Question: Precursor to question 5 and 6: An Insurance Example This example will be used in Questions 5 and 6. An insurance company wants to predict
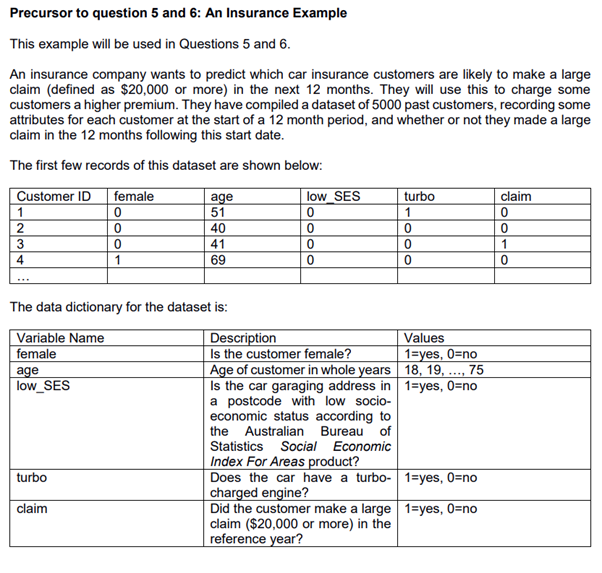

Precursor to question 5 and 6: An Insurance Example This example will be used in Questions 5 and 6. An insurance company wants to predict which car insurance customers are likely to make a large claim (defined as $20,000 or more) in the next 12 months. They will use this to charge some customers a higher premium. They have compiled a dataset of 5000 past customers, recording some attributes for each customer at the start of a 12 month period, and whether or not they made a large claim in the 12 months following this start date. The first few records of this dataset are shown below: The data dictionary for the dataset is: Question 5: Decision Tree (2+2+2+2+2 marks) The output below comes from running the rpart function in the R Statistical Environment on the car insurance dataset just described. 1) root 500012500(0.750.25) 2) female >=0.525305060(0.80,0.20) 4) 1 OWSES =0.5 6602310(0.650.35). 3) females 0.524707410(0.700.30) 6) age>m3.5 18204550(0.750.25) * 7) ages 31.56502990(0.540.46) 14) turbos 0.54701410(0.700.30). 15) turbo >=0.5180451(0.250.75) * (A) List the terminal nodes (also called leaves) from the Rpart classification tree. (B) Calculate the entropy improvement from the first split. (C) Produce the confusion matrix for the classification tree. (D) Calculate the averaged class error for the classification tree. (E) Which node does the customer with ID 2 belong to? For a new customer with the same values of the female, age, turbo and low_SES attributes, do you predict that they will make a large claim within 12 months
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


