.com use there when ofte water te weet www.free en we wy 1. Smarter products and services Am www wwwww - 2. hate .. wwwwww wwwwwww www.ro is tnps 3.tusourermainy - whosen 4. Data commercialisation New ways of using costs take place the Gluing sing date internally when whichacorns.com Selling or giving data to come became an improve the possible to rest where 5. *X-a-as-service-models Some of the greater the defender aste Ma+seruka passed Medievaleno+Gaana Ocaraya Servitation. In this modelos funcionamentform Business models detail that concertes cerca de product results and Povlservers that has there to read andmete na offerentiation and cont design providing to One aspect of the essence Businesses the transfer of risk on the customer to se pred need themed to produce the service. This naturally our new forms of searagement with them, which is made www ways to come. Herconected 6. Platforms The larger social role of plomes from brusness we discussed The wholeheads site Generally, burtums can be divided into Internal platforms tous on companies operationssences and products Internal pompe Produse efficient and peoproduisant sences Eternal platforms a 200 calorators in a patan har pompen business cystem, where moscador often colabore on the pistoot te meer with the en plsforms where personal eficiencies and anong or as well a serch and innocented the fore when nota piose can' choles around what they by and who they considerata MET GENERO TOODEDA NEWATI !!! ATGE COME coge afweg. ) Phases of the process Theme www we The Pour tools we used in the ce CA 5. Conclusions Hoe L w 6. About Naked Approach & TOP VIL at were and som prohrwehr Tel. indepe De 1. The world is becoming hyperconnected Human beings, machines and their surroundings are connected by trillions of tiny sensors, which make our world hyperconnected. This development is called Internet of Things, Internet of Everything, Programmable World and so on. These are all terms used to describe the development towards evermore enhanced exchange of information between us and our surroundings. The hyperconnected technologies change the way to do business. The future business is all about recognising the best new ways to create efficiency through better use of technology and data. The joint effects of digitalisation, new sensor technologies, machine learning, robotics, printable electronics, and the ability to gather vast amounts of data and often use it in real-time alter the way businesses create and capture value now and in the future. This briefing paper firstly describes four business cases of hyperconnected technologies that have been co-created together with companies and researchers in the project called Towards Digital Paradise. The paper shows how the increased availability of data moves businesses from hunch to insight - in other words, how to base value creation on facts rather than educated guesses. Secondly, this briefing paper aims to recognize the possibilities of using hyperconnected technologies to improve human capabilities in the digitalized era. Towards Digital Paradise is funded by Business Finland (former Tekes). The research teams come from Demos Helsinki, VTT, Tampere University of Technology, the University of Lapland, and the University of Oulu, which collaborate with Nokia. Skandal Technology. Streamr. Innovation+. Napapiiri Hub of Barrabes. Premix and group of other companies. 2. Six value creation models of hyperconnected business In the first phase of the Towards Digital Paradise -project, six distinct value creation models were identified to describe the technological development that allows new perspectives to business and strategy (Demos Helsinki 2016). These are obviously not the only ones, but they play a key role in how successful businesses shape their operations, management strategy, and both long and short-term development. You may have heard of them before - many are used by companies now, and currently form the foundations of some of the largest businesses in the world. The new insight is that these value creation models will form the basis for value creation in the hyperconnected world, and with some of them not yet mainstream, their effects will span the next decades. With the right mix of these six models, organizations are able to capture temporary monopoly positions, if they choose the right context in which to apply them. These six value creation models are introduced below in greater detail. 1. Smarter products and services Products and services can be smart on three levels: Being able to sense its own operation is a quality already embedded into many products today. A product can "develop its own consciousness by having its own feedback loop, and be able to communicate information regarding maintenance, for example. A typical example of this is the warning light in a car's control panel, which lights up to inform you when something is wrong. Being aware of its environment means that the product can interact with information from its surroundings and respond accordingly. For example, a smart radiator can detect the weather outside and adjust inside temperature depending on this input. Being aware of its context represents more sophisticated understanding. To continue with the thermostat example, in this case the thermostat would be able to adjust its temperature in anticipation of the personal preferences of individuals entering the room. For example, when a tired guest ready to go to bed is about to arrive, the room will be set a slightly cooler temperature in anticipation. 