Question: Please read: The chapter is too long and i really cannot send it via here. can you suggest any other way to sent the chapter
Please read: The chapter is too long and i really cannot send it via here. can you suggest any other way to sent the chapter
3. Learning objectives or competencies covered by the course and a supporting or enabling objective(i.e., an objective that has to be reached in order for the learning objective to be accomplished).
4. The format of the content and course expectations. Expectations might relate to the type of content to be covered, how the content will be presented, and the structure of the content.
5. Delivery method for the content (e.g., online, classroom, blended learning). Design Document A design document can be used to guide the development of training and to explain the training to managers, SMEs, reviewers, or other trainers. Table 5.4 shows a design document template.38 Information for the design document is based on the information obtained from the needs assessment discussed in Chapter Three
The level of detail in the design document can vary. Scope of project includes the goals, outcomes, or achievement expectations for trainees; a description of the trainees; a description of how long it will take to develop the course and the checkpoints or tasks that need to be completed as the course is developed; and the length of the course. The length of a course is determined by considering trainees abilities and their availability for training, the resources needed for training, whether the course is part of a larger curriculum or is a stand-alone course, and the need to develop modules in order to provide an opportunity for trainees to practice concepts and skills to avoid being overwhelmed. Delivery includes what the course will cover, how it will be delivered (e.g., face-to-face or online), an estimate of the training time, and the identification of any special conditions or issues that may affect the course (e.g., problems getting equipment for video role-plays and providing feedback). Objectives refers to the course or program objectives. Those are broader summary statements of the purpose of the program. Resources refers to the materialscases, DVDs, videos, models, process maps, podcasts, lesson plans, or guides for use by the facilitator or participantsthat need to be purchased or developed for the course. Who is involved includes trainers, program designers, and individuals who will be involved in the design, delivery, and evaluation of the program. The topical outline includes a brief outline of the topics that will be covered in the program. Administration and evaluation refers to who will be in charge of course scheduling, how trainees will enroll, how the course will be evaluated, and who will review and update the course. Links to other programs refers to any other needs, such as a train-the-trainer program or manager introduction or kickoff for the program. Table 5.5 shows a simple design document for the performance appraisal review course designed to increase managers effectiveness in conducting performance appraisal reviews. Performance appraisal review sessions are meetings between a manager and employee, during which the strengths and weaknesses of the employees performance are discussed and improvement goals agreed upon.
 charts, or markers that may be used in instruction. Any exercises needed for trainees practice or preparation, such as readings, role-play exercises, assessments, or pretests, need to be ordered or reproduced (after copyright permission is obtained). In considering instructor and trainee activity, the focus should be on ensuring that the lesson has as many features of a positive learning process as possible, including communication of objectives.
charts, or markers that may be used in instruction. Any exercises needed for trainees practice or preparation, such as readings, role-play exercises, assessments, or pretests, need to be ordered or reproduced (after copyright permission is obtained). In considering instructor and trainee activity, the focus should be on ensuring that the lesson has as many features of a positive learning process as possible, including communication of objectives.
| For Learning That Requires | Suggested Training Rooms |
| High collaboration, low self-direction | Classroom with breakout rooms Lecture hall with breakout rooms |
| High collaboration, high self-direction | Breakout rooms Project room Conference room |
| Low collaboration, low self-direction | Classroom Computer classroom Lecture hall |
| Low collaboration, high self-direction | Distance learning room Media lab Computer la |
An Example of Program Design
Consider the steps that Saudi Aramco, an oil company headquartered in Dhahran, Saudi Arabia, took to develop a program to train geoscientists and petroleum engineers to en- courage critical thinking and exploration of options.45 To develop the program, they relied on a development team, including an instructional designer, a technical writer, a graphics professional, a professional development advisor, and a subject-matter expert. The pro- gram included courses, modules within the courses, and activities within the modules. The program design included the following steps:
- They worked with key job performers to determine what work processes and tasks were considered critical for effective performance and to identify if they could be improved through training.
- Structured interviews were conducted and they observed jobs to collect data about job functions, tasks within those functions, key performance elements included in the tasks, important job outcomes, and the knowledge required to perform the tasks.
- Work processes and tasks that needed training were identified. The team analyzed the tasks and identified ways to achieve important performance outcomes. This resulted in a framework to show how work gets done.
- The tasks were analyzed to design the content and sequence the course activities. This involved identifying how to combine concepts and tasks into modules.
- Program topics were identified as well as how they would be delivered, and the order in which they would be trained was identified. Also, program prerequisites and evaluation outcomes were discussed.
