Question: PLEASE SOLVE THIS QUICKLY I WILL UPVOTE PLEASE 19.15 A group-technology cell is organized to produce a family of products. The cell consists of three
PLEASE SOLVE THIS QUICKLY I WILL UPVOTE PLEASE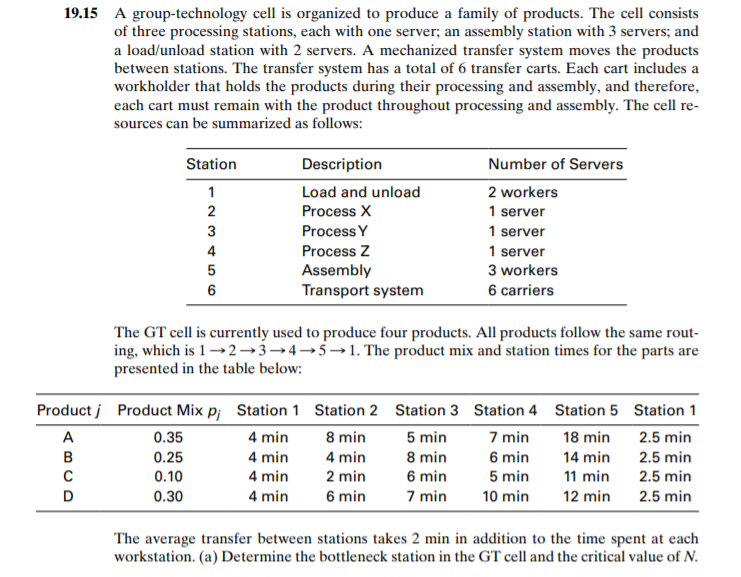

19.15 A group-technology cell is organized to produce a family of products. The cell consists of three processing stations, each with one server, an assembly station with 3 servers; and a load/unload station with 2 servers. A mechanized transfer system moves the products between stations. The transfer system has a total of 6 transfer carts. Each cart includes a workholder that holds the products during their processing and assembly, and therefore, each cart must remain with the product throughout processing and assembly. The cell re- sources can be summarized as follows: Station 1 2 3 4 5 6 Description Load and unload Process X Process Y Process Z Assembly Transport system Number of Servers 2 workers 1 server 1 server 1 server 3 workers 6 carriers The GT cell is currently used to produce four products. All products follow the same rout- ing, which is 12-3-4-5-1. The product mix and station times for the parts are presented in the table below: Product Product Mix pj Station 1 Station 2 Station 3 Station 4 Station 5 Station 1 A 0.35 4 min 8 min 5 min 7 min 18 min 2.5 min B 0.25 4 min 4 min 8 min 6 min 14 min 2.5 min 0.10 4 min 2 min 6 min 5 min 11 min 2.5 min D 0.30 4 min 6 min 7 min 10 min 12 min 2.5 min The average transfer between stations takes 2 min in addition to the time spent at each workstation. (a) Determine the bottleneck station in the GT cell and the critical value of N. Determine the overall production rate, manufacturing lead time, and waiting time of parts in the cell, given that the number of parts in the system = N*. If N* is not an integer, use the integer that is closest to N*. (b) Compute the utilizations of the six stations for part (a). (c) Compute the overall production rate, manufacturing lead time, and waiting time of parts in the cell, given that the number of parts in the system = N* + 4. If N* is not an integer, use the integer that is closest to N* + 4. (d) Compute the utilizations of the six stations for part (c). (e) Determine the average manufacturing lead times for each product for the two cases: N = N* and N = N* + 4. A spreadsheet calculator is recommended for parts (a), (b), and (d) of this problem. 19.15 A group-technology cell is organized to produce a family of products. The cell consists of three processing stations, each with one server, an assembly station with 3 servers; and a load/unload station with 2 servers. A mechanized transfer system moves the products between stations. The transfer system has a total of 6 transfer carts. Each cart includes a workholder that holds the products during their processing and assembly, and therefore, each cart must remain with the product throughout processing and assembly. The cell re- sources can be summarized as follows: Station 1 2 3 4 5 6 Description Load and unload Process X Process Y Process Z Assembly Transport system Number of Servers 2 workers 1 server 1 server 1 server 3 workers 6 carriers The GT cell is currently used to produce four products. All products follow the same rout- ing, which is 12-3-4-5-1. The product mix and station times for the parts are presented in the table below: Product Product Mix pj Station 1 Station 2 Station 3 Station 4 Station 5 Station 1 A 0.35 4 min 8 min 5 min 7 min 18 min 2.5 min B 0.25 4 min 4 min 8 min 6 min 14 min 2.5 min 0.10 4 min 2 min 6 min 5 min 11 min 2.5 min D 0.30 4 min 6 min 7 min 10 min 12 min 2.5 min The average transfer between stations takes 2 min in addition to the time spent at each workstation. (a) Determine the bottleneck station in the GT cell and the critical value of N. Determine the overall production rate, manufacturing lead time, and waiting time of parts in the cell, given that the number of parts in the system = N*. If N* is not an integer, use the integer that is closest to N*. (b) Compute the utilizations of the six stations for part (a). (c) Compute the overall production rate, manufacturing lead time, and waiting time of parts in the cell, given that the number of parts in the system = N* + 4. If N* is not an integer, use the integer that is closest to N* + 4. (d) Compute the utilizations of the six stations for part (c). (e) Determine the average manufacturing lead times for each product for the two cases: N = N* and N = N* + 4. A spreadsheet calculator is recommended for parts (a), (b), and (d) of this