2. Real-time directed resources Real-time directed resources can be understood through three levels, which are already used by businesses to some extent. Based on the type of the information used, they can be categorized followingly: Using historical information can offer an advantage when investigating hidden correlations in the company's past data, for example. Using historical information can pinpoint the factors of previous decision-making and guide behavior to correct mistakes made in the past. Using instant information in operations helps businesses find failures and respond to critical situations faster. Instant information can pinpoint the factors that are in need of attention right now, and help prioritising action and behavior to correct mistakes as fast as possible Using predictive information is becoming more and more feasible, and it offers big gains for example in healthcare. Using predictive information can pinpoint issues and challenges before they arise, and offer insight for better decision-making by providing information from the future". 3. Resource efficiency Resource efficiency can be categorised into four models (Demos Helsinki 2015): Sharing simply means increasing the utilisation rate of physical resources by distributing and allocating their use more efficiently. This is a very typical and the most commonly used model to improve resource smartness. Optimisation refers to improving energy efficiency through, for example, new data management, smart energy management and metering applications, as well as track-and-trace logistics Refurbishment refers to improving the efficiency of physical assets by integrating sensors into existing things, in order to create energy efficiency in the existing value chain, product development and manufacturing. Dematerialisation and smart substitution mean replacing resource-intensive practices with new solutions. Examples include teleconferencing, virtual reality applications, and the replacement of energy-intensive animal proteins in the food production chain with something that takes fewer resources to produce. 4. Data commercialisation New ways of using data take place in three spheres Giving, using or selling data internally within the company's internal value chain, which a lot of companies are already doing. Selling or giving data to companies in the same value chain can improve the competitiveness of the business ecosystem due to new information links. Selling or giving data externally to selected value networks (or to anyone) offers possibilities to create value within a larger business ecosystem. 5. "X-a-as-service" -models Some of the greatest potential in the business models of today's world lies in the change from product sales to X-as-a-service models, often referred to as the outcome Economy or Servitization. In this model, abilities or functions (such as mobility), are offered in the form of a service, traditionally through the purchase of a product (such as a car). X-as-a-service business models entail that companies compete in their ability to produce results and provide services rather than their ability to sell products. These service models aim at differentiation and/or cost leadership, often providing both. One aspect of the X-as-a-service business model is the transfer of risk from the customer to the provider, since the providing companies are in charge of the assets used to produce the service. This naturally requires new forms of asset management within the fim, which is made easier by new ways to control connected assets through smart solutions. Hyperconnected business allows the use of X-as-a-service models in many different domains. 6. Platforms The larger social role of platforms and the effects of platforms for business are discussed in Theses 2 and 3, so what is described here are the more technical business definitions in brief. Generally, platforms can be divided into three categories: Internal platforms focus on companies' own operations, services and products. Internal platforms are assets organised in a common structure, which helps the company produce efficient and innovative operations, products, and services. External platforms are extended to include partners and collaborators in a platform that is specific to some purpose of the host company. External platforms create an innovative business ecosystem, where innovators can develop complementary products, technologies or services. Providers or platform owners open up platforms to any third parties, and parties can often collaborate on the platform without the need to necessarily interact with the platform owner. In general, hyperconnected business allows for more advanced and open platforms, where operational efficiencies and value creation among actors as well as research and innovation, can be generated at a faster pace than before. When media platforms are taken into consideration, companies' ability to direct behavior and people's choices around what they buy and who they interact with is considerably greater than before. MEGATRENDS DIGITALIZATION GLOBAL ECONOMY SCARCE RESOURCES CHANGING POPULATION COMMUNITY ORIENTED INDIVIDUALS NEW ENVIRONMENT HYPERCONNECTED WORLD THE INCREASING DIGITAL INTERCONNECTION OF PEOPLE AND THINGS. ANYTIME, ANYWHERE HYPERCONNECTIVITY INTERNET OF NETWORKS, PEOPLE, THINGS, MACHINES, AND COMPUTERS ENABLING INTELLIGENT OPERATIONS USING ADVANCED DATA ANALYTICS FOR TRANSFORMATIONAL OUTCOMES, TO REDEFINE THE LANDSCAPE FOR INDIVIDUALS AND ORGANISATIONS ALIKE TECHNOLOGY STACK SMARTER PRODUCTS AND SERVICES NEW WAYS OF VALUE CREATION SERVICE MODELS MACHINE LEARNING REAL-TIME DIRECTED RESOURCES RESOURCE EFFICIENCY DATA COMMERCIA LIZATION PLATFORMS