Question: Plz answer two frqs in DETAIL. Especially questions with Explain mark. The following one is the 1st question. 8. Include correctly labeled diagrams, if useful
Plz answer two frqs in DETAIL. Especially questions with "Explain" mark.
The following one is the 1st question.
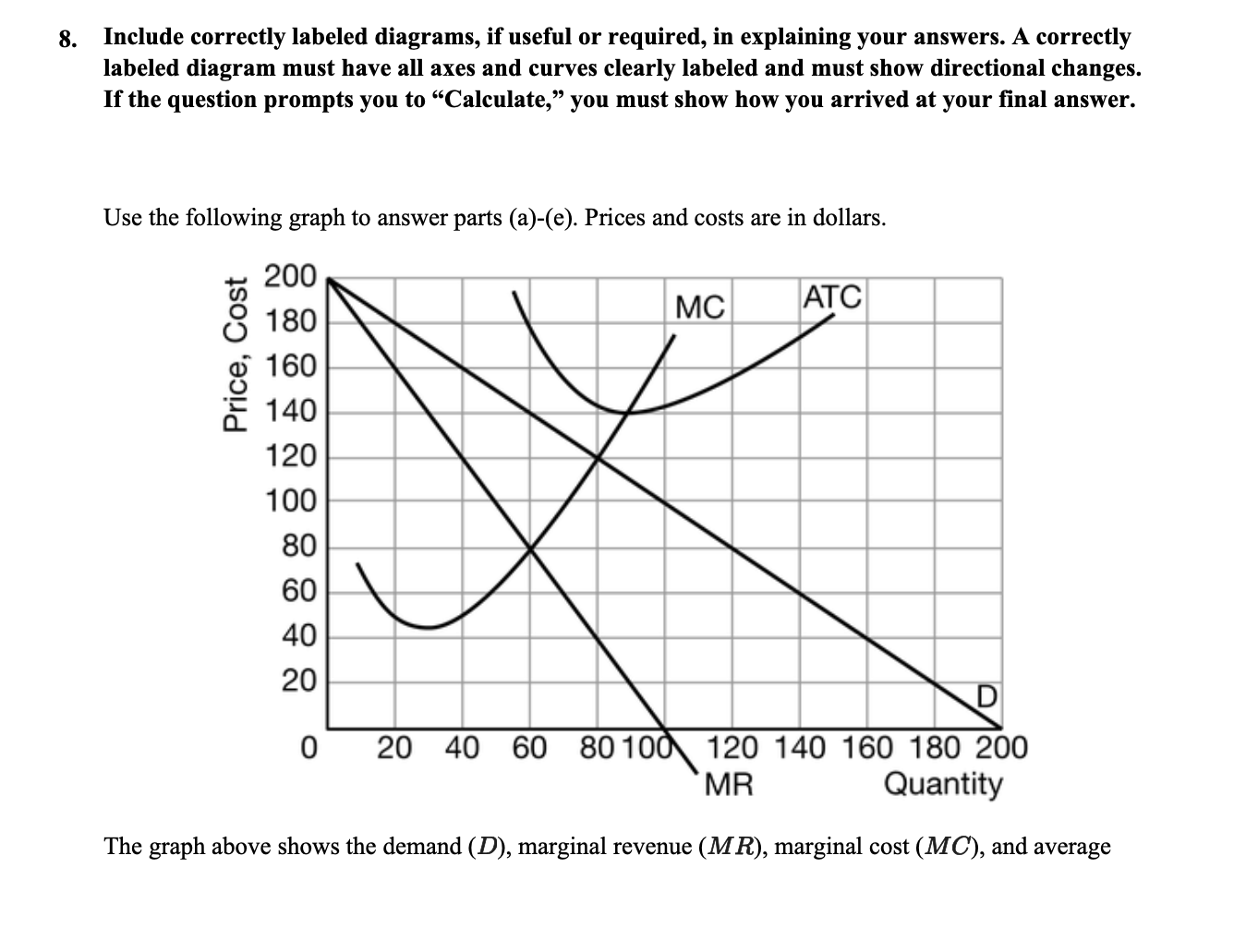


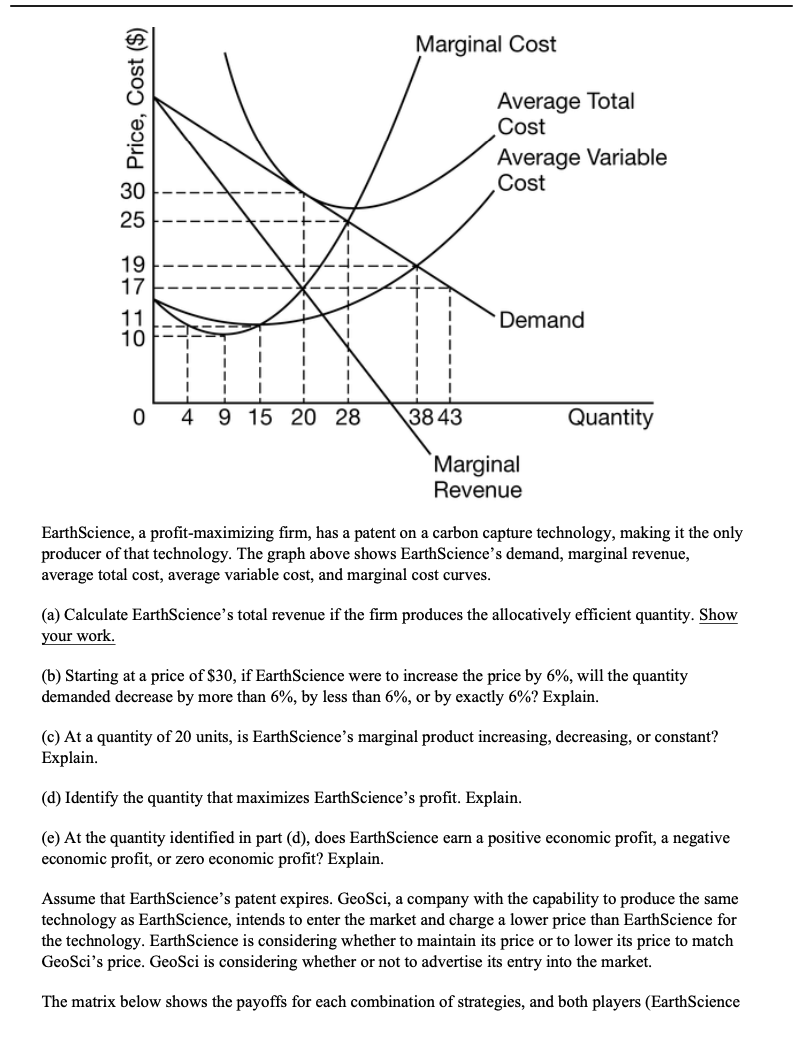
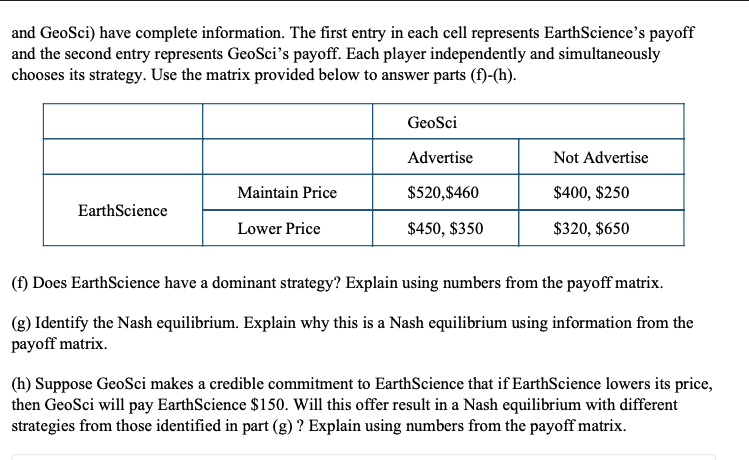
8. Include correctly labeled diagrams, if useful or required, in explaining your answers. A correctly labeled diagram must have all axes and curves clearly labeled and must show directional changes. If the question prompts you to "Calculate," you must show how you arrived at your final answer. Use the following graph to answer parts (a)-(e). Prices and costs are in dollars. 200 180 MC ATC Price, Cost 160 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 MR Quantity The graph above shows the demand (D), marginal revenue (MR), marginal cost (MC), and averagetotal cost (ATC) curves for one of many profit-maximizing firms operating in the short run in an industry in which there are no barriers to entry. Each firm sells a similar but not identical product. (a) Calculate the total revenue of producing 40 units. Show your work. (b) For quantities between 160 and 180 units, is the demand curve elastic, inelastic, or unit elastic? Explain. (c) Assume that this firm is currently charging a price of $100. In order to maximize its profit, should the firm increase its price, decrease its price, or keep its price the same? Explain. (d) At a quantity of 20 units, does this firm have increasing marginal returns or diminishing marginal returns? Explain. (e) Identify the firm's allocation efficient quantity, and explain how you determined it.9. Include correctly labeled diagrams, if useful or required, in explaining your answers. A correctly labeled diagram must have all axes and curves clearly labeled and must show directional changes. If the question prompts you to \"Calculate,\" you must show how you arrived at your nal answer. Use the graph provided below to answer parts (a)-(e). Marginal Cost Average Total Cost Average Variable Cost Demand 0 49152028 Marginal Revenue EarthScience, a prot-maximizing rm, has a patent on a carbon capture