Question: Please use C programming A directed graph is a graph where edges are directional; that is, edges (p,q) and (q,p) are distinct. An important class
Please use C programming
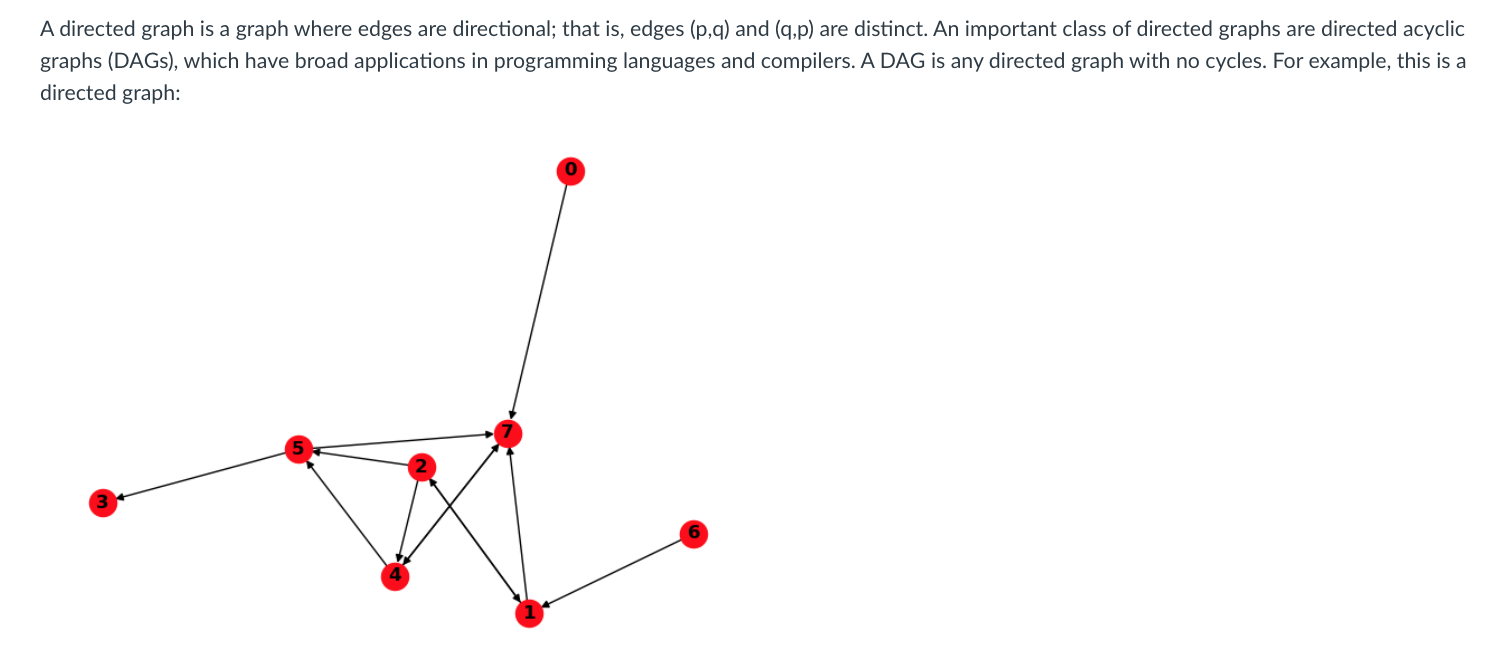
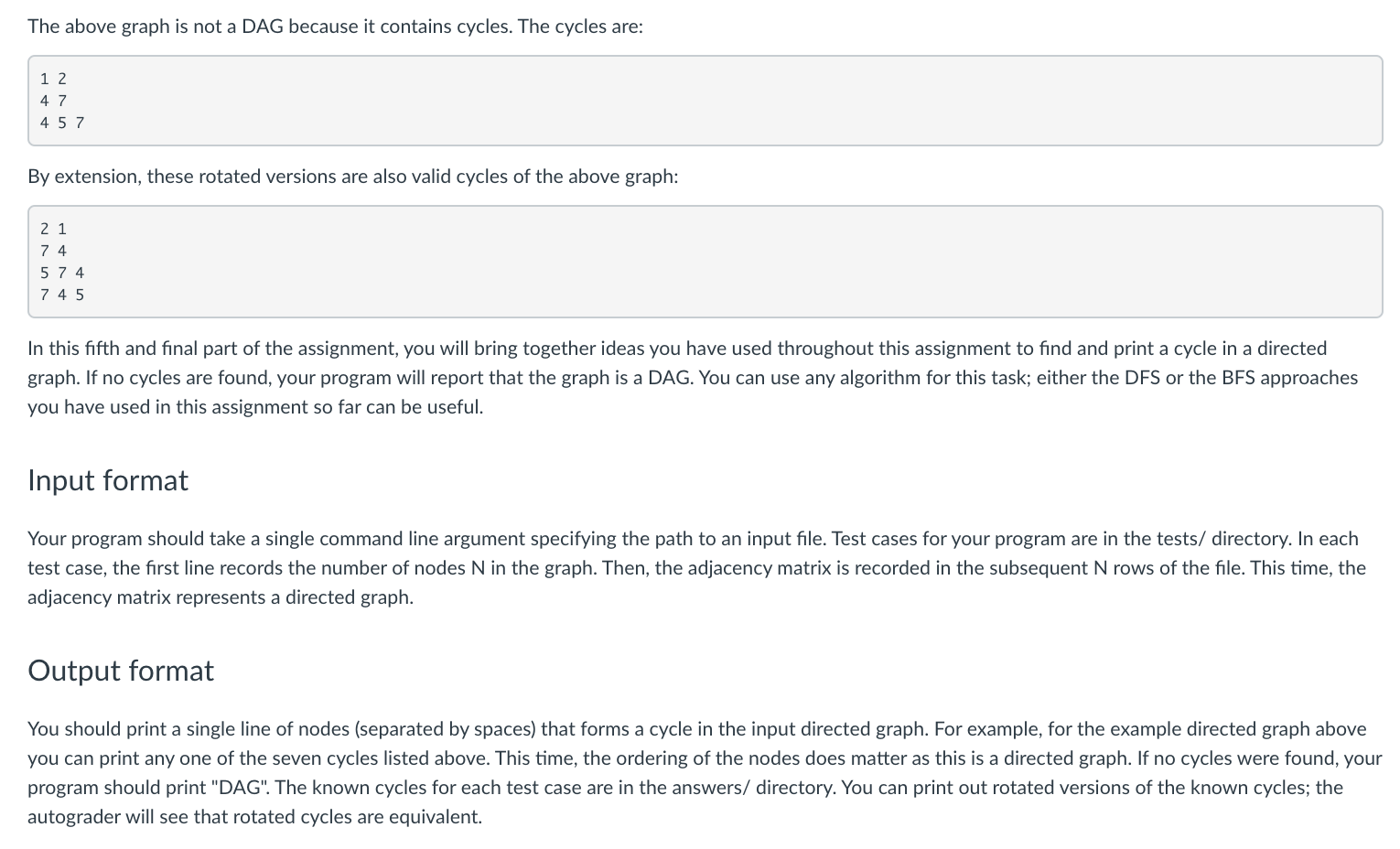

A directed graph is a graph where edges are directional; that is, edges (p,q) and (q,p) are distinct. An important class of directed graphs are directed acyclic graphs (DAGs), which have broad applications in programming languages and compilers. A DAG is any directed graph with no cycles. For example, this is a directed graph: The above graph is not a DAG because it contains cycles. The cycles are: 1 2 4 7 4 5 7 By extension, these rotated versions are also valid cycles of the above graph: 21 74 5 74 7 4 5 In this fifth and final part of the assignment, you will bring together ideas you have used throughout this assignment to find and print a cycle in a directed graph. If no cycles are found, your program will report that the graph is a DAG. You can use any algorithm for this task; either the DFS or the BFS approaches you have used in this assignment so far can be useful. Input format Your program should take a single command line argument specifying the path to an input file. Test cases for your program are in the tests/ directory. In each test case, the first line records the number of nodes N in the graph. Then, the adjacency matrix is recorded in the subsequent N rows of the file. This time, the adjacency matrix represents a directed graph. Output format You should print a single line of nodes (separated by spaces) that forms a cycle in the input directed graph. For example, for the example directed graph above you can print any one of the seven cycles listed above. This time, the ordering of the nodes does matter as this is a directed graph. If no cycles were found, your program should print "DAG". The known cycles for each test case are in the answers/ directory. You can print out rotated versions of the known cycles; the autograder will see that rotated cycles are equivalent. Hint Suppose you enter the graph from 0, and find a cycle by following the path 0->7->4->5->7 Upon seeing 7 again, you know you have detected