Question: Please solve part e, f , g Consolidation subsequent to date of acquisition-upstream intercompany inventory sale-Equity method with noncontrolling interest, AAP, and upstream intercompany inventory
Please solve part e, f , g


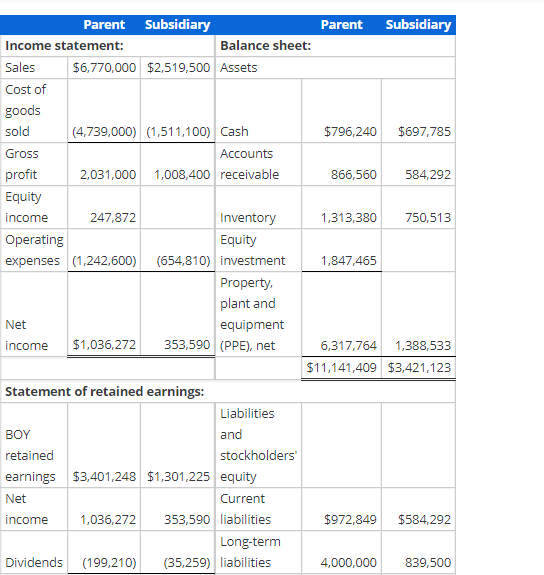
![to the following [A] assets: Initial Useful [A] Asset Fair Value Life](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/07/66952d9326fbf_56266952d92c0475.jpg)

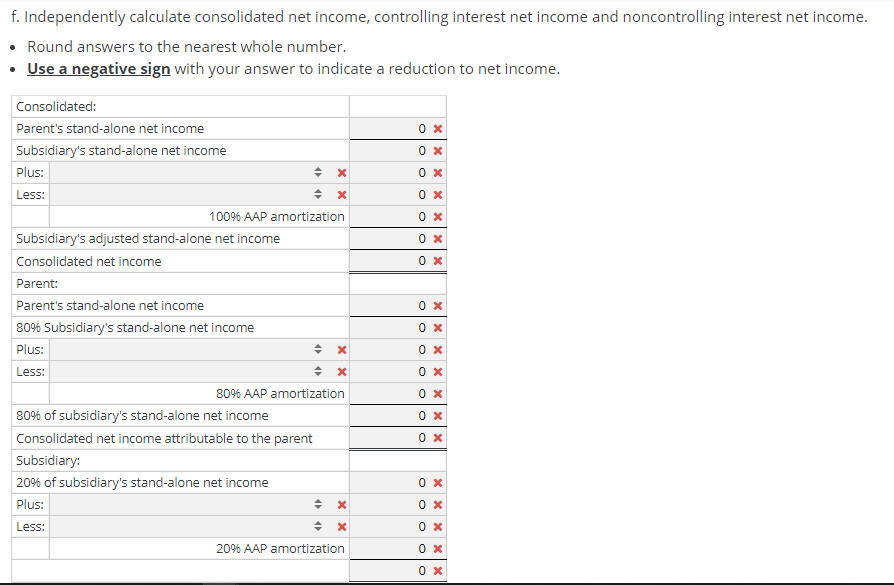
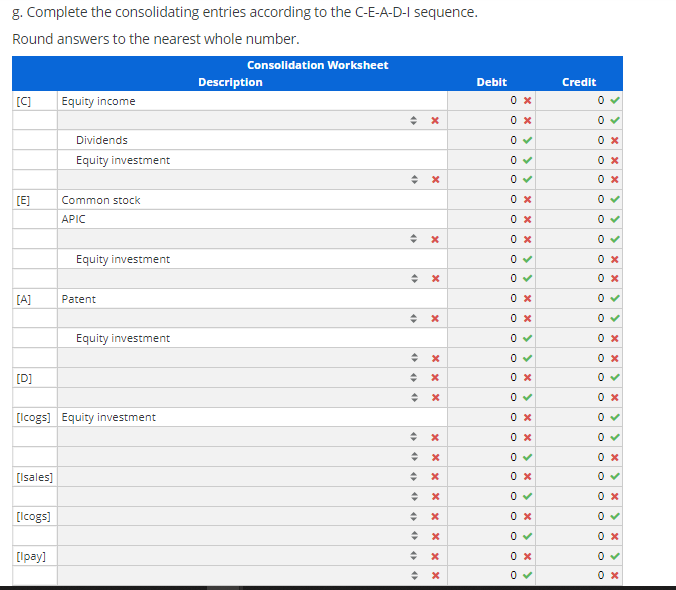
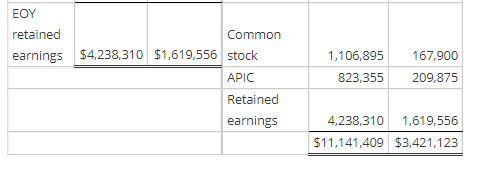
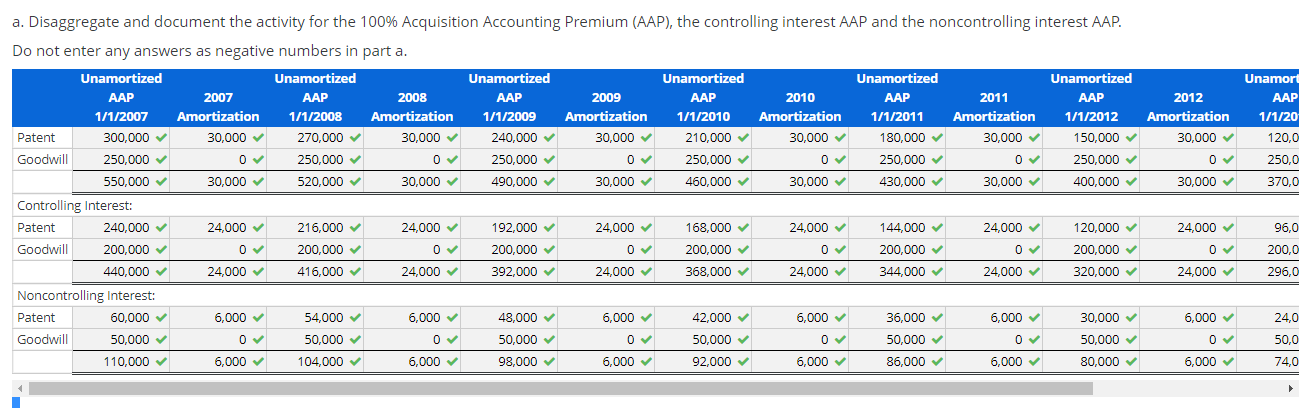
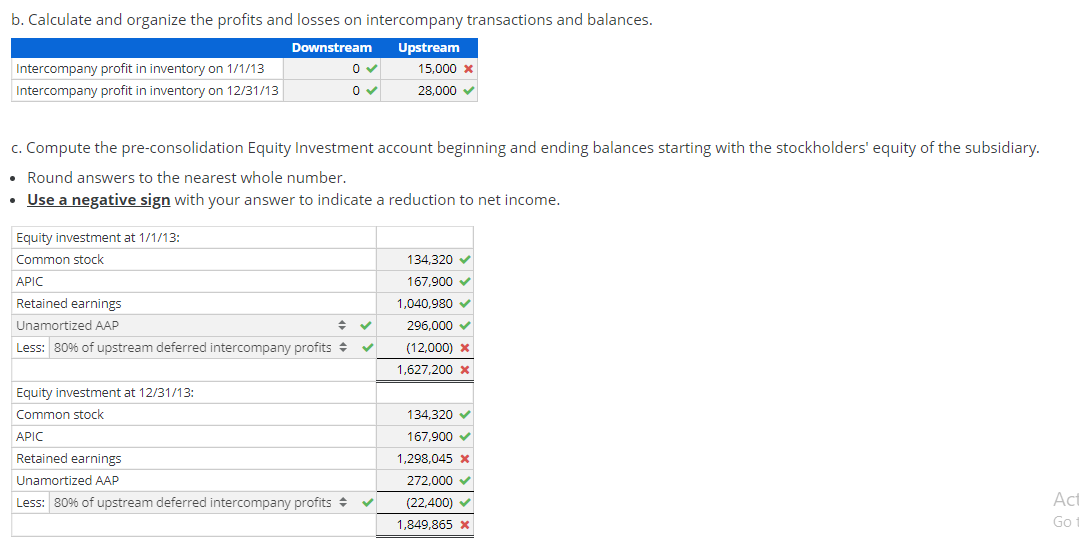
Consolidation subsequent to date of acquisition-upstream intercompany inventory sale-Equity method with noncontrolling interest, AAP, and upstream intercompany inventory sale Assume that, on January 1, 2007, a parent company acquired an 80% interest in its subsidiary. The total fair value of the controlling and noncontrolling interests was $550,000 over the book value of the subsidiary's Stockholders' Equity on the acquisition date. the parent assigned the excess to the following [A] assets: Initial Useful [A] Asset Fair Value Life (years) Patent $300,000 Goodwill 250,000 Indefinite $550,000 10 80% of the Goodwill is allocated to the parent. Assume that the subsidiary sells inventory to the parent (upstream) which includes that inventory in products that it ultimately sells to customers outside of the controlled group. You have compiled the following data as of 2012 and 2013: 80% of the Goodwill is allocated to the parent. Assume that the subsidiary sells inventory to the parent (upstream) which includes that inventory in products that it ultimately sells to customers outside of the controlled group. You have compiled the following data as of 2012 and 2013: 2012 2013 Transfer price for inventory sale $672,000 $733,000 Cost of goods sold (615,000) (653,000) Gross profit $57,000 $80,000 96 inventory remaining 2596 3596 Gross profit deferred $14,250 $28,000 EOY receivable/payable $91,000 $90,000 The inventory not remaining at the end of the year has been sold outside of the controlled group.The parent and the subsidiary report the following financial statements at December 31, 2013: Parent Subsidiary Parent Subsidiary Income statement: Balance sheet: Sales $6,770,000 $2,519,500 Assets Cost of goods sold (4,739,000) (1,511,100) Cash $796,240 $697,785 Gross Accounts profit 2,031,000 1,008,400 receivable 866,560 584,292 Equity income 247,872 Inventory 1,313,380 750,513 Operating Equity expenses (1,242,600) (654,810) investment 1,847,465 Property plant and Net equipment income $1,036,272 353,590 (PPE), net 6,317,764 1,388,533 $11,141,409 $3,421,123 Statement of retained earnings: Liabilities BOY and retained stockholders' earnings $3,401,248 $1,301,225 equity Net Current income 1,036,272 353,590 liabilities $972,849 $584,292 Long-term Dividends (199,210) (35,259) liabilities 4,000,000 839,500 EOY retained Common earnings $4,238,310 $1,619,556 stock APIC Retained earnings 1,106,895 823,355 167,900 209,875 4,238,310 1,619,556 $11,141,409 $3,421,123 2012 Amortization 30,000 Unamor 1/1/20 120,0 250,0 0 30,000 370,0 a. Disaggregate and document the activity for the 100% Acquisition Accounting Premium (AAP), the controlling interest AAP and the noncontrolling interest AAP. Do not enter any answers as negative numbers in part a. Unamortized Unamortized Unamortized Unamortized Unamortized Unamortized 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 1/1/2007 Amortization 1/1/2008 Amortization 1/1/2009 Amortization 1/1/2010 Amortization 1/1/2011 Amortization 1/1/2012 Patent 300,000 30,000 270,000 30,000 240,000 30,000 210,000 30,000 180,000 30,000 