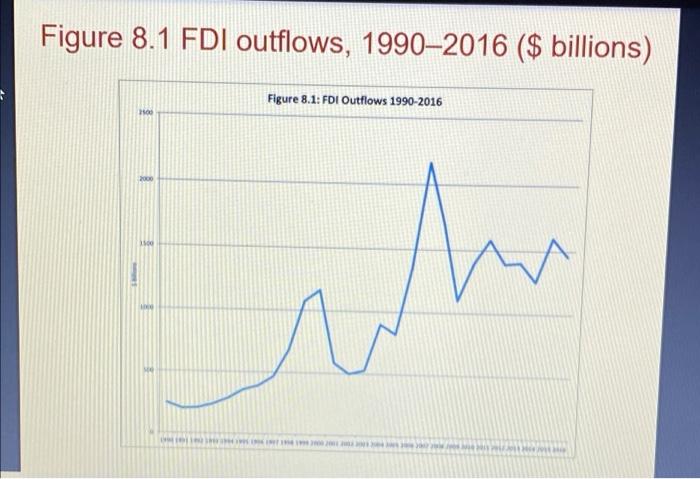
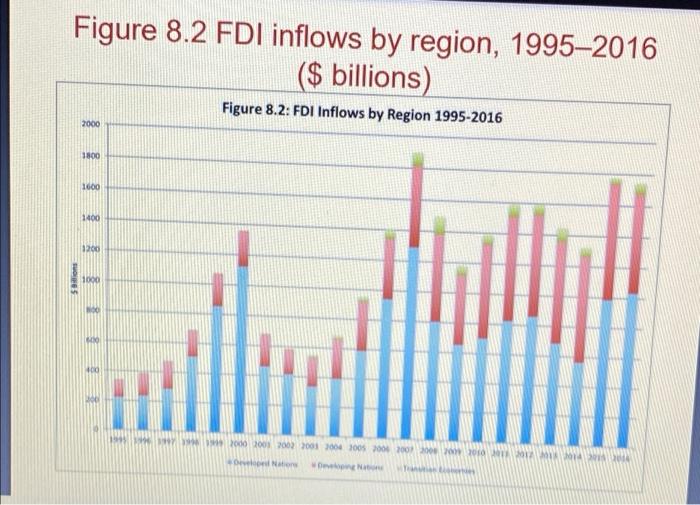
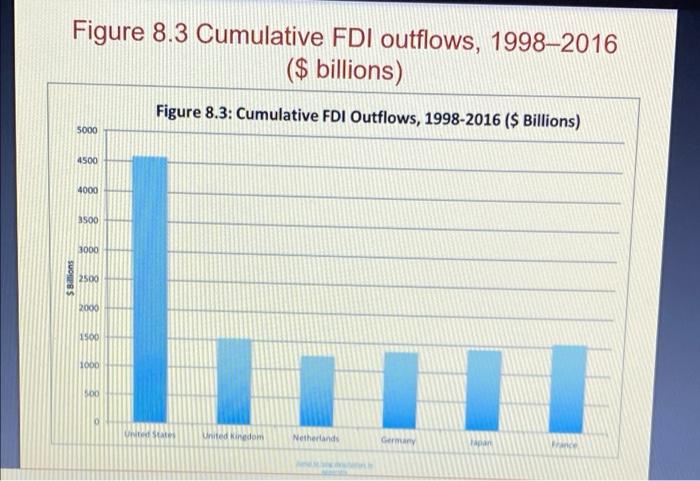
Question: Pls Answer All Questions 1)? 2)? 3)? Pls Don't use Google too much because of the Plagiarism . After you read chapter 8, please answer
Pls Answer All Questions
1)?
2)?
3)?
Pls
Don't use Google too much because of the
Plagiarism.
