Question: Please show work on all steps taken to get to the answer. 1. Diverge or converge conditionally or converge absolutely: (-1) In(n?) In(n3) n=2 2.
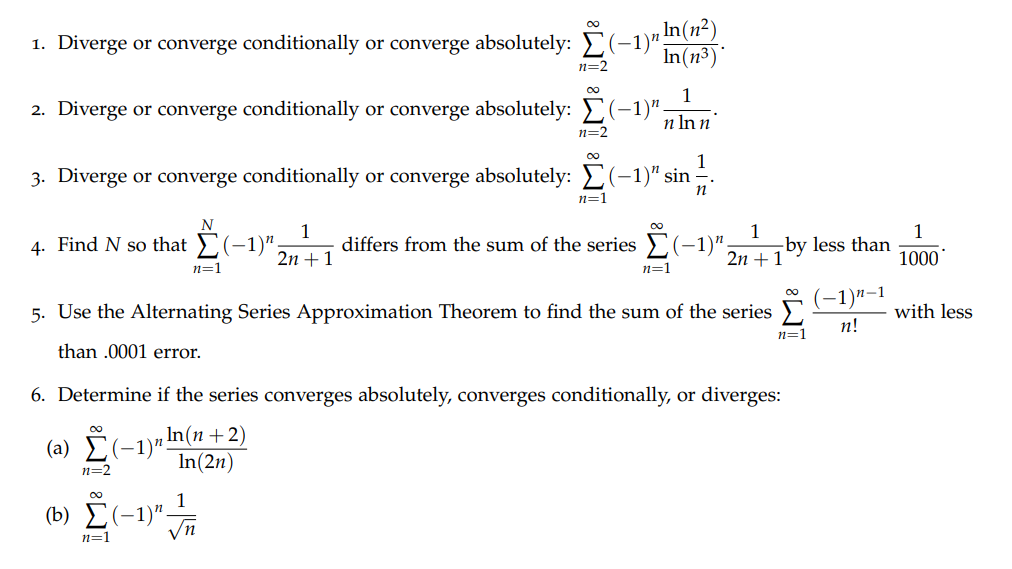

Please show work on all steps taken to get to the answer.
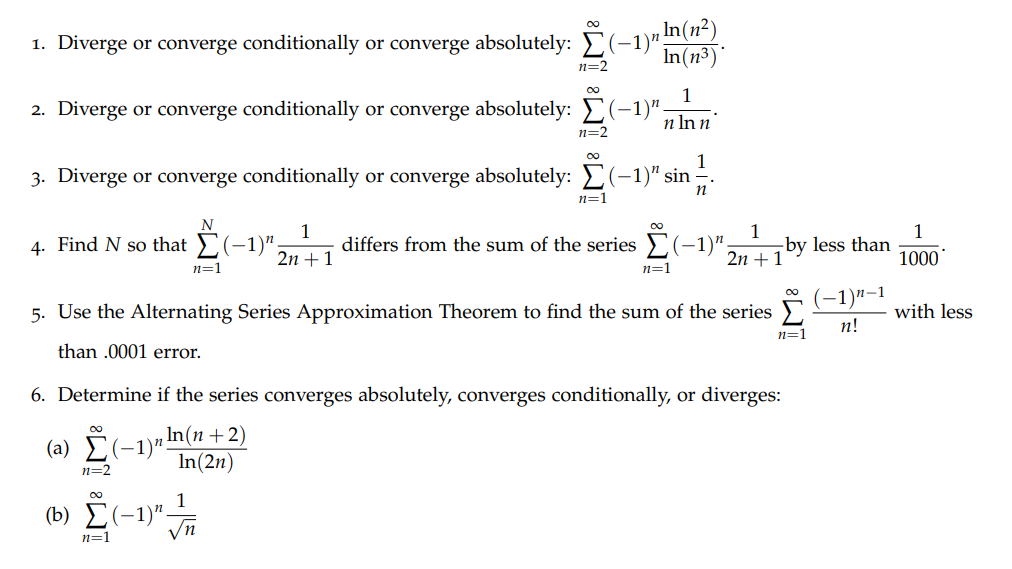

1. Diverge or converge conditionally or converge absolutely: (-1)" In(n?) In(n3) n=2 2. Diverge or converge conditionally or converge absolutely: (-1)" n Inn n=2 00 3. Diverge or converge conditionally or converge absolutely: _(-1)" sin -. n=1 n N 4. Find N so that _(-1)" 1 2n + 1 differs from the sum of the series _ (-1)" 1 by less than n=1 n=1 2n + 1 1000 (-1)n-1 5. Use the Alternating Series Approximation Theorem to find the sum of the series M : with less n=1 n! than .0001 error. 6. Determine if the series converges absolutely, converges conditionally, or diverges: (a) (-1)" In(n + 2) n=2 In(2n) 00 (b) E (-1) 1 n=1 Vn(C) \"2(4)\" G)\" _ \"1 7. Use the Alternating Series Approximation Theorem to find N so that z % gives the sum of the n n=1 1 111 series \"E (_ n) with less than .000001 error
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Certainly Lets go through each problem stepbystep Problem 1 Determine if the series converges conditionally converges absolutely or diverges sumn2inft... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


