Question: Please use MATLAB. Struggling and could really use some help! Please do all parts. All information is given You are to develop a computer program


Please use MATLAB. Struggling and could really use some help! Please do all parts.
All information is given
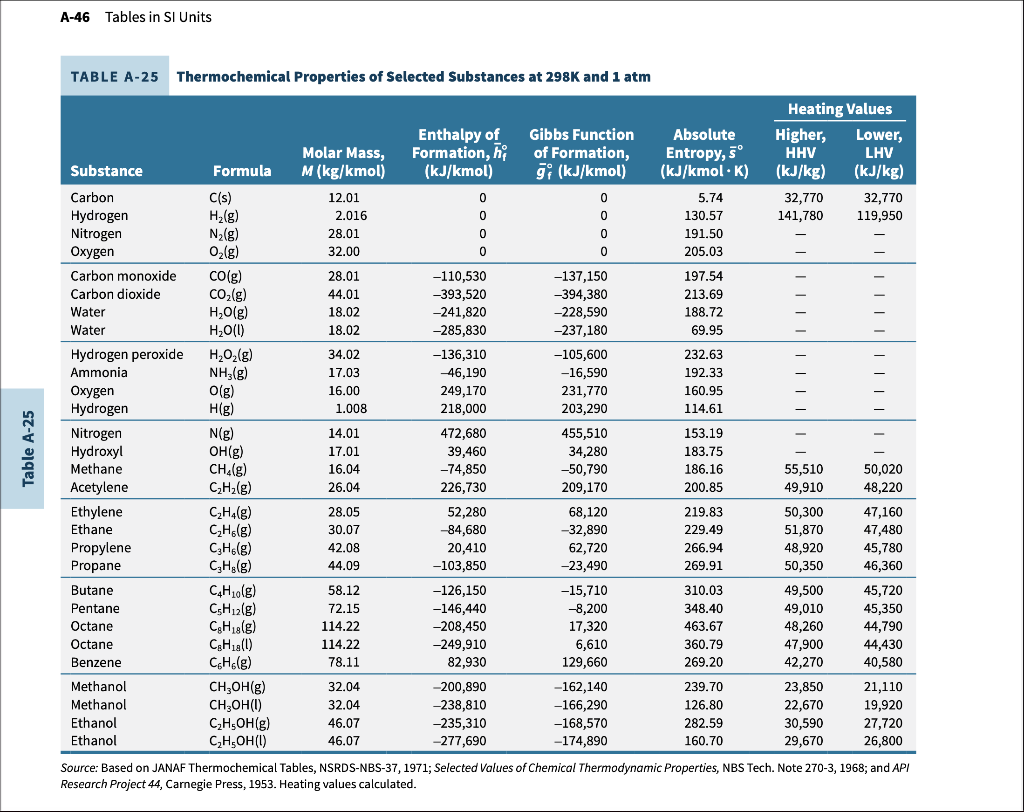
You are to develop a computer program (in MATLAB or any computer programming code) on fuel combustion. Your program should balance the combustion equation of any hydrocarbon fuel (CnHy) as listed in Table A-25 for 100% or higher amount of moist air. Assume moist air is available at 25 C, 1 atm, and a relative humidity value that you choose. Assume complete combustion. Your program output should include: (work in SI units) Complete combustion equation when fuel type and percent moist air are given. Air fuel ratio on a mass basis and on a mole basis, water dew point temperature (total products pressure is 1 atm). Heat transfer calculations when reactants (1 atm, 25 C, and relative humidity), and products pressure (1 atm) and product temperature are given. a) Run your source code for a hydrocarbon of your choice as listed in Table A-25 at 25 C to develop the following: (You need to show complete program formulation and prove that your programming code is working by showing sample formulations/calculations for at least one point. Attach a copy of your code and complete set of data to show that your program is working correctly. Note that your coding will require best-fit data for molar enthalpy values of CO2, H20, O2, and N2 as a function of temperature from 298 K to 2000 K temperature range. Use the enthalpy data in Table 23 to get the best fit in 2nd or higher degree polynomial forms. Check and prove the goodness of your curve fits.) 1) For a range of % moist air (at a fixed relative humidity value set by you) from 100% to 200% (increments of 20%) tabulate and plot: AF ratio (mass/mole basis), and the dew point temperature versus the % air. Comment. For 150% moist air at 1 atm, 25 C, and relative humidity used in part (a1) above, tabulate and plot the heat transfer release in kJ per kmole of hydrocarbon versus product temperature. Vary the product temperature from 298 K (assume water in vapor form for 25 C point for heat transfer calculations) to 2000 K. Consider 298 K, 500 K, 1000 K, 1500 k, and 2000 K points. Comment. A-46 Tables in SI Units TABLE A-25 Thermochemical Properties of Selected Substances at 298K and 1 atm H2(g) ||||||| UTII Table A-25 Heating Values Enthalpy of Gibbs Function Absolute Higher, Lower, Molar Mass, Formation, of Formation, Entropy, 5 HHV LHV Substance Formula M(kg/kmol) (kJ/kmol) gi (kJ/kmol) (kJ/kmol.K) (kJ/kg) (kJ/kg) Carbon C(s) 12.01 0 0 5.74 32,770 32,770 Hydrogen 2.016 0 0 130.57 141,780 119,950 Nitrogen N2(g) 28.01 0 0 191.50 Oxygen O2(g) 32.00 0 0 205.03 Carbon monoxide CO(g) 28.01 -110,530 -137,150 197.54 Carbon dioxide CO2(g) 44.01 -393,520 -394,380 213.69 Water H2O(g) 18.02 -241,820 -228,590 188.72 Water H2O(0) 18.02 -285,830 -237,180 69.95 Hydrogen peroxide H2O2(g) 34.02 -136,310 -105,600 232.63 Ammonia NH3(g) 17.03 -46,190 -16,590 192.33 Oxygen O(g) 16.00 249,170 231,770 160.95 Hydrogen Hig) 1.008 218,000 203,290 114.61 Nitrogen Nig) 14.01 472,680 455,510 153.19 Hydroxyl OH(g) 17.01 39,460 34,280 183.75 Methane CH.(g) 16.04 -74,850 -50,790 186.16 55,510 50,020 Acetylene CzH2(g) 26.04 226,730 209,170 200.85 49,910 48,220 Ethylene CzH4g) 28.05 52,280 68,120 219.83 50,300 47,160 Ethane CH&(g) 30.07 -32,890 229.49 51,870 47,480 Propylene CzHe(g) 42.08 20,410 62,720 266.94 48,920 45,780 Propane CzHg(g) 44.09 -103,850 -23,490 269.91 50,350 46,360 Butane CH10(g) 58.12 -126,150 -15,710 310.03 49,500 45,720 Pentane CsH2(g) 72.15 -146,440 -8,200 348.40 49,010 45,350 Octane C.H.(g) 114.22 -208,450 17,320 463.67 48,260 44,790 Octane CgHua() 114.22 -249,910 6,610 360.79 47,900 44,430 Benzene CeHelg) 78.11 82,930 129,660 269.20 42,270 40,580 Methanol CH2OH(g) 32.04 -200,890 -162,140 239.70 23,850 21,110 Methanol CH3OH(U) 32.04 -238,810 -166,290 126.80 22,670 19,920 Ethanol C2H5OH(g) 46.07 -235,310 -168,570 282.59 30,590 27,720 Ethanol C,H,OH(U) 46.07 -277,690 -174,890 160.70 29,670 26,800 Source: Based on JANAF Thermochemical Tables, NSRDS-NBS-37, 1971; Selected Values of Chemical Thermodynamic Properties, NBS Tech. Note 270-3, 1968; and API Research Project 44, Carnegie Press, 1953. Heating values calculated. 84,680 You are to develop a computer program (in MATLAB or any computer programming code) on fuel combustion. Your program should balance the combustion equation of any hydrocarbon fuel (CnHy) as listed in Table A-25 for 100% or higher amount of moist air. Assume moist air is available at 25 C, 1 atm, and a relative humidity value that you choose. Assume complete combustion. Your program output should include: (work in SI units) Complete combustion equation when fuel type and percent moist air are given. Air fuel ratio on a mass basis and on a mole basis, water dew point temperature (total products pressure is 1 atm). Heat transfer calculations when reactants (1 atm, 25 C, and relative humidity), and products pressure (1 atm) and product temperature are given. a) Run your source code for a hydrocarbon of your choice as listed in Table A-25 at 25 C to develop the following: (You need to show complete program formulation and prove that your programming code is working by showing sample formulations/calculations for at least one point. Attach a copy of your code and complete set of data to show that your program is working correctly. Note that your coding will require best-fit data for molar enthalpy values of CO2, H20, O2, and N2 as a function of temperature from 298 K to 2000 K temperature