Question: Prepare Hardware Study the various components of the environment discussed above. Modify the Linksys WRT54GL hardware as follows: Obtain the parts as given in the
Prepare Hardware Study the various components of the environment discussed above. Modify the Linksys WRT54GL hardware as follows: Obtain the parts as given in the list. Parts list (available upon request). Open the router. Attach the serial header. Wire serial header to MAX233A RS232 receiver/transmitter. Wire the DB9 connectors to MAX233A. Make sure you solder the socket before mounting the chip itself.
Prepare Software Download and cross-compile the embedded XINU code. Download TFTP for loading compiled XINU into the router via CFE. Study the XINU code in the subdirectories. Connect the serial port UART0 to the host (laptop/computer) with embedded XINU code and load it. Configure the serial communication software. Power-up the router. Access the CFE and upload the embedded XINU.
Test the setup (5 points) Build and deploy XINU and examine the commands available. Write a simple test program Hello XINU world and test the setup. This can be done by updating xsh_test.c file in the shell directory. This file will be seed file for all the commands you are going to add to EXINU.
Study Embedded XINU Directory Structure and CodeDownload the Embedded XINU bundle/source from here. Examine the directory structure and understand the purpose of various directories. Specifically, study these files in the directories:
include (header files): shell.h, device.h, gpio.h, interrupt.h, shell.h, tty.h, uart.h
shell (shell command files): shell.c, xsh_led.c, xsh_help.c
system (system operations): devtable.c, getc.c, putc.c, read.c, write.c, initialize.c, kprintf.c, open.c, close.c, startup.S
all the files in tty and uart directories.
Simple edits to the kernel (5 points) Now edit the xinu code so that it prints out your own personal logo instead of XINU. Example: BINA, AJAY, QILI, ANDY.. etc. Dont print our names. Print yours when the system starts.
Write simple shell commands (10 points) The XINU shell is a subsystem designed as an interface for interacting with the operating system. The shell relies on the TTY driver to receive user input and provide output to the user. When XINU starts, a shell process is spawned for each serial port (or TTY). TTY operates on the UART driver. Study the steps given in http://xinu.mscs.mu.edu/Shell to understand how to create a shell command. Add this shell command: palindrome string that checks of the given string is a palindrome or not and prints a message. The string can be given as a command line argument See the sample interaction below:
palindrome unix no palindrome beboxeb yes
Study and understand some more commands 1. system (system operations): initialize.c, main.c The following code from initialize.c will create the main process and shell 0 (TTY0/Console):
open(CONSOLE, SERIAL0); ready(create((void *)main, INITSTK, INITPRIO, "MAIN", 2, 0, NULL), RESCHED_NO); The following code in main (main.c) initializes the Shell 1 to be TTY1/SERIAL1: process main(int argc, char **argv) { /* Associate TTY1 with second serial port. */ open(TTY1, SERIAL1); enable(); /* Launch one shell process for each TTY device. */ ready(create((void *)shell, INITSTK, INITPRIO, "SHELL0", 1, CONSOLE),RESCHED_NO); ready(create((void *)shell, INITSTK, INITPRIO, "SHELL1", 1, TTY1), RESCHED_NO); Thus there is a root process and main process and shell0 and shell1 (corresponding to uart0 and uart1 of the UART). 2. Shell directory: Shell.c file Read the data structure associated with a shell process and how a line buffer is handled, tokenized etc.
process shell(ushort descrp) { char buf[SHELL_BUFLEN]; /* line input buffer */ ushort buflen; /* length of line input */ Do you understand how to create a new process now by looking at the above process definitions and process creations? 3. all the files in tty and uart directories.
Periodic real-time Tasks Scheduling (30 points) In this component of the project you will use Xinu threads to implement n periodic tasks. For the task set given below design a cyclic schedule: (i) determine the hyper-period (ii) determine frame size, (iii) provide a timing chart and (iv) a cyclic (executive) schedule. ti is the task#, ri is the arrival time, ei is the execution time, pi is the period and Di is the relative deadline. 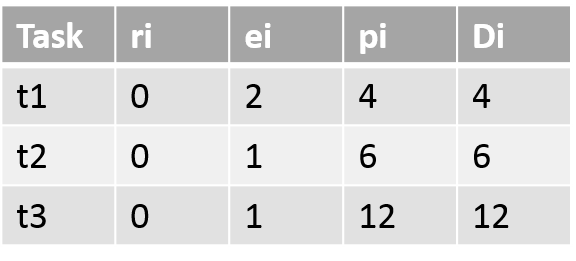 Based on the schedule write a Xinu program with (i) built-in schedule and (ii) built-in schedule to carry our these periodic tasks. Each task will be represented by a xinu process (thread). We discussed this in class and a solution is available in your text and in the demoes directory. You have to port it to XINU environment. Repeat it for another set of tasks. Write a data-driven code that can execute without recompilation.
