Question: ***Please use C++*** Since dynamic variables are created in a different portion of memory (heap) and are not associated with an identifier, you need pointers
***Please use C++***
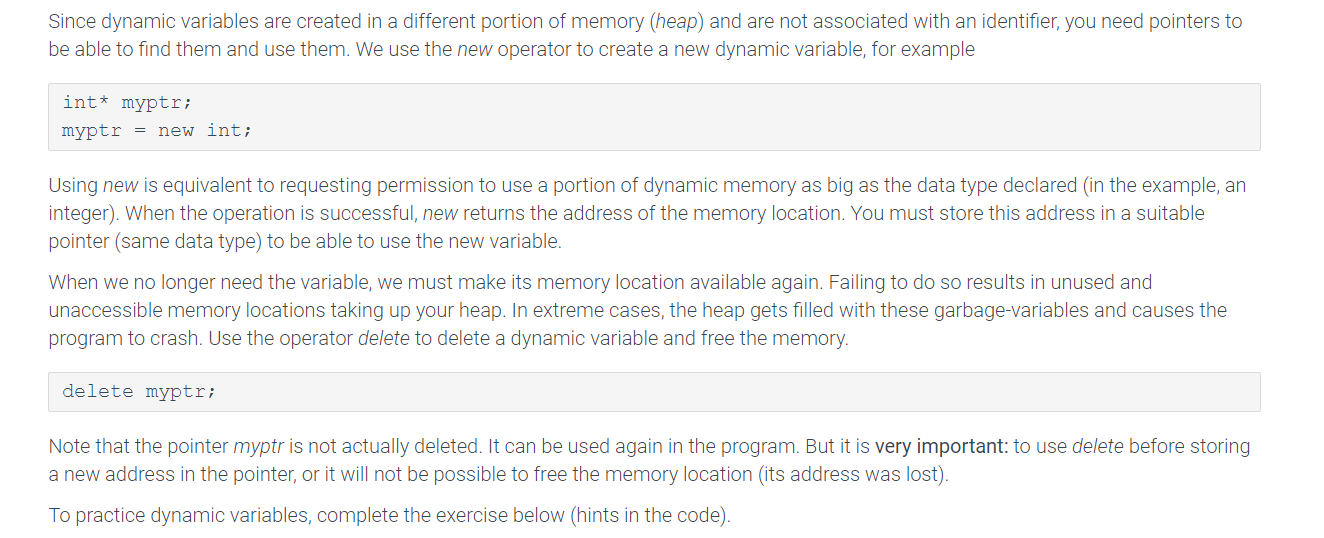
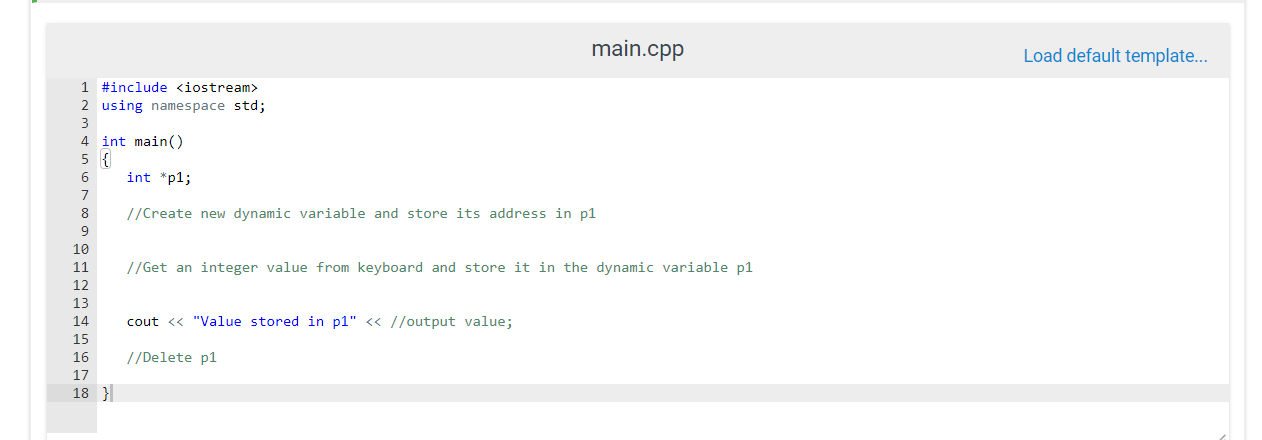
Since dynamic variables are created in a different portion of memory (heap) and are not associated with an identifier, you need pointers to be able to find them and use them. We use the new operator to create a new dynamic variable, for example int* myptr: myptr new int: Using new is equivalent to requesting permission to use a portion of dynamic memory as big as the data type declared (in the example, arn integer). When the operation is successful, new returns the address of the memory location. You must store this address in a suitable pointer (same data type) to be able to use the new variable When we no longer need the variable, we must make its memory location available again. Failing to do so results in unused and unaccessible memory locations taking up your heap. In extreme cases, the heap gets filled with these garbage-variables and causes the program to crash. Use the operator delete to delete a dynamic variable and free the memory delete myptr: Note that the pointer myptr is not actually deleted. It can be used again in the program. But it is very important: to use delete before storing a new address in the pointer, or it will not be possible to free the memory location (its address was lost) To practice dynamic variables, complete the exercise below (hints in the code)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