OTHERS STRATEGIC CHOICES COMPANIES Hyperconnected technologies affect how organizations create value and what kind of strategic choices are available, directing companies towards more sustainable and resource smart ways of doing business. The above figure shows the six value creation models as strategic choices, through which individual companies make use of the new hyperconnected business environment. It is important to realize that there are vast amounts of underlying devices, sensors, applications, and other technology that are not discussed in depth here. These underlying technological tools can be termed the "technology stack" (e.g. Porter & Heppelmann 2014). In short, it captures the technical features that the processes, products, and services require: data, analytics, real-time connectivity, cloud-services, application platforms, sensors, databases, network communication, product software, product hardware, application of external information sources, and ways to integrate all these to business systems. Through analysis of these six value creation models, companies can gain more in-depth understanding of how they can benefit from the hyperconnected technologies. All materials related to this part of the research are available at www.hyperconnectedbusiness.com, where it is also possible to create your own personalised report on value creation in the hyperconnected world. 3. Four business cases towards digital paradise Business cases from TDP are technology-oriented in the sense that all of the cases wish to push new, disruptive technology to existing business cases. Having many different potential customer segments showcase the multiple opportunities present for the technologies developed in the Digital Paradise -project. This, in turn, means that the essential step for these cases is the identification of a key customer segment and then focusing on the value proposition that is specifically relevant for this customer segment. This is a critical step towards a successful business model. 1. Nokia's KUHA Nokia's KUHA provides a simple and affordable mobile network to areas without coverage, or places where it is too expensive to deploy mobile networks. Here, the emphasis is in the local mobile networks with no connection to outside world. The services could for example enable connection in small communities consisting of 3000-5000 people. Even though this was only a local network, it would still connect these people with each other and enable local services. 2. Ambient communication service Skandal Technology is developing an ambient communication service, which uses intelligent lighting service to attract people's attention, guiding and providing information for them. Potential scenarios include public spaces, large premises and other environments, where people need to be communicated with (route finding, promotional services, other communication via intelligent lighting service). 3. Modular smart floor Nextfloor is an integrative modular floor structure that helps to bring sensoring systems and utility connections exactly where they are needed without costly construction work and permanent structures. The product is based on roll-to-roll manufacturable, flexible LED luminaire concepts. 4. Smart shopping malls Working with outside ecosystems and parties, the Towards Digital Paradise -project arranged a themed workshop in cooperation with Napapiiri Hub. The purpose was to see what could be achieved with the technologies developed in the TDP retail domain and what could be the different scenarios in the future mall. These business scenarios are implementations of cases 1-3 in the retail domain: Chameleon Mall: The concept of the future of malls, that turns them into highly adaptable spaces. This is done through analytics, adapting usage and dynamizing the expression. For example, better shopping experiences are created by personalization of the experience. Virtual one time bonus token: The concept is based on getting information about consumer needs without compromising privacy. Virtual one time bonus token is a digital platform for malls with API's for chains. If a customer grab a card when entering the shop, it profiles the customer automatically and help in treasure hunting. It is personalized, instant card, that makes the experience of shopping entertaining and helps to do ethical choices. Fitting room cafe: The concept brings the benefits of online-shops into the physical walls and makes the shopping experience easy and fast. It refers to modular cells ("fitting room cafes) with printed mirror-like displays with AR. It offers to customers good way to test products, get purchase recommendations and find out which products are available. 4. The process of open innovation In the Towards Digital Paradise -project, the co-creation process was done in seven different phases to create an open and meaningful atmosphere for new innovations between different partners. First five of those phases were implemented in 2017. The process is based on an idea of a world of widely distributed knowledge, where companies cannot afford to rely entirely on their own research, but should instead cooperate with wide range of stakeholders, such as researchers, users and other companies. SHARED VISION; LIST OF POSSIBLE BUSINESS CASES OPEN INNOVATION PROCESS OF TOWARDS DIGITAL PARADISE ECOSYSTEM 2 3 1 Identifying business concepts Vision Breakfast Session TOP Business Workshop Peloton Club Space as service" 5 SMART SURFACES INNOVATION CAMP Common alms and goals Business concept related to Nextfloor's and Barrabes challenges New partnerships, ecosystem