Question: Please show every single mathematic step and box final answers! Material a (C-]) c (J/(kg K)) C (J/ (mol K)) Ly (J/kg) Ly (J/kg) density
Please show every single mathematic step and box final answers!
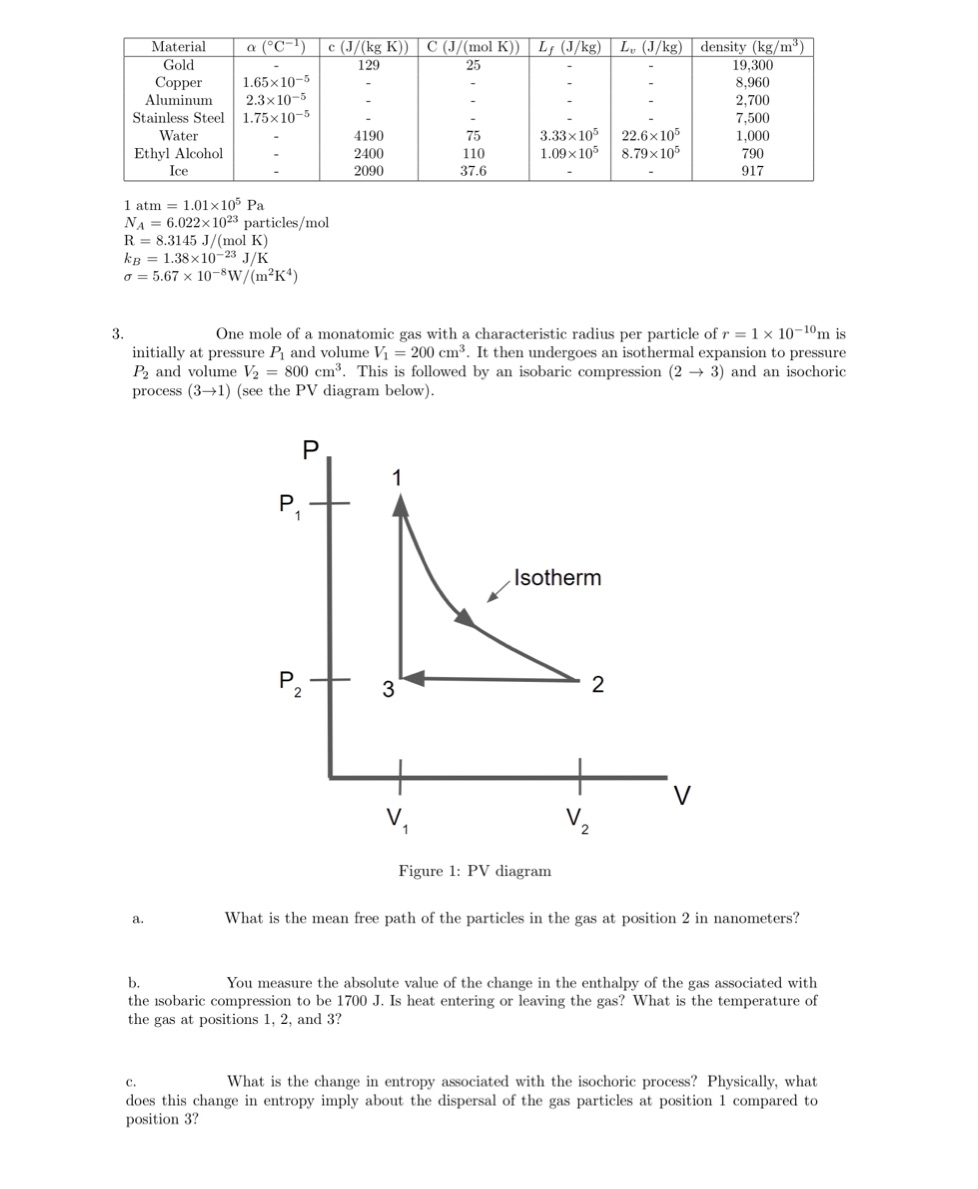
Material a (C-]) c (J/(kg K)) C (J/ (mol K)) Ly (J/kg) Ly (J/kg) density (kg/my) Gold 129 25 19,300 Copper 1.65 x10-5 8,960 Aluminum 2.3x10-5 2,700 Stainless Steel 1.75x10-5 7,500 Water 4190 75 3.33 x 105 22.6x105 1,000 Ethyl Alcohol 2400 110 1.09x 105 8.79x105 790 Ice 2090 37.6 917 1 atm = 1.01 x105 Pa NA = 6.022x 1023 particles/mol R = 8.3145 J/(mol K) KB = 1.38x10-23 J/K 0 = 5.67 x 10-8W/(m?K) 3. One mole of a monatomic gas with a characteristic radius per particle of r = 1 x 10-10m is initially at pressure P and volume Vi = 200 cms. It then undergoes an isothermal expansion to pressure P2 and volume V2 = 800 cm". This is followed by an isobaric compression (2 - 3) and an isochoric process (3-+1) (see the PV diagram below). P Isotherm P, - 3 2 V V2 Figure 1: PV diagram a What is the mean free path of the particles in the gas at position 2 in nanometers? b. You measure the absolute value of the change in the enthalpy of the gas associated with the isobaric compression to be 1700 J. Is heat entering or leaving the gas? What is the temperature of the gas at positions 1, 2, and 3? C. What is the change in entropy associated with the isochoric process? Physically, what does this change in entropy imply about the dispersal of the gas particles at position 1 compared to position 3
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