150,000 Goodwill 250,000 0 250,000 0 250,000 0 250,000 0 250,000 0 250,000 550,000 30,000 520,000 30,000 490,000 30,000 460,000 30,000 430,000 30,000 400,000 Controlling Interest: Patent 240,000 24,000 216,000 24,000 192,000 24,000 168,000 24,000 144,000 24,000 120,000 Goodwill 200,000 0 200,000 0 200,000 0 200,000 0 200,000 0 200,000 440,000 24,000 416,000 24,000 392,000 24,000 368,000 24,000 344,000 24,000 320,000 Noncontrolling Interest: Patent 60,000 6,000 54,000 6,000 48,000 6,000 42,000 6,000 36,000 6,000 30,000 Goodwill 50,000 0 50,000 0 50,000 0 50,000 07 50,000 0 50,000 110,000 6,000 104,000 6,000 98,000 6,000 92,000 6,000 86,000 6,000 80,000 24,000 96,0 200,0 0 24,000 296,0 6,000 24,0 0 50,0 6,000 74,0 b. Calculate and organize the profits and losses on intercompany transactions and balances. Downstream Upstream Intercompany profit in inventory on 1/1/13 0 15,000 X Intercompany profit in inventory on 12/31/13 0 28,000 C. Compute the pre-consolidation Equity Investment account beginning and ending balances starting with the stockholders' equity of the subsidiary. Round answers to the nearest whole number. Use a negative sign with your answer to indicate a reduction to net income. Equity investment at 1/1/13: Common stock 134,320 APIC Retained earnings Unamortized AAP Less: 80% of upstream deferred intercompany profits - 167,900 1,040,980 296,000 (12,000) X 1,627,200 X Equity investment at 12/31/13: Common stock APIC Retained earnings Unamortized AAP Less: 80% of upstream deferred intercompany profits - 134,320 167.900 1,298,045 X 272,000 (22,400) 1,849,865 x Act Got d. Reconstruct the activity in the parent's pre-consolidation Equity Investment T-account for the year of consolidation. Round answers to the nearest whole number. Equity Investment Balance at 1/1/13 1,627,200 x Net income 285,272 x 28,207 Dividends BOY upstream