business model development. skills & capabilities CO-CREATION PARTNERSHIPS Phases of the process PHASE 1: Identifying business concepts The process started by identifying potential business concepts and the points of collaboration with companies and researchers. PHASE 2: Creating shared vision In voluntary collaboration for innovation happening between different types of actors, it is very important to be explicit about the motivations of each actor and to find a shared vision that gives a clear reason for the collaboration. Finding a shared vision and a common objective helps to build trust that is crucial for sharing ideas, information or resources and working together. However, the shared vision cannot just be stated by an individual actor, but it needs to be formulated together, which we did in the workshops. Another important factor that needs to be achieved is the spirit of the collaboration, as it is crucial to understand that we are not competing with each other. PHASE 385: Developing business models With identified business concepts we worked together with the methods of co-creation to find out the business potential of these concepts. We did this together with researchers, business experts, potential customers and users, and created service models for technology products and roadmaps to enter to markets. Part of these phases will be done during 2018 PHASE 4: Creating ecosystem in Peloton Club The important phase of the process was to build open and trust-based model, where partners are able to ideate, transfer and even transform knowledge more openly than in conventional innovation collaboration. In Peloton Club, the companies were able to present their concepts, as well as find new partnerships and customers. Four tools we used in the co-creation sessions Speakers' insight: Understanding business development, food for thoughts Canvases: Asking right questions, document and visualise thinking, structure working Mentoring: Helping to solve the challenges, widen the perspective Peer mentoring: Helping to widen the perspective and answer the questions 5. Conclusions Hyperconnected technologies change how companies do business and create value, by gathering more precise insights for better decision-making. In the era of hyperconnected business, we have an unprecedented amount of data available. This means that we are able to coordinate resources and produce value in new ways. Hyperconnectivity enables a new framework of value creation, as demonstrated in the six value creation models in this briefing paper. Additionally, to create successful business cases in the changing competitive environment, we need to understand the following conclusions. 1. Digitalization and other megatrends require more resource efficient ways of operating Companies in all industries are affected by this change. 2. Nevertheless, digitalization and the new environment do not necessarily change the basic tenets of strategy: to gain competitive advantage, companies have to be able to differentiate themselves to command a price premium and operate at a lower cost than their rivals, or both. The value proposition for the paying customer needs to be clear. 3. The New Competitive Environment is defined by the opportunities allowed by Hyperconnectivity - the Internet of networks, people, things, machines, and computers enabling intelligent operations using advanced data analytics for transformational outcomes that redefine the landscape for individuals and organizations alike. 4. To gain successful business cases, instead of technology push, understanding on users and changing environment are needed. 5. To reach the previous point, co-creation in an ecosystem is a good tool. This requires openness and trust between all the partners involved in the ecosystem. 6. About Naked Approach & TDP The Naked Approach strategic opening will start a research and development path towards a significant paradigm shift in the relationship between us: the humans, the citizens, the users and the digital world: a change from gadget centric to user centric and gadget free Naked digital interface. In our vision, the digital surroundings will form an "omnipotential" environment around the user, providing all the information, tools, and services that the user needs in his or her everyday life in the Hyper connected society of 2020's and 2030's. The research program is built on the strong Finnish assets: the Nordic excellence in the user centric design, and the globally respected excellence in ICT, including the emerging technologies in electronics manufacturing and integration. Our project team covers the major Finnish research institutes: VTT, Tampere University of Technology, Aalto University, the University of Lapland, and the University of Oulu, complemented with Demos Helsinki, an agile partner for the emerging businesses and future needs research. See more at www.nakedapproach.fi. Towards Digital Paradise -project develops new businesses that are related to sensor technology, help to solve societal problems and are based on Nordic values such as trust privacy and participation. The project is part of a Naked approach -project, where Finnish universities develop sensor technology, energy harvesters and printed electronics. In the Towards Digital Paradise -project, researchers and companies find ways to commercialize new technologies. Demos Helsinki is responsible of finding future business Towards Digital Paradise models that create Nordic perspective to gadget-free society. 1. The world is becoming hyperconnected rytter og thaigal www HT- Ger pur tes www.es . 