range. Use the enthalpy data in Table 23 to get the best fit in 2nd or higher degree polynomial forms. Check and prove the goodness of your curve fits.) 1) For a range of % moist air (at a fixed relative humidity value set by you) from 100% to 200% (increments of 20%) tabulate and plot: AF ratio (mass/mole basis), and the dew point temperature versus the % air. Comment. For 150% moist air at 1 atm, 25 C, and relative humidity used in part (a1) above, tabulate and plot the heat transfer release in kJ per kmole of hydrocarbon versus product temperature. Vary the product temperature from 298 K (assume water in vapor form for 25 C point for heat transfer calculations) to 2000 K. Consider 298 K, 500 K, 1000 K, 1500 k, and 2000 K points. Comment. A-46 Tables in SI Units TABLE A-25 Thermochemical Properties of Selected Substances at 298K and 1 atm H2(g) ||||||| UTII Table A-25 Heating Values Enthalpy of Gibbs Function Absolute Higher, Lower, Molar Mass, Formation, of Formation, Entropy, 5 HHV LHV Substance Formula M(kg/kmol) (kJ/kmol) gi (kJ/kmol) (kJ/kmol.K) (kJ/kg) (kJ/kg) Carbon C(s) 12.01 0 0 5.74 32,770 32,770 Hydrogen 2.016 0 0 130.57 141,780 119,950 Nitrogen N2(g) 28.01 0 0 191.50 Oxygen O2(g) 32.00 0 0 205.03 Carbon monoxide CO(g) 28.01 -110,530 -137,150 197.54 Carbon dioxide CO2(g) 44.01 -393,520 -394,380 213.69 Water H2O(g) 18.02 -241,820 -228,590 188.72 Water H2O(0) 18.02 -285,830 -237,180 69.95 Hydrogen peroxide H2O2(g) 34.02 -136,310 -105,600 232.63 Ammonia NH3(g) 17.03 -46,190 -16,590 192.33 Oxygen O(g) 16.00 249,170 231,770 160.95 Hydrogen Hig) 1.008 218,000 203,290 114.61 Nitrogen Nig) 14.01 472,680 455,510 153.19 Hydroxyl OH(g) 17.01 39,460 34,280 183.75 Methane CH.(g) 16.04 -74,850 -50,790 186.16 55,510 50,020 Acetylene CzH2(g) 26.04 226,730 209,170 200.85 49,910 48,220 Ethylene CzH4g) 28.05 52,280 68,120 219.83 50,300 47,160 Ethane CH&(g) 30.07 -32,890 229.49 51,870 47,480 Propylene CzHe(g) 42.08 20,410 62,720 266.94 48,920 45,780 Propane CzHg(g) 44.09 -103,850 -23,490 269.91 50,350 46,360 Butane CH10(g) 58.12 -126,150 -15,710 310.03 49,500 45,720 Pentane CsH2(g) 72.15 -146,440 -8,200 348.40 49,010 45,350 Octane C.H.(g) 114.22 -208,450 17,320 463.67 48,260 44,790 Octane CgHua() 114.22 -249,910 6,610 360.79 47,900 44,430 Benzene CeHelg) 78.11 82,930 129,660 269.20 42,270 40,580 Methanol CH2OH(g) 32.04 -200,890 -162,140 239.70 23,850 21,110 Methanol CH3OH(U) 32.04 -238,810 -166,290 126.80 22,670 19,920 Ethanol C2H5OH(g) 46.07 -235,310 -168,570 282.59 30,590 27,720 Ethanol C,H,OH(U) 46.07 -277,690 -174,890 160.70 29,670 26,800 Source: Based on JANAF Thermochemical Tables, NSRDS-NBS-37, 1971; Selected Values of Chemical Thermodynamic Properties, NBS Tech. Note 270-3, 1968; and API Research Project 44, Carnegie Press, 1953. Heating values calculated. 84,680
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