a cycle. You have to carefully determine where the cycle begins and ends in the path you have traversed. A directed graph is a graph where edges are directional; that is, edges (p,q) and (q,p) are distinct. An important class of directed graphs are directed acyclic graphs (DAGs), which have broad applications in programming languages and compilers. A DAG is any directed graph with no cycles. For example, this is a directed graph: The above graph is not a DAG because it contains cycles. The cycles are: 1 2 4 7 4 5 7 By extension, these rotated versions are also valid cycles of the above graph: 21 74 5 74 7 4 5 In this fifth and final part of the assignment, you will bring together ideas you have used throughout this assignment to find and print a cycle in a directed graph. If no cycles are found, your program will report that the graph is a DAG. You can use any algorithm for this task; either the DFS or the BFS approaches you have used in this assignment so far can be useful. Input format Your program should take a single command line argument specifying the path to an input file. Test cases for your program are in the tests/ directory. In each test case, the first line records the number of nodes N in the graph. Then, the adjacency matrix is recorded in the subsequent N rows of the file. This time, the adjacency matrix represents a directed graph. Output format You should print a single line of nodes (separated by spaces) that forms a cycle in the input directed graph. For example, for the example directed graph above you can print any one of the seven cycles listed above. This time, the ordering of the nodes does matter as this is a directed graph. If no cycles were found, your program should print "DAG". The known cycles for each test case are in the answers/ directory. You can print out rotated versions of the known cycles; the autograder will see that rotated cycles are equivalent. Hint Suppose you enter the graph from 0, and find a cycle by following the path 0->7->4->5->7 Upon seeing 7 again, you know you have detected a cycle. You have to carefully determine where the cycle begins and ends in the path you have traversed
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