2. Six value creatlon models of hyperconnected business eatpar www2015 www.elem www.com use there when ofte water te weet www.free en we wy 1. Smarter products and services Am www wwwww - 2. hate .. wwwwww wwwwwww www.ro is tnps 3.tusourermainy - whosen 4. Data commercialisation New ways of using costs take place the Gluing sing date internally when whichacorns.com Selling or giving data to come became an improve the possible to rest where 5. *X-a-as-service-models Some of the greater the defender aste Ma+seruka passed Medievaleno+Gaana Ocaraya Servitation. In this modelos funcionamentform Business models detail that concertes cerca de product results and Povlservers that has there to read andmete na offerentiation and cont design providing to One aspect of the essence Businesses the transfer of risk on the customer to se pred need themed to produce the service. This naturally our new forms of searagement with them, which is made www ways to come. Herconected 6. Platforms The larger social role of plomes from brusness we discussed The wholeheads site Generally, burtums can be divided into Internal platforms tous on companies operationssences and products Internal pompe Produse efficient and peoproduisant sences Eternal platforms a 200 calorators in a patan har pompen business cystem, where moscador often colabore on the pistoot te meer with the en plsforms where personal eficiencies and anong or as well a serch and innocented the fore when nota piose can' choles around what they by and who they considerata MET GENERO TOODEDA NEWATI !!! ATGE COME coge afweg. ) Phases of the process Theme www we The Pour tools we used in the ce CA 5. Conclusions Hoe L w 6. About Naked Approach & TOP VIL at were and som prohrwehr Tel. indepe De 1. The world is becoming hyperconnected Human beings, machines and their surroundings are connected by trillions of tiny sensors, which make our world hyperconnected. This development is called Internet of Things, Internet of Everything, Programmable World and so on. These are all terms used to describe the development towards evermore enhanced exchange of information between us and our surroundings. The hyperconnected technologies change the way to do business. The future business is all about recognising the best new ways to create efficiency through better use of technology and data. The joint effects of digitalisation, new sensor technologies, machine learning, robotics, printable electronics, and the ability to gather vast amounts of data and often use it in real-time alter the way businesses create and capture value now and in the future. This briefing paper firstly describes four business cases of hyperconnected technologies that have been co-created together with companies and researchers in the project called Towards Digital Paradise. The paper shows how the increased availability of data moves businesses from hunch to insight - in other words, how to base value creation on facts rather than educated guesses. Secondly, this briefing paper aims to recognize the possibilities of using hyperconnected technologies to improve human capabilities in the digitalized era. Towards Digital Paradise is funded by Business Finland (former Tekes). The research teams come from Demos Helsinki, VTT, Tampere University of Technology, the University of Lapland, and the University of Oulu, which collaborate with Nokia. Skandal Technology. Streamr. Innovation+. Napapiiri Hub of Barrabes. Premix and group of other companies. 2. Six value creation models of hyperconnected business In the first phase of the Towards Digital Paradise -project, six distinct value creation models were identified to describe the technological development that allows new perspectives to business and strategy (Demos Helsinki 2016). These are obviously not the only ones, but they play a key role in how successful businesses shape their operations, management strategy, and both long and short-term development. You may have heard of them before - many are used by companies now, and currently form the foundations of some of the largest businesses in the world. The new insight is that these value creation models will form the basis for value creation in the hyperconnected world, and with some of them not yet mainstream, their effects will span the next decades. With the right mix of these six models, organizations are able to capture temporary monopoly positions, if they choose the right context in which to apply them. These six value creation models are introduced below in greater detail. 1. Smarter products and services Products and services can be smart on three levels: Being able to sense its own operation is a quality already embedded into many products today. A product can "develop its own consciousness by having its own feedback loop, and be able to communicate information regarding maintenance, for example. A typical example of this is the warning light in a car's control panel, which lights up to inform you when something is wrong. Being aware of its environment means that the product can interact with information from its surroundings and respond accordingly. For example, a smart radiator can detect the weather outside and adjust inside temperature depending on this input. Being aware of its context represents more sophisticated understanding. To continue with the thermostat example, in this case the thermostat would be able to adjust its temperature in anticipation of the personal preferences of individuals entering the room. For example, when a tired guest ready to go to bed is about to arrive, the room will be set a slightly cooler temperature in anticipation. 