inventory 12,000 x 24,000 AAP amortization 22,400 EOY upstream inventor Balance at 12/31/13 1,849,865 x 0 0 e. Independently compute the owners' equity attributable to the noncontrolling interest beginning and ending balances starting with the owners' equity of the subsidiary. Round answers to the nearest whole number. Use a negative sign with your answer to indicate a reduction to net income. Noncontrolling interest at 1/1/13: Common stock APIC Retained earnings Ox OX + x Less: X OX Noncontrolling interest at 12/31/13: Common stock APIC Retained earnings OX OX Less: X OX OX f. Independently calculate consolidated net income, controlling interest net income and noncontrolling interest net income. Round answers to the nearest whole number. Use a negative sign with your answer to indicate a reduction to net income. 0 x OX ox Consolidated: Parent's stand-alone net income Subsidiary's stand-alone net income Plus: x Less: 4 x 100% AAP amortization Subsidiary's adjusted stand-alone net income Consolidated net income Parent: Parent's stand-alone net income 80% Subsidiary's stand-alone net income Plus: X Less: X 80% AAP amortization 80% of subsidiary's stand-alone net income Consolidated net income attributable to the parent Subsidiary: 20% of subsidiary's stand-alone net income Plus: x Less: 4 x 20% AAP amortization 0x 0X g. Complete the consolidating entries according to the C-E-A-D-1 sequence. Round answers to the nearest whole number. Consolidation Worksheet Description [C] Equity income ** Dividends Equity investment Credit Debit 0x 0 0 x 0 0 OX 0 X 0 0 X [E] 0x 0 Common stock APIC 0 X 07 OX 0 Equity investment OX [A] Patent 0x 0 x 07 Equity investment 0 OX 0 [D] + x 0 X 0 x 0 0 X [lcogs] Equity investment OX 0 0 X 0 X 0 x [Isales] 0 x 07 X X OX [lcogs] 0 x 07 . X OX [lpayl 0 x X 0 0 x
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