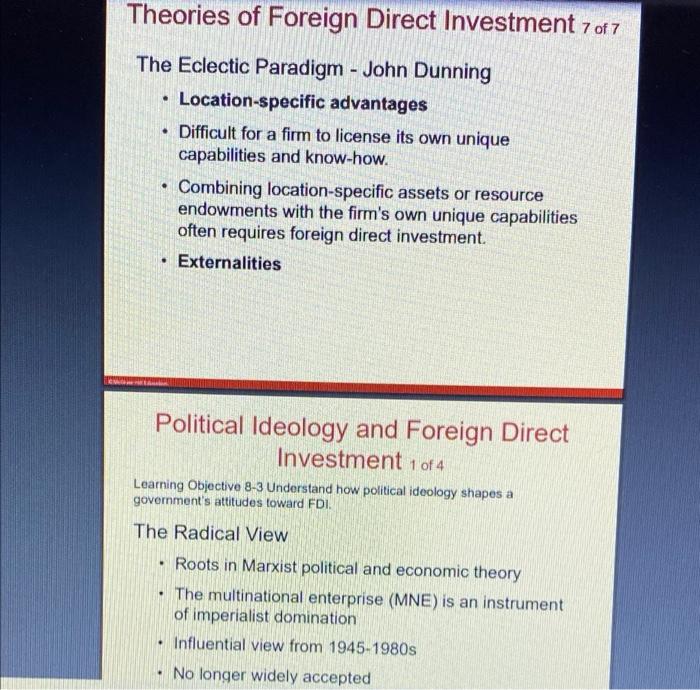
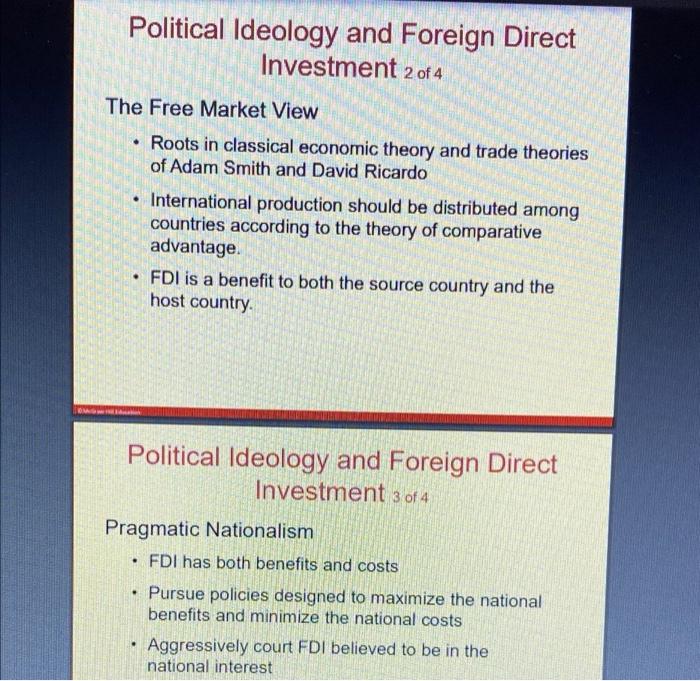
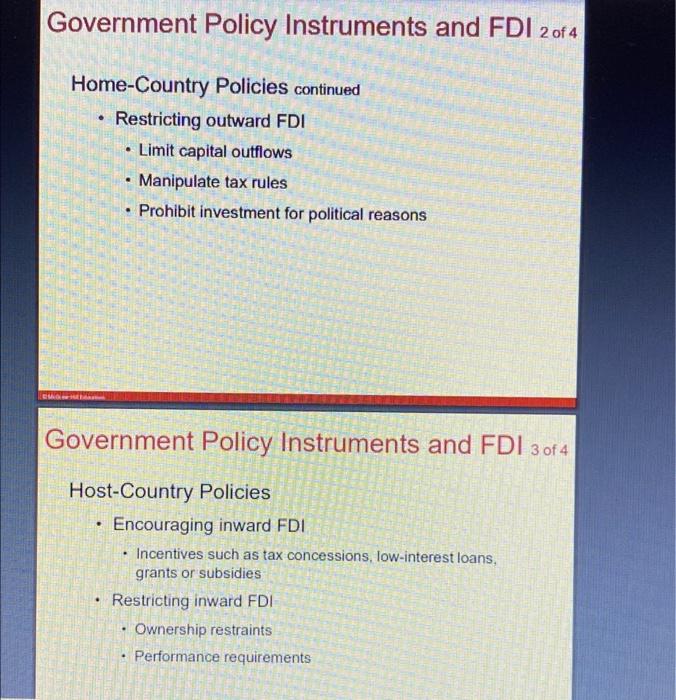
After you read chapter 8, please answer all the following questions. 1. How does the free market view support FDI? 2. Discuss the benefits and costs of FDI from the perspective of a host country and from the perspective of the home country. 3. Describe some of the home country policies that encourage outward FDI. Introduction . a Foreign direct investment (FDI) Occurs when a firm invests directly in new facilities to produce and/or market in a foreign country (10 percent or more) The firm becomes a multinational enterprise . Foreign Direct Investment in the World Economy 1 of 5 Learning Objective 8-1 Recognize current trends regarding foreign direct investment (FDI) in the world economy. Flow of FDI - the amount of FDI undertaken over a given time period Outflows-flows of FDI out of a country Inflows-flows of FDI into a country Stock of FDI - the total accumulated value of foreign-owned assets at a given time Foreign Direct Investment in the World Economy 2 of 5 Trends in FDI . Increase in both flow and stock of FDI over past 25 years Growing more rapidly than world trade and world output Way to circumvent trade barriers Political and economic changes Shift toward democratic political institutions and free market economies Globalization . . Figure 8.1 FDI outflows, 19902016 ($ billions) Figure 8.1: FDI Outflows 1990-2016 1100 hr . . Foreign Direct Investment in the World Economy 3 of 5 The Direction of FDI Historically, mostly directed at developed nations U.S. is a target for FDI inflows Large and wealthy domestic market Dynamic and stable economy Favorable political environment and openness to FDI European inflows mainly from the U.S. and other European nations China has also been a recipient of FDI recently . . Figure 8.2 FDI inflows by region, 19952016 ($ billions) Figure 8.2: FDI Inflows by Region 1995-2016 2000 1800 1600 1400 1200 1000 400 IT 11000 2001 2002 2003 2004 100 100 100 200 200 MM Nation Foreign Direct Investment in the World Economy 4 of 5 The Source of FDI U.S. is the largest source since WWII Six countries (U.S., UK, France, Germany, Japan, and the Netherlands) account for 60 percent of all FDI outflows China became a major foreign investor around 2005, especially in less developed nations Figure 8.3 Cumulative FDI outflows, 19982016 ($ billions) Figure 8.3: Cumulative FDI Outflows, 1998-2016 ($ Billions) 5000 4500 4000 3500 3000 Billions 2500 2000 1500 100D TE 500 UN States United Kingdom Netherlands Germany Foreign Direct Investment in the World Economy 5 of 5 The Form of FDI: Acquisitions versus Greenfield Investments Greenfield investment . Acquisitions and mergers Quicker to execute Can acquire valuable strategic assets Can increase the efficiency of the acquired unit by transferring capital, technology, or management skills . Theories of Foreign Direct Investment 1 of 7 Learning Objective 8-2 Explain the different theories of FDI. Three complementary perspectives 1. Seeks to explain why a firm will favor direct investment as a means of entering a foreign market when two other alternatives, exporting and licensing, are open to it 2. Attempts to explain the observed pattern of foreign direct investment flows 3. The eclectic paradigm, attempts to combine the two other perspectives into a single holistic explanation of foreign direct investment Theories of Foreign Direct Investment 20f 7 2 7 Why Foreign Direct Investment? Exporting Licensing FDI is expensive and risky compared with exporting and licensing CMG Theories of Foreign Direct Investment 3 of 7 Why Foreign Direct Investment? continued