Question: please read the following case study and answer the questions below: please give as much information as you can and answer in paragraphs!!! there is
please read the following case study and answer the questions below: please give as much information as you can and answer in paragraphs!!! there is no word limit so give as much information as you can provide!!!!
1) Discuss the entrepreneurial skills displayed by Buffett during his early days. How did these skills contribute to his success in his later years?
2) Analyze Buffett's investment strategies and comment on Buffett's decision not to invest in technology stocks?


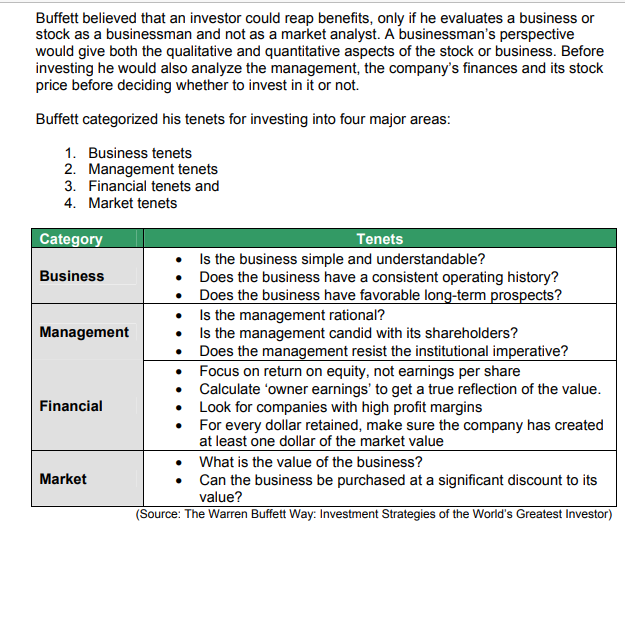



1. Introduction Warren Edward Buffett (Buffett) is the 77-year-old CEO of Berkshire Hathaway Inc. 1 and regarded by many as the world's greatest investor. He is among the richest persons in the world and his estimated net worth is about $62 billion. He is known for his investing style "value investing" m2 and is the most famous disciple of value investing's inventor Benjamin Graham 3. A simple, honest man with grandfatherly looks, Buffett is considered an intellectual genius who makes rapid decisions 4 and decides on a major purchase with just a few days of research. He has figured consistently among the top five in the Forbes magazine's list of the 400 richest Americans (the elite Forbes 400). In the early 90s he was number one and was the only person in the top five whose source of wealth was from the stock market. And for a billionaire, he has a surprisingly frugal life style. Buffett's salary (annual compensation) is meager by most CEO standards (approx. $100,000 ). Buffett still lives in the home he purchased in Omaha, Nebraska, in 1958 for $31,500. 2. Warren Buffett - Early Days "Well, I worked for my grandfather, which was really tough, in the [family] grocery store. But if you gave me the choice of being CEO of General Electric or IBM or General Motors, you name it, or delivering papers, I would deliver papers. I would. I enjoyed doing that. I can think about what I want to think. I don't have to do anything I don't want to do." - Warren Buffett in Fortune. Warren Buffett was born in Omaha, Nebraska in 1930. The only son to his parents Howard (a local stockbroker) and Leila Buffett (they had three children) he showed keen interest in numbers since early childhood. He could remember baseball scores, horseracing odds and first started making money by the age of five by selling gum (lemonade in summer) on the sidewalk near his home. At the age of nine, he collected golf balls from the local golf course along with his friends and repacked \& sold them (earning $3 per day) as per their brands. His favorite childhood books included - 'One -Warren Buffett in 2007 Annual Report, Berkshire Hathaway Buffett's success in the stock market can be attributed to his ability of acquiring businesses or stocks in spite of what the Wall Street had to say about them. Whether it was Buffett's acquisition of a stake in American Express in the early 60 s or his acquisition of stocks of Coca-Cola in the late 80s, Wall Street analysts had thought otherwise. Analysts believed that American Express was on the verge of bankruptcy and Warren Buffett - The Investment Leader (B) Www.casestudyinc.com 5 that there was nothing special about the stocks of Coca-Cola which was trading at $10.96 at the time. However, Buffett went on to acquire a five percent stake in American Express when he observed that customers were still using AmEx cards. His decision proved right as the company gained substantially in later years in the stock market. Similarly, Coca-Cola also performed very well and its stock price rose to $74.50 in less than five years. Another feature of Buffett's strategy was to acquire stocks while they were at historically low prices. This was very unlike common investors who typically discarded their stocks when their value decreased and accumulated stocks when their value increased. Buffett felt that, "The most common cause of low prices is pessimism - sometimes pervasive, sometimes specific to a company or industry. We want to do business in such an environment, not because we like pessimism but because we like the prices it produces. It's optimism that is the enemy of the rational buyer." Buffett believed that an investor could reap benefits, only if he evaluates a business or stock as a businessman and not as a market analvst. A businessman's perspective Buffett believed that an investor could reap benefits, only if he evaluates a business or stock as a businessman and not as a market analyst. A businessman's perspective would give both the qualitative and quantitative aspects of the stock or business. Before investing he would also analyze the management, the company's finances and its stock price before deciding whether to invest in it or not. Buffett categorized his tenets for investing into four major areas: 1. Business tenets 2. Management tenets 3. Financial tenets and 4. Market tenets 4. Buffett's Investing Strategies "I just read. I read all day. I mean, we put $500 million in PetroChina. All I did was read the annual report." - Warren Buffett commenting on how he gets his ideas to invest. Buffett's investment strategies