Based on the schedule write a Xinu program with (i) built-in schedule and (ii) built-in schedule to carry our these periodic tasks. Each task will be represented by a xinu process (thread). We discussed this in class and a solution is available in your text and in the demoes directory. You have to port it to XINU environment. Repeat it for another set of tasks. Write a data-driven code that can execute without recompilation. 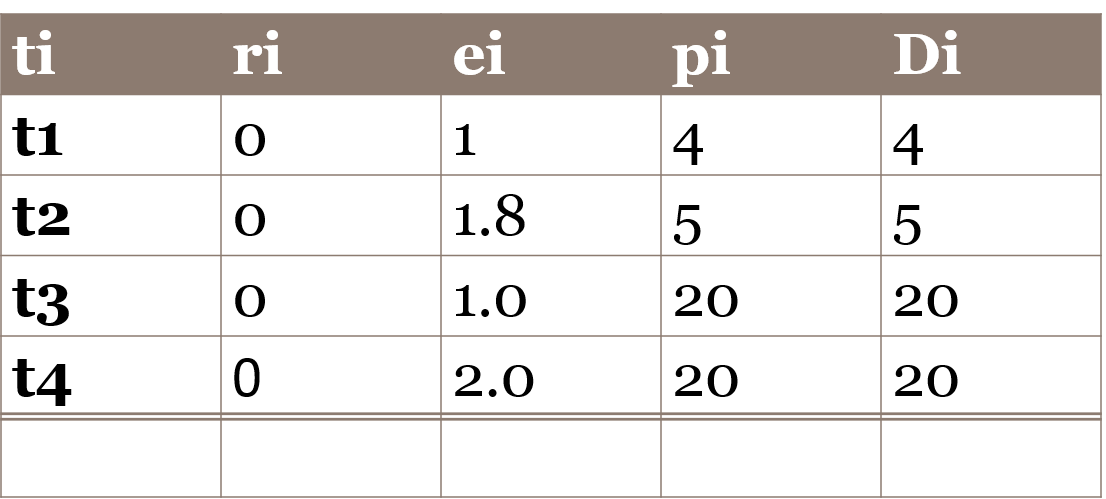
Write a chat program (30 points) using UART serial connection Add a chat program with login feature that will prefix messages with the originators name and print it on the device (lap top). Extend the chat program to allow multiple user (more than 2) and allow chatters to join and leave. In this case there is a super user admin who can kick out chatters with problems. Assume that each chatter (person) is inherently a problem chatter with certain probability!
XINU Semaphores for Synchronization and Mutual exclusion (10 points) Add two programs as shell commands that will illustrate use of XINU semaphores for (i) synchronization (ii) mutual exclusion. For (i) use threes tasks that will work in sequence passing data from one to the next. For (ii) Create three tasks that will have to share a resource like a counter and update it one at a time. Let the threads/tasks sleep for random amount of time for simulating computation.
Appendix A
How to get started with XINU: How to copy (or download) xinu baseline code, compile, deploy and run it. 1. Obtain the tarball from home directory cd /home 2. Copy the tarball to your directory cp xinu_mips-1.0.2.tar.gz ~ 3. Go to your directory and untar the package cd ~ tar zxf xinu_mips-1.0.2.tar.gz 4. Go to xinu_mips-1.0.2 cd xinu_mips-1.0.2 5. View all the files and folders ls 6. Go to the compile folder cd compile 7. Compile all the source files make 8. View available routers xinu-status 9. You need the file xinu.boot so stay in the compile folder mips-console router_name For example, mips-console moiz After a lot of messages a prompt appears. Test the xinu deployement using some of the shell commands. 10. You have to release the router once you are done using it. Press ctrl + spacebar and then q
Appedix B: Adding a Shell Command
Adding shell commands. You will adding all the commands as shell programs, we have described below the steps for adding a shell command. This is adapted from exinu wiki; see http://xinu.mscs.mu.edu/Shell This page was added to the wiki on our request. Lets say we want to add an echo command that echo s the words that list after the command echo 1. Update include directory shell.h file include/shell.h to include prototype command xsh_echo(ushort stdin, ushort stdout, ushort stderr, ushort nargs, char *args[]) 2. Update shell/shell.c command table to include command as an entry {echo, FALSE, xsh_echo} The second parameter says FALSE because echo is not a built-in function. 3. Add xsh_command.c in the shell directory Add xsh_echo.c file in the shell directory. Its content is as follows: ========================================================================= /** * @file xsh_echo.c * @provides xsh_echo * * $Id$ */ /* Embedded XINU, Copyright (C) 2007. All rights reserved. */ #include #include #include /** * Shell command echos input text to standard out. * @param stdin descriptor of input device * @param stdout descriptor of output device * @param stderr descriptor of error device * @param args array of arguments * @return OK for success, SYSERR for syntax error */ command xsh_echo(ushort stdout, ushort stdin, ushort stderr, ushort nargs, char *args[]) { int i; /* counter for looping through arguments */ /* Output help, if '--help' argument was supplied */ if (nargs == 2 && strncmp(args[1],"--help",6) == 0) { fprintf(stdout, "Usage: clear "); fprintf(stdout, "Clears the terminal. "); fprintf(stdout, "\t--help\t display this help and exit "); return SYSERR; } /* loop through the arguments printing each as it is displayed */ for ( i = 1; i prompt. 7. Type help to see echo listed as one of the shell commands 8. Type the command echo and some words. You will see the words you types echoed back. Task ri t1 t2 t3 ei pi Di 12 12 Task ri t1 t2 t3 ei pi Di 12 12
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


