Question: pls ans correctly....I will thumb up QUESTION 49 Consider the POSIX-based Linux command for shared memory synchronization between a producer and consumer pair of processes
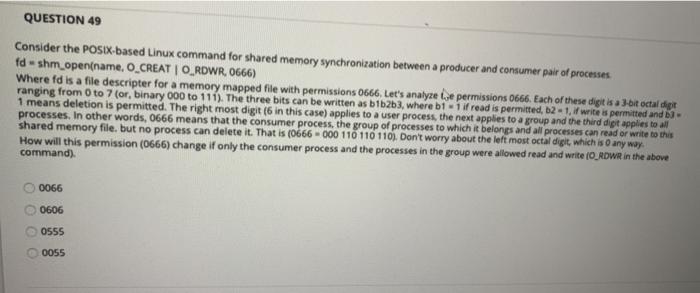
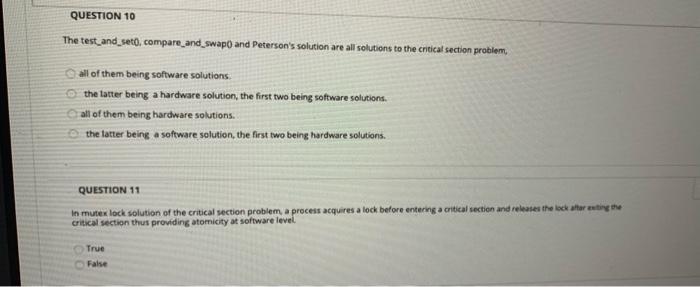
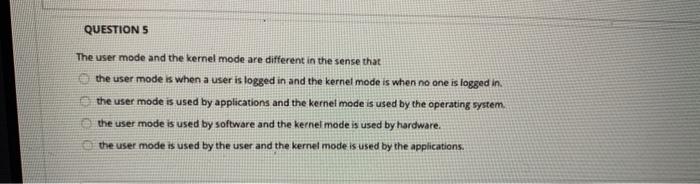
QUESTION 49 Consider the POSIX-based Linux command for shared memory synchronization between a producer and consumer pair of processes fd - shm_open(name, O_CREATO_RDWR, 0666) Where fd is a file descripter for a memory mapped file with permissions 0666. Let's analyze ise permissions 0666. Each of these digit is a bit octal spr ranging from 0 to 7 (or, binary 000 to 111). The three bits can be written as b1b2b3, where b1 - 1 if read is permitted, b2 -1, if writes permitted and 3 - 1 means deletion is permitted. The right most digit 6 in this case) applies to a user process, the next applies to a group and the third dipt applies to all processes. In other words, 0666 means that the consumer process, the group of processes to which it belongs and all processes can read or write to this shared memory file, but no process can delete it. That is (0666-000 110 110 110). Don't worry about the left most octal digit which is any way. How will this permission (0666) change if only the consumer process and the processes in the group were allowed read and write (O_RDWR in the above command). 0066 0606 0555 0055 QUESTION 10 The test_and_seto, compare_and_swap and Peterson's solution are all solutions to the critical section problem, all of them being software solutions the latter being a hardware solution, the first two being software solutions. all of them being hardware solutions the latter being a software solution, the first two being hardware solutions. QUESTION 11 In mutex lock solution of the critical section problem, a process acquires a lock before entering a critical section and releases the lock after eating the Critical section thus providing atomicity at software level True False QUESTIONS The user mode and the kernel mode are different in the sense that the user mode is when a user is logged in and the kernel mode is when no one is logged in. the user mode is used by applications and the kernel mode is used by the operating system. the user mode is used by software and the kernel mode is used by hardware. the user mode is used by the user and the kernel mode is used by the applications
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