2. Real-time directed resources Real-time directed resources can be understood through three levels, which are already used by businesses to some extent. Based on the type of the information used, they can be categorized followingly: Using historical information can offer an advantage when investigating hidden correlations in the company's past data, for example. Using historical information can pinpoint the factors of previous decision-making and guide behavior to correct mistakes made in the past. Using instant information in operations helps businesses find failures and respond to critical situations faster. Instant information can pinpoint the factors that are in need of attention right now, and help prioritising action and behavior to correct mistakes as fast as possible Using predictive information is becoming more and more feasible, and it offers big gains for example in healthcare. Using predictive information can pinpoint issues and challenges before they arise, and offer insight for better decision-making by providing information from the future". 3. Resource efficiency Resource efficiency can be categorised into four models (Demos Helsinki 2015): Sharing simply means increasing the utilisation rate of physical resources by distributing and allocating their use more efficiently. This is a very typical and the most commonly used model to improve resource smartness. Optimisation refers to improving energy efficiency through, for example, new data management, smart energy management and metering applications, as well as track-and-trace logistics Refurbishment refers to improving the efficiency of physical assets by integrating sensors into existing things, in order to create energy efficiency in the existing value chain, product development and manufacturing. Dematerialisation and smart substitution mean replacing resource-intensive practices with new solutions. Examples include teleconferencing, virtual reality applications, and the replacement of energy-intensive animal proteins in the food production chain with something that takes fewer resources to produce. 4. Data commercialisation New ways of using data take place in three spheres Giving, using or selling data internally within the company's internal value chain, which a lot of companies are already doing. Selling or giving data to companies in the same value chain can improve the competitiveness of the business ecosystem due to new information links. Selling or giving data externally to selected value networks (or to anyone) offers possibilities to create value within a larger business ecosystem. 5. "X-a-as-service" -models Some of the greatest potential in the business models of today's world lies in the change from product sales to X-as-a-service models, often referred to as the outcome Economy or Servitization. In this model, abilities or functions (such as mobility), are offered in the form of a service, traditionally through the purchase of a product (such as a car). X-as-a-service business models entail that companies compete in their ability to produce results and provide services rather than their ability to sell products. These service models aim at differentiation and/or cost leadership, often providing both. One aspect of the X-as-a-service business model is the transfer of risk from the customer to the provider, since the providing companies are in charge of the assets used to produce the service. This naturally requires new forms of asset management within the fim, which is made easier by new ways to control connected assets through smart solutions. Hyperconnected business allows the use of X-as-a-service models in many different domains. 6. Platforms The larger social role of platforms and the effects of platforms for business are discussed in Theses 2 and 3, so what is described here are the more technical business definitions in brief. Generally, platforms can be divided into three categories: Internal platforms focus on companies' own operations, services and products. Internal platforms are assets organised in a common structure, which helps the company produce efficient and innovative operations, products, and services. External platforms are extended to include partners and collaborators in a platform that is specific to some purpose of the host company. External platforms create an innovative business ecosystem, where innovators can develop complementary products, technologies or services. Providers or platform owners open up platforms to any third parties, and parties can often collaborate on the platform without the need to necessarily interact with the platform owner. In general, hyperconnected business allows for more advanced and open platforms, where operational efficiencies and value creation among actors as well as research and innovation, can be generated at a faster pace than before. When media platforms are taken into consideration, companies' ability to direct behavior and people's choices around what they buy and who they interact with is considerably greater than before. MEGATRENDS DIGITALIZATION GLOBAL ECONOMY SCARCE RESOURCES CHANGING POPULATION COMMUNITY ORIENTED INDIVIDUALS NEW ENVIRONMENT HYPERCONNECTED WORLD THE INCREASING DIGITAL INTERCONNECTION OF PEOPLE AND THINGS. ANYTIME, ANYWHERE HYPERCONNECTIVITY INTERNET OF NETWORKS, PEOPLE, THINGS, MACHINES, AND COMPUTERS ENABLING INTELLIGENT OPERATIONS USING ADVANCED DATA ANALYTICS FOR TRANSFORMATIONAL OUTCOMES, TO REDEFINE THE LANDSCAPE FOR INDIVIDUALS AND ORGANISATIONS ALIKE TECHNOLOGY STACK SMARTER PRODUCTS AND SERVICES NEW WAYS OF VALUE CREATION SERVICE MODELS MACHINE LEARNING REAL-TIME DIRECTED