Limitations of exporting Transportation costs and trade barriers By limiting imports through quotas and tariffs, governments increase the attractiveness of FDI and licensing . Theories of Foreign Direct Investment 4 of 7 Why Foreign Direct Investment? continued Limitations of licensing Internalization theory Market imperfections Licensing may result in a firm's giving away valuable technological know-how to a potential foreign competitor. Licensing does not give a firm the tight control over production, marketing, and strategy in a foreign country that may be required to maximize its profitability. The firm's competitive advantage is based on the management, marketing, and manufacturing capabilities, which is not amenable to licensing. . Theories of Foreign Direct Investment 5 of 7 Why Foreign Direct Investment? continued Advantages of Foreign Direct Investment When transportation costs or trade barriers make exporting unattractive When a firm wishes to maintain control over its technological know-how, or over its operations and business strategy, or when the firm's capabilities are simply not amenable to licensing, Theories of Foreign Direct Investment 5 of 7 Why Foreign Direct Investment? continued Advantages of Foreign Direct Investment When transportation costs or trade barriers make exporting unattractive When a firm wishes to maintain control over its technological know-how, or over its operations and business strategy, or when the firm's capabilities are simply not amenable to licensing. Theories of Foreign Direct Investment 6 of 7 The Pattern of Foreign Direct Investment Strategic Behavior Knickerbocker - relationship between FDI and rivalry in oligopolistic industries Oligopoly Interdependence between firms in an oligopoly leads to imitative behavior Imitative behavior also occurs in FDI Multipoint competition . . Theories of Foreign Direct Investment 7 of 7 . The Eclectic Paradigm - John Dunning Location-specific advantages Difficult for a firm to license its own unique capabilities and know-how. Combining location-specific assets or resource endowments with the firm's own unique capabilities often requires foreign direct investment. Externalities Political Ideology and Foreign Direct Investment 1 of 4 Learning Objective 8-3 Understand how political ideology shapes a government's attitudes toward FDI. . The Radical View Roots in Marxist political and economic theory The multinational enterprise (MNE) is an instrument of imperialist domination Influential view from 1945-1980s No longer widely accepted . . Political Ideology and Foreign Direct Investment 2 of 4 . The Free Market View Roots in classical economic theory and trade theories of Adam Smith and David Ricardo International production should be distributed among countries according to the theory of comparative advantage. FDI is a benefit to both the source country and the host country. Political Ideology and Foreign Direct Investment 3 of 4 . Pragmatic Nationalism FDI has both benefits and costs Pursue policies designed to maximize the national benefits and minimize the national costs Aggressively court FDI believed to be in the national interest . . Political Ideology and Foreign Direct Investment 4 of 4 . Shifting Ideology Decline in radical ideology Increase in free market ideology, more liberal foreign investment regime Surge in FDI worldwide China, Vietnam, India Some nations more hostile to FDI Venezuela and Bolivia . Benefits and Costs of FDI 1 of 8 Learning Objective 8-4 Describe the benefits and costs of FDI to home and host countries . Host-Country Benefits Resource-transfer effects Capital, technology, management resources Employment effects Brings jobs to a host