- Module objectives, outcomes, sequence, instructional methods, and practice activities were developed. Learners were required to demonstrate the desired performance level before returning to their jobs.
- Media, tools, and equipment needed for each activity included in the modules were chosen. These choices were based on the actions expected from learners.
CASE # 1: TRAINING FOR STUDENT SERVICE SPECIALISTS
As a part of the Vice Chancellor's initiative to remove " barriers to learning" at UNITECH, private university in Petaling Jaya, Selangor, an analysis of student services operations was conducted. The analysis revealed that the barriers deemed most important by students were those that would delay or prevent them from registering for classes. These barriers fell into three areas:
- Resolving issues relating to fines accrued over the previous terms (e.g., library, parking, late fees)
- Completing forms accurately and meeting processing deadlines for financial aid in time to enroll in classes.
- Acquiring appropriate advice so that they enrolled in the right classes (avoiding the problems associated with drops and adds)
As a result of this analysis, the university decided to create a new position called student service specialist (SSS). The job descriptions are presented here.
Essential Duties
- Provide and ensure that student support staff provide positive student service experience throughout the work unit, including greeting departmental students in person or over the telephone, identifying their needs, obtaining necessary and appropriate information, and processing student requests in a manner that will best meet the needs of the student.
- Monitor staff and ensure that students perceive student service support staff as treating them with courtesy, respect, tact, and a sincere desire to meet their needs.
- Provide mediation and resolution to student complaints and requests as long as they are consistent with departmental policies.
- Communicate to students the departmental policies and procedures related to their needs and provide students with the appropriate forms and instructions.
- Design and implement systems to ensure that forms turned in by students are the correct forms for their service request and that they are complete and as accurate as possible.
- Work with the appropriate departmental administrator to identify the training needs of designated support staff in the work unit who provide direct student service.
- Identify processes and procedures in the department that are causing problems for students, and work with department management toward their improvement and implementation.
- Develop and maintain a network of contacts with other university departments that commonly interface with the work unit.
- Interact with other university departments to resolve a student's problem or meet the student's needs.
- Receive, read, and interpret correspondence, and determine proper handling. Perform other related duties as assigned.
Working Conditions
Work is performed in an office environment or in other settings as appropriate.
Required Qualifications
- Ability to read, write, interpret instructions, perform basic arithmetic, and communicate orally and in writing
- Computing skills sufficient to use work processing and spreadsheet applications and to perform file management and data input/retrieval functions are necessary. Knowledge of specific software applications and university information systems utilized in the work unit assigned is a plus.
- Good supervisory skills
- The ability to communicate accurately and pleasantly with students from a diverse background
- The ability to understand university and regulatory policies, procedures, and regulations and to ensure understanding of these while working under pressure.
- Possess effective problem-solving abilities.
- Have good conflict management skills
Those hired without the preceding competencies will undergo training before assuming job responsibilities. During the training period, these individuals will be put under probation. Upon successful and satisfactory completion of the training, the classification will be changed to permanent. Failure to complete training successfully will result in termination of employment or reassignment to another position, at the discretion of the university.
After the position was posted and advertised, 25 applicants were selected. Unfortunately, only seven applicants were assessed as demonstrating the desired level of problem solving and student service knowledge and skills. You are assigned the challenge of designing the training program for the 25 Student Service Specialists, who must complete training before they become permanent employees.
Questions:
- Design a training program for the 25 candidates to go through to prepare them for the job.
- In designing the training program, you may choose to focus on only one or two modules based on the case above (modules refer to training modules for example: - communication skills, problem solving, conflict management, supervisory skills etc.)
- In designing the training program use the knowledge and skills that you acquire from the chapter on Program Design (Chapter 5 in the textbook given)
- Use the design document template (see Table 5.4 in textbook) as well as the detailed lesson plan (see Table 5.6 in textbook) as a guide on how to design a training program.
- Explain and elaborate on the items contained in the design document template and lesson plan to show how the program will be carry out. You may add other information that you think is necessary to design a complete and proper training program.