RESOURCES RESOURCE EFFICIENCY DATA COMMERCIA LIZATION PLATFORMS OTHERS STRATEGIC CHOICES COMPANIES Hyperconnected technologies affect how organizations create value and what kind of strategic choices are available, directing companies towards more sustainable and resource smart ways of doing business. The above figure shows the six value creation models as strategic choices, through which individual companies make use of the new hyperconnected business environment. It is important to realize that there are vast amounts of underlying devices, sensors, applications, and other technology that are not discussed in depth here. These underlying technological tools can be termed the "technology stack" (e.g. Porter & Heppelmann 2014). In short, it captures the technical features that the processes, products, and services require: data, analytics, real-time connectivity, cloud-services, application platforms, sensors, databases, network communication, product software, product hardware, application of external information sources, and ways to integrate all these to business systems. Through analysis of these six value creation models, companies can gain more in-depth understanding of how they can benefit from the hyperconnected technologies. All materials related to this part of the research are available at www.hyperconnectedbusiness.com, where it is also possible to create your own personalised report on value creation in the hyperconnected world. 3. Four business cases towards digital paradise Business cases from TDP are technology-oriented in the sense that all of the cases wish to push new, disruptive technology to existing business cases. Having many different potential customer segments showcase the multiple opportunities present for the technologies developed in the Digital Paradise -project. This, in turn, means that the essential step for these cases is the identification of a key customer segment and then focusing on the value proposition that is specifically relevant for this customer segment. This is a critical step towards a successful business model. 1. Nokia's KUHA Nokia's KUHA provides a simple and affordable mobile network to areas without coverage, or places where it is too expensive to deploy mobile networks. Here, the emphasis is in the local mobile networks with no connection to outside world. The services could for example enable connection in small communities consisting of 3000-5000 people. Even though this was only a local network, it would still connect these people with each other and enable local services. 2. Ambient communication service Skandal Technology is developing an ambient communication service, which uses intelligent lighting service to attract people's attention, guiding and providing information for them. Potential scenarios include public spaces, large premises and other environments, where people need to be communicated with (route finding, promotional services, other communication via intelligent lighting service). 3. Modular smart floor Nextfloor is an integrative modular floor structure that helps to bring sensoring systems and utility connections exactly where they are needed without costly construction work and permanent structures. The product is based on roll-to-roll manufacturable, flexible LED luminaire concepts. 4. Smart shopping malls Working with outside ecosystems and parties, the Towards Digital Paradise -project arranged a themed workshop in cooperation with Napapiiri Hub. The purpose was to see what could be achieved with the technologies developed in the TDP retail domain and what could be the different scenarios in the future mall. These business scenarios are implementations of cases 1-3 in the retail domain: Chameleon Mall: The concept of the future of malls, that turns them into highly adaptable spaces. This is done through analytics, adapting usage and dynamizing the expression. For example, better shopping experiences are created by personalization of the experience. Virtual one time bonus token: The concept is based on getting information about consumer needs without compromising privacy. Virtual one time bonus token is a digital platform for malls with API's for chains. If a customer grab a card when entering the shop, it profiles the customer automatically and help in treasure hunting. It is personalized, instant card, that makes the experience of shopping entertaining and helps to do ethical choices. Fitting room cafe: The concept brings the benefits of online-shops into the physical walls and makes the shopping experience easy and fast. It refers to modular cells ("fitting room cafes) with printed mirror-like displays with AR. It offers to customers good way to test products, get purchase recommendations and find out which products are available. 4. The process of open innovation In the Towards Digital Paradise -project, the co-creation process was done in seven different phases to create an open and meaningful atmosphere for new innovations between different partners. First five of those phases were implemented in 2017. The process is based on an idea of a world of widely distributed knowledge, where companies cannot afford to rely entirely on their own research, but should instead cooperate with wide range of stakeholders, such as researchers, users and other companies. SHARED VISION; LIST OF POSSIBLE BUSINESS CASES OPEN INNOVATION PROCESS OF TOWARDS DIGITAL PARADISE ECOSYSTEM 2 3 1 Identifying business concepts Vision Breakfast Session TOP Business Workshop Peloton Club Space as service" 5 SMART SURFACES INNOVATION CAMP Common alms and goals Business concept related to Nextfloor's