received worldwide attention from security analysts. While his mentor Ben Graham had a major influence on his investment decisions, Buffett was also influenced by Philip A. Fisher 5 especially in the later years. His partner Charles Munger was responsible for driving his thinking towards Fisher's principles. Graham paid attention on the quantitative analysis of the company involving the financial statements, while Fisher concentrated on the qualitative analysis of a company. Graham focused on buying stocks while they were cheap. Fischer on the other hand advocated that an investor could make more profits by investing in firms, which had good potential, and a good management team. Over the years, Buffett combined Graham's basic idea of looking out for a safety margin in all his investments, and also adopting points from Fisher's theory. Robert G. Hagstorm, the author of 'The Warren Buffett Way: Investment Strategies of the World's Greatest Investor', wrote in his book, "Graham gave Buffett the intellectual basis of investing, the margin of safety, and helped Buffett learn to master his emotions in order to take advantage of market fluctuations. Fisher gave Buffett an updated, workable methodology that enabled him to identify good long-term investments. The frequent confusion surrounding Buffett's investment actions is easily understood when people acknowledge that Buffett is synthesis of both Graham's and Fisher's philosophy." Buffett opted to acquire stocks while they were at historically low prices. This was very unlike other investors, who sold their stocks when their value decreases and acquired their stock when their value increased. Buffet believed that when buying a stock of any company an investor should analyze the business from a businessman's point of view not as a market analyst. He examined the qualitative and quantitative aspects of the stock or business. He believed that an investor must understand the business where he/she is investing in order to reap financial rewards. In accordance with this principle he did not invest in technology stocks during the dotcom boom in the late 1990 s. He always he/she is investing in order to reap financial rewards. In accordance with this principle he did not invest in technology stocks during the dotcom boom in the late 1990 s. He always avoided companies whose operations he did not understand. Buffett also avoided investing in companies with inconsistent operations. He believed that companies which maintained consistency in business over the years performed better than those that changed their line of business frequently. Buffett also focused on companies with high demand products or services and which had no close substitutes. He preferred companies that did not operate in highly regulated markets. 5 Philip A. Fisher was one of the first investment philosophers. He graduated from the Stanford Graduate Investment Program and started his career as a security analyst for a bank in San Francisco. Later in 1932, he founded an investment-counseling firm called Fisher \& Co. He authored three books on security analysis. His most famous work, 'Common Stocks and Uncommon Profits,' was considered a classic investment theory book. Warren Buffett - The Investment Leader () Www.casestudyinc.com 7 5. Buffett's Management Style and Criticism "But if a business requires a superstar to produce great results, the business itself cannot be deemed great. A medical partnership led by your area's premier brain surgeon may enjoy outsized and growing earnings, but that tells little about its future. The partnership's moat will go when the surgeon goes. You can count, though, on the moat of the Mayo Clinic to endure, even though you can't name its CEO." -Warren Buffett in 2007 Annual Report, Berkshire Hathaway While many acknowledged Buffett's investing abilities, some analysts felt that his approach to investing was conservative. Some even commented that the super-investor invested like a girl and like most female investors is patient and does his research. His critics felt he failed to invest in companies that could have fetched him greater returns. His campaign for the implementation of corporate governance in companies was also criticized because his own company Berkshire Hathaway did not have any outsiders as directors on its board. Buffett was against employee stock options and high CEO compensation packages in the tech companies. His support for the Federal Terrorism Insurance fund also drew criticism from many insurance industry players. He established the Buffett foundation in mid 1960s. The foundation received donations from the shareholders of Berkshire Hathaway. However he drew flak from human rights activists because the foundation disbursed meager amount towards charity when compared to other foundations in the US. He strongly advocated family planning and abortion 6 and this also was not liked by many. 6. Questions for Discussion 1) Discuss the entrepreneurial skills displayed by Buffett during his early days. How did these skills contribute to his success in his later years? 2) Analyze Buffett's investment strategies and comment on Buffett's decision not to invest in technology stocks
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