country that would otherwise not be created there Mav he offset by loss of lobs in home country Benefits and Costs of FDI 2 of 8 Host-Country Benefits continued Balance-of-Payments Effects Balance of payments accounts track payments and receipts Current account tracks exports and imports A current account deficit, or trade deficit, arises when a country is importing more goods and services than it is exporting. . Benefits and Costs of FDI 3 of 8 Host-Country Benefits continued Balance-of-Payments Effects continued FDI helps with a current account surplus By substituting for imports When the MNE uses a foreign subsidiary to export goods and services to other countries Benefits and Costs of FDI 4 of 8 Host-Country Benefits continued Effect on competition and economic growth Greenfield investment creates new enterprise Services where exporting is not an option Increases competition, stimulates investment, lower prices . Benefits and Costs of FDI 5 of 8 Host-Country Costs Adverse effects on competition Subsidiaries of foreign MNEs may have greater economic power than indigenous competitors Adverse effects on the balance of payments Subsequent capital outflow Imports of inputs from abroad Possible effects on national sovereignty and autonomy Benefits and Costs of FDI 6 of 8 Home-Country Benefits The home country's balance of payments benefits from the inward flow of foreign earnings Employment effects Reverse resource-transfer effect MNE learns valuable skills from its exposure to foreign markets that can subsequently be transferred back to the home country. . Benefits and Costs of FDI 7 of 8 . . Home-Country Costs Balance-of-payments effects of outward FDI Initial capital outflow The current account of the balance of payments suffers if the purpose of the foreign investment is to serve the home market from a low-cost production location. The current account of the balance of payments suffers if the FDI is a substitute for direct exports Employment effects Benefits and Costs of FDI 8 of 8 International Trade Theory and FDI Offshore production May stimulate economic growth in home country May result in lower prices Makes a company more competitive . . Government Policy Instruments and FDI 1 of 4 Learning Objective 8-5 Explain the range of policy instruments that governments use to influence FDI. . Home-Country Policies Encouraging outward FDI Government-backed insurance programs Government loans Elimination of double taxation of foreign income Relaxation of restrictions on FDI by host countries Government Policy Instruments and FDI 2 of 4 . Home-Country Policies continued Restricting outward FDI Limit capital outflows Manipulate tax rules Prohibit investment for political reasons . Government Policy Instruments and FDI 3 of 4 Host-Country Policies Encouraging inward FDI Incentives such as tax concessions, low-interest loans, grants or subsidies Restricting inward FDI Ownership restraints Performance requirements Government Policy Instruments and FDI 4 of 4 . International Institutions and the Liberalization of FDI World Trade Organization Push for liberalization of regulations governing FDI Two extensive multinational agreements were reached in 1997 to liberalize trade in telecommunications and financial services . Managerial Implications Learning Objective 8-6 Identify the implications for managers of the theory and government policies associated with FDI. FDI and Government Policy The Theory of FDI Dunning's locations specific advantages argument explains the direction of FDI, but not why firms prefer FDI to exporting or licensing Internalization theories identify the relative profitability of FDI, exporting, and licensing Government policy