and Barrabes challenges New partnerships, ecosystem business model development. skills & capabilities CO-CREATION PARTNERSHIPS Phases of the process PHASE 1: Identifying business concepts The process started by identifying potential business concepts and the points of collaboration with companies and researchers. PHASE 2: Creating shared vision In voluntary collaboration for innovation happening between different types of actors, it is very important to be explicit about the motivations of each actor and to find a shared vision that gives a clear reason for the collaboration. Finding a shared vision and a common objective helps to build trust that is crucial for sharing ideas, information or resources and working together. However, the shared vision cannot just be stated by an individual actor, but it needs to be formulated together, which we did in the workshops. Another important factor that needs to be achieved is the spirit of the collaboration, as it is crucial to understand that we are not competing with each other. PHASE 385: Developing business models With identified business concepts we worked together with the methods of co-creation to find out the business potential of these concepts. We did this together with researchers, business experts, potential customers and users, and created service models for technology products and roadmaps to enter to markets. Part of these phases will be done during 2018 PHASE 4: Creating ecosystem in Peloton Club The important phase of the process was to build open and trust-based model, where partners are able to ideate, transfer and even transform knowledge more openly than in conventional innovation collaboration. In Peloton Club, the companies were able to present their concepts, as well as find new partnerships and customers. Four tools we used in the co-creation sessions Speakers' insight: Understanding business development, food for thoughts Canvases: Asking right questions, document and visualise thinking, structure working Mentoring: Helping to solve the challenges, widen the perspective Peer mentoring: Helping to widen the perspective and answer the questions 5. Conclusions Hyperconnected technologies change how companies do business and create value, by gathering more precise insights for better decision-making. In the era of hyperconnected business, we have an unprecedented amount of data available. This means that we are able to coordinate resources and produce value in new ways. Hyperconnectivity enables a new framework of value creation, as demonstrated in the six value creation models in this briefing paper. Additionally, to create successful business cases in the changing competitive environment, we need to understand the following conclusions. 1. Digitalization and other megatrends require more resource efficient ways of operating Companies in all industries are affected by this change. 2. Nevertheless, digitalization and the new environment do not necessarily change the basic tenets of strategy: to gain competitive advantage, companies have to be able to differentiate themselves to command a price premium and operate at a lower cost than their rivals, or both. The value proposition for the paying customer needs to be clear. 3. The New Competitive Environment is defined by the opportunities allowed by Hyperconnectivity - the Internet of networks, people, things, machines, and computers enabling intelligent operations using advanced data analytics for transformational outcomes that redefine the landscape for individuals and organizations alike. 4. To gain successful business cases, instead of technology push, understanding on users and changing environment are needed. 5. To reach the previous point, co-creation in an ecosystem is a good tool. This requires openness and trust between all the partners involved in the ecosystem. 6. About Naked Approach & TDP The Naked Approach strategic opening will start a research and development path towards a significant paradigm shift in the relationship between us: the humans, the citizens, the users and the digital world: a change from gadget centric to user centric and gadget free Naked digital interface. In our vision, the digital surroundings will form an "omnipotential" environment around the user, providing all the information, tools, and services that the user needs in his or her everyday life in the Hyper connected society of 2020's and 2030's. The research program is built on the strong Finnish assets: the Nordic excellence in the user centric design, and the globally respected excellence in ICT, including the emerging technologies in electronics manufacturing and integration. Our project team covers the major Finnish research institutes: VTT, Tampere University of Technology, Aalto University, the University of Lapland, and the University of Oulu, complemented with Demos Helsinki, an agile partner for the emerging businesses and future needs research. See more at www.nakedapproach.fi. Towards Digital Paradise -project develops new businesses that are related to sensor technology, help to solve societal problems and are based on Nordic values such as trust privacy and participation. The project is part of a Naked approach -project, where Finnish universities develop sensor technology, energy harvesters and printed electronics. In the Towards Digital Paradise -project, researchers and companies find ways to commercialize new technologies. Demos Helsinki is responsible of finding future business Towards Digital Paradise models that create Nordic perspective to gadget-free society Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