technology, making it the only producer of that technology. The graph above shows Earthcience's demand, marginal revenue, average total cost, average variable cost, and marginal cost curves. (a) Calculate EarthScience's total revenue if the rm produces the allocatively efcient quantity. Show your work. Cb} Starting at a price of $30, if Earthcience were to increase the price by 6%, will the quantity demanded decrease by more than 6%, by less than 6%, or by exactly 6%? Explain. (c) At a quantity of 20 units, is Earthcience's marginal product increasing, decreasing, or constant? Explain. (d) Identify the quantity that maximizes EarthScience's prot. Explain. (e) At the quantity identied in part ((1), does Earthcience earn a positive economic prot, a negative economic prot, or zero economic prot? Explain. Assume that EarthScience's patent expires. GeoSci, a company withthe capability to produce the same technology as EarthScience, intends to enter the market and charge a lower price than EarthScience for the technology. EarthScience is considering whether to maintain its price or to lower its price to match GeoSci's price. GeoSci is considering whether or not to advertise its entry into the market. The matrix below shows the payoffs for each combination of strategies, and both players (EarthScience and GeoSci) have complete information. The first entry in each cell represents EarthScience's payoff and the second entry represents GeoSci's payoff. Each player independently and simultaneously chooses its strategy. Use the matrix provided below to answer parts (f)-(h). GeoSci Advertise Not Advertise Maintain Price $520,$460 $400, $250 EarthScience Lower Price $450, $350 $320, $650 (f) Does EarthScience have a dominant strategy? Explain using numbers from the payoff matrix. (g) Identify the Nash equilibrium. Explain why this is a Nash equilibrium using information from the payoff matrix. (h) Suppose GeoSci makes a credible commitment to EarthScience that if EarthScience lowers its price, then GeoSci will pay EarthScience $150. Will this offer result in a Nash equilibrium with different strategies from those identified in part (g) ? Explain using numbers from the payoff matrix
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


