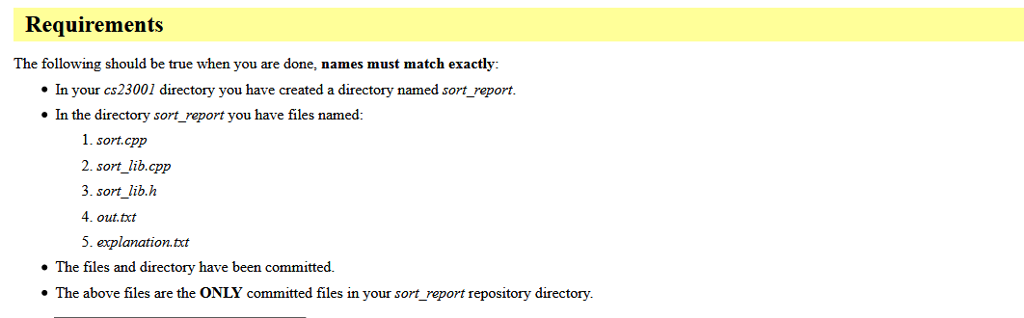
Question: PLEASE USE C++, Make a directory sort_report Copy sort.cpp, sort_lib.cpp, and sort_lib.h from shared/project4 into sort_report i need finish will generate the following during the
PLEASE USE C++,
Make a directory sort_report Copy sort.cpp, sort_lib.cpp, and sort_lib.h from shared/project4 into sort_report i need finish will generate the following during the lab: out.txt explanatation.txt



sort.cpp
/** * @brief Application to run sorting algorithms on random int data * * @author Dale Haverstock * @date 2012-04-19 */
//============================================================================== #include "sort_lib.h" #include #include #include #include
//============================================================================== // Using declarations using std::string; using std::vector; using std::cout; using std::cerr;
//============================================================================== // Function declarations void process_command_line(Options& opts, int argc, char* argv[]); void generate_random_data(vector& data, int size, int seed, int mod); void output_data(const vector&); void output_usage_and_exit(const string& cmd); void output_error_and_exit(const string& msg);
//============================================================================== int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { // Options container Options opts;
// Get values from the command line, opts may be changed process_command_line(opts, argc, argv);
// Generate data vector data; generate_random_data(data, opts._data_size, opts._seed, opts._mod);
// Output data before sorting if(opts._output_data) { cout
// Sort, if a sort was specified, there is no default if (opts._quick_sort) { quick_sort(data); } if (opts._selection_sort) { selection_sort(data); } if (opts._bubble_sort) { bubble_sort(data); } if ( !opts._quick_sort && !opts._selection_sort && !opts._bubble_sort ) { output_error_and_exit("No sort specified."); }
// Output data after sorting if(opts._output_sorted_data) { cout
return 0; }
//============================================================================== void generate_random_data(vector& vec, int size, int seed, int mod) { // Resize vector vec.resize(size);
// Set random number generator seed srandom(static_cast(seed));
// Put random values in vector for (vector::size_type idx = 0; idx
//============================================================================== void output_data(const vector& vec) { // Number of columns, column width const int cols = 7; const int width = 10;
// Output vector elements for (vector::size_type idx = 0; idx
cout
cout
//============================================================================== // Note: // * No check for C-string to int conversion success // void process_command_line(Options& opts, int argc, char* argv[]) { // Useage message if no command line args if (argc == 1) { output_usage_and_exit(argv[0]); }
// Go through the argumets for (int idx = 1; idx
// Process the option if (opt == "-h") { output_usage_and_exit(argv[0]); } if (opt == "-qs") { opts._quick_sort = true; } if (opt == "-ss") { opts._selection_sort = true; } if (opt == "-bs") { opts._bubble_sort = true; } if (opt == "-od") { opts._output_data = true; } if (opt == "-osd") { opts._output_sorted_data = true; } if (opt == "-sz") { if (idx + 1
//============================================================================== void output_usage_and_exit(const string& cmd) { cout
exit(0); }
//============================================================================== void output_error_and_exit(const string& msg) { cerr
exit(1); }
sort_lib.cpp
/** * @brief Application to run sorting algorithms on random int data * * @author Dale Haverstock * @date 2012-04-19 */
// sort library //
//============================================================================== #include "sort_lib.h" #include
//============================================================================== // Make shorter type names typedef std::vector::size_type Vec_Idx;
//============================================================================== // Function declarations, uppercase so those stand out void quick_sort(std::vector& data, int left, int right); void SWAP(int& n1, int& n2); bool LESS_THAN(int n1, int n2); bool GREATER_THAN(int n1, int n2);
//============================================================================== void quick_sort(std::vector& data) { // Do nothing if empty vector if (data.size() == 0) { return; }
// Do the sort quick_sort(data, 0, data.size() - 1); }
//============================================================================== // The unsigned ints cause problems here, jdx may go to -1. // Subscripts are cast so there are no warnings. void quick_sort(std::vector& data, int left, int right) { // Calculate the pivot int pivot = data[Vec_Idx((left + right) / 2)];
// Partition int idx = left, jdx = right; while (idx
while (GREATER_THAN(data[Vec_Idx(jdx)], pivot)) jdx--;
if (idx
// Recurse if (left
if (idx
//============================================================================== void selection_sort(std::vector& data) { // Do nothing if empty vector (note unsigned 0 - 1 is a big number) if (data.size() == 0) { return; }
// Index of last element in vector, also last in unsorted part Vec_Idx last = data.size() - 1;
// Do the sort while (last > 0) { // Find greatest in unsorted part Vec_Idx idx_of_greatest = 0; for (Vec_Idx idx = 0; idx
// Swap last in unsorted with greatest in unsorted part SWAP(data[last], data[idx_of_greatest]);
// Increase sorted part --last; } }
//============================================================================== void bubble_sort(std::vector& data) { // Go through vector repeatedly for(Vec_Idx limit = data.size(); limit > 0; limit--) { // Go through vector once, swap element and next element if out of order for(Vec_Idx idx = 0; idx
//============================================================================== // This is here so the number of calls can be counted. void SWAP(int& n1, int& n2) { std::swap(n1, n2); }
//============================================================================== // This is here so the number of calls can be counted. bool LESS_THAN(int n1, int n2) { return n1
//============================================================================== // This is here so the number of calls can be counted. bool GREATER_THAN(int n1, int n2) { return n1 > n2; }
sort_lib.h
/** * @brief Application to run sorting algorithms on random int data * * @author Dale Haverstock * @date 2012-04-19 */
#ifndef SORT_LIB_H #define SORT_LIB_H
//============================================================================== #include
//============================================================================== struct Options { // Option values int _seed; int _data_size; int _mod; bool _output_data; bool _output_sorted_data; bool _bubble_sort; bool _selection_sort; bool _quick_sort;
// Defaults Options() : _seed(0), _data_size(0), _mod(0), _output_data(false), _output_sorted_data(false), _bubble_sort(false), _selection_sort(false), _quick_sort(false) { } };
//============================================================================== void selection_sort(std::vector&); void quick_sort(std::vector&); void bubble_sort(std::vector&);
#endif
Setup Make a directory sort_report Copy sort.cpp, sort lib.cpp, and sort_lib h from shared/project4 into sort_report . You will generate the following during the lab: o out.tct o explanatation.tct Setup Make a directory sort_report Copy sort.cpp, sort lib.cpp, and sort_lib h from shared/project4 into sort_report . You will generate the following during the lab: o out.tct o explanatation.tct
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