(20 MARKS)
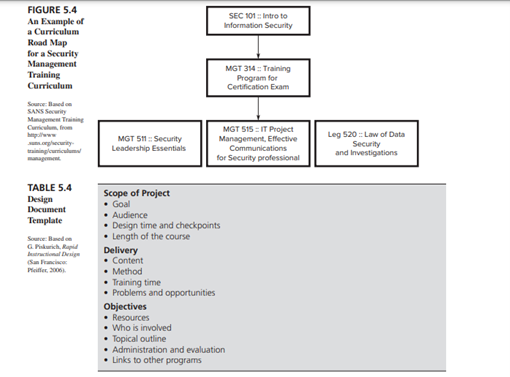
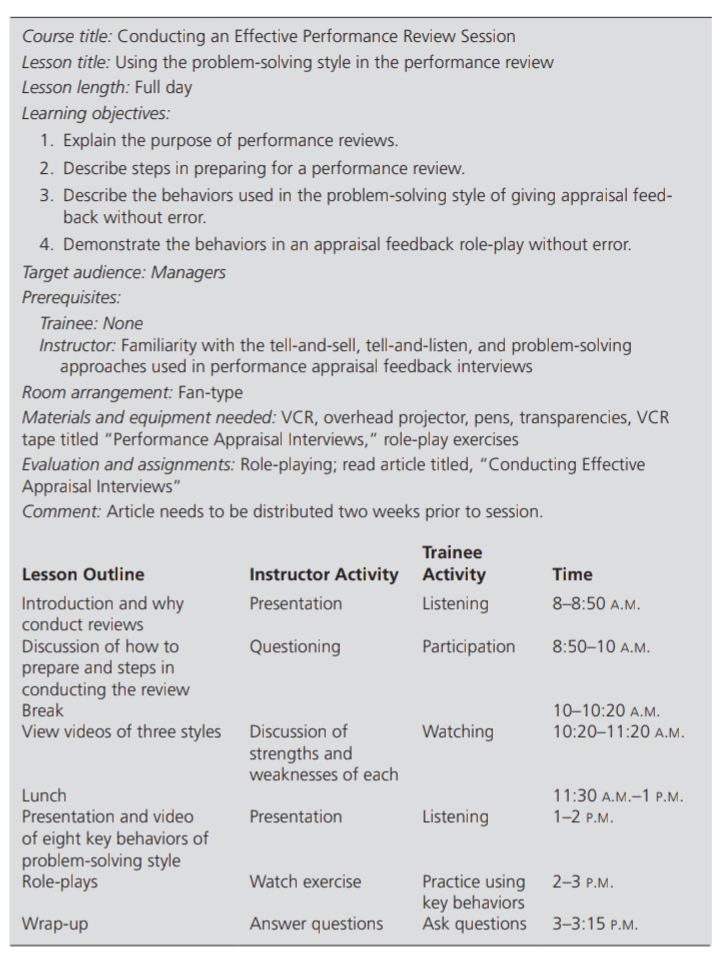
SEC 101: Intro to Information Security FIGURE 5.4 An Example of a Curriculum Road Map for a Security Management Training Curriculum MGT 314 Training Program for Certification Exam SANS Security Management Training MGT 511 Security Leadership Essentials MGT 515 : IT Project Management, Effective Communications for Security professional Leg 520 : Law of Data Security and Investigations plearestler| TABLE 5.4 Design Document Template Source: Belce GP, Rap Piffer 2006 Scope of Project Goal Audience Design time and checkpoints Length of the course Delivery Content Method Training time Problems and opportunities Objectives Resources Who is involved Topical outline Administration and evaluation Links to other programs Course title: Conducting an Effective Performance Review Session Lesson title: Using the problem-solving style in the performance review Lesson length: Full day Learning objectives: 1. Explain the purpose of performance reviews. 2. Describe steps in preparing for a performance review. 3. Describe the behaviors used in the problem-solving style of giving appraisal feed- back without error. 4. Demonstrate the behaviors in an appraisal feedback role-play without error. Target audience: Managers Prerequisites: Trainee: None Instructor: Familiarity with the tell-and-sell, tell-and-listen, and problem-solving approaches used in performance appraisal feedback interviews Room arrangement: Fan-type Materials and equipment needed: VCR, overhead projector, pens, transparencies, VCR tape titled "Performance Appraisal Interviews," role-play exercises Evaluation and assignments: Role-playing; read article titled, "Conducting Effective Appraisal Interviews" Comment: Article needs to be distributed two weeks prior to session. Lesson Outline Trainee Instructor Activity Activity Presentation Listening Time 88:50 A.M. Questioning Participation 8:50-10 A.M. Introduction and why conduct reviews Discussion of how to prepare and steps in conducting the review Break View videos of three styles 10-10:20 A.M. 10:2011:20 A.M. Watching Discussion of strengths and weaknesses of each 11:30 A.M.-1 P.M. 1-2 P.M. Presentation Listening Lunch Presentation and video of eight key behaviors of problem-solving style Role-plays Watch exercise 2-3 P.M. Practice using key behaviors Ask questions Wrap-up Answer questions 3-3:15 P.M
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


