Question: Please us R programming 1. Suppose the joint probability distribution function Fx,y is given by: Y X = - 0 X = 1 Y Y
Please us R programming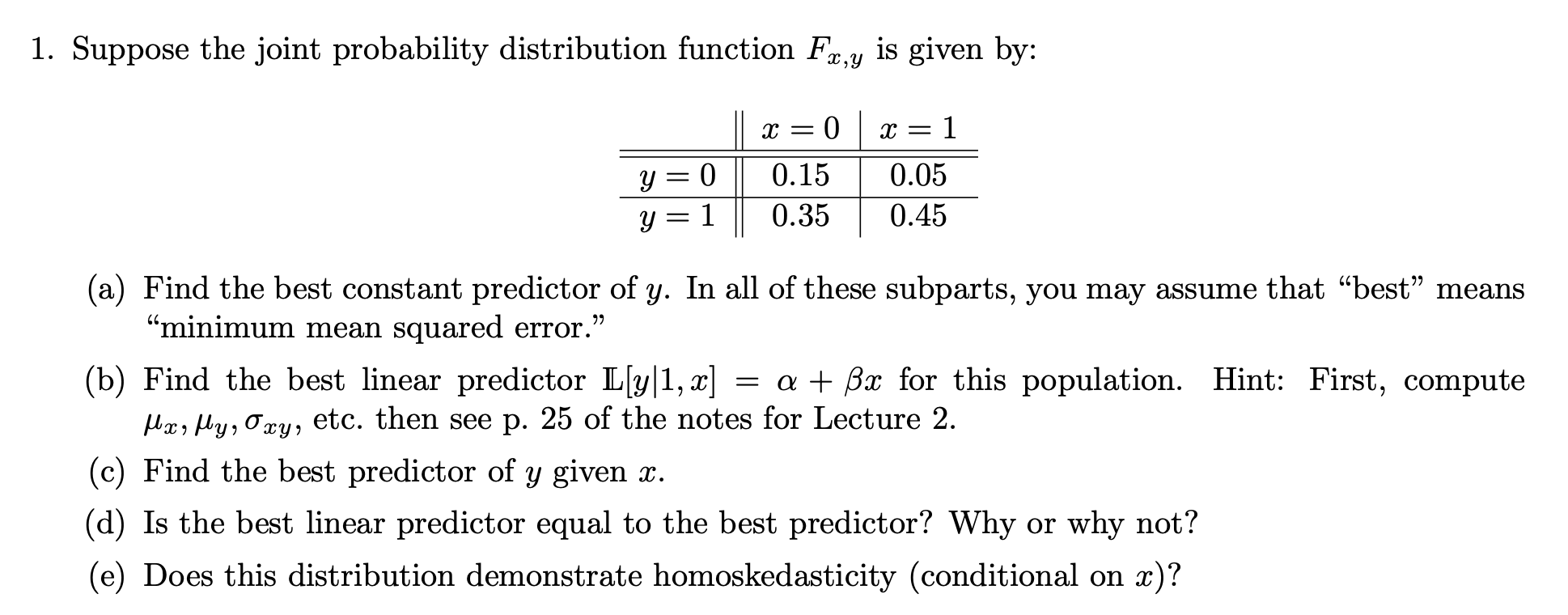
1. Suppose the joint probability distribution function Fx,y is given by: Y X = - 0 X = 1 Y Y 0 1 0.15 0.35 0.05 0.45 = (a) Find the best constant predictor of y. In all of these subparts, you may assume that best means "minimum mean squared error. (b) Find the best linear predictor L[y|1, x] = a + Bx for this population. Hint: First, compute , Mixi My, Oxy, etc. then see p. 25 of the notes for Lecture 2. (c) Find the best predictor of y given x. (d) Is the best linear predictor equal to the best predictor? Why or why not? (e) Does this distribution demonstrate homoskedasticity (conditional on x)? 2 1. Suppose the joint probability distribution function Fx,y is given by: Y X = - 0 X = 1 Y Y 0 1 0.15 0.35 0.05 0.45 = (a) Find the best constant predictor of y. In all of these subparts, you may assume that best means "minimum mean squared error. (b) Find the best linear predictor L[y|1, x] = a + Bx for this population. Hint: First, compute , Mixi My, Oxy, etc. then see p. 25 of the notes for Lecture 2. (c) Find the best predictor of y given x. (d) Is the best linear predictor equal to the best predictor? Why or why not? (e) Does this distribution demonstrate homoskedasticity (conditional on